-
Contents
-
Table of Contents
-
Troubleshooting
-
Bookmarks
Quick Links
User Manual
Puritan Bennett
TM
560 Ventilator
Related Manuals for Covidien Puritan Bennett 560
Summary of Contents for Covidien Puritan Bennett 560
-
Page 1
User Manual Puritan Bennett 560 Ventilator… -
Page 2
Nothing in this manual shall limit or restrict in any way Covidien’s right to revise or otherwise change or modify the equipment (including its software) described herein, without notice. In the absence of… -
Page 3: Table Of Contents
Table of Contents Preface Purpose of This Manual …………xi Qualification of Personnel .
-
Page 4
Table of Contents 2.11 USB Memory Device Menu ……….2-11 2.12 If Ventilator Failure Occurs . -
Page 5
Table of Contents Operating Procedures Turning on the Ventilator ……….. 5-1 USB Menu Parameters . -
Page 6
Table of Contents Indicators and Alarms …………A-2 Performance . -
Page 7
List of Figures Figure 1-1. Locations of Labels—Top-Front View ……….. . 1-25 Figure 1-2. … -
Page 8
List of Figures Figure 4-24. Mounting the Ventilator on the Utility Cart……….4-29 Figure 4-25. … -
Page 9
List of Tables Table 1-1. Ventilator Symbols …………..1-19 Table 1-2. … -
Page 10
Page Left Intentionally Blank… -
Page 11: Purpose Of This Manual
Information regarding your product warranty is available from your sales representative or Covidien. Extended Service The Puritan Bennett™ 560 ventilator offers extended service contracts/warranties for purchase when the ventilator is purchased. Please contact your local Covidien sales or service representative for addi- tional information.
-
Page 12: Service Centers
Here, you will find answers to frequently asked questions about the product and other Covidien products 24 hours a day, 7 days a week. If you require further assistance, contact your local Covidien representative.
-
Page 13
Service Centers Covidien France SAS Covidien Hong Kong Covidien ECE s.r.o. Covidien India C-Mill Gebouw K Unit 12 — 16, 18/F Magyarországi Fióktelepe 10th Floor Building No 9B Jan Campertstraat 21-A BEA Tower Mariássy u.7. DLF Cyber City Phase III Gurgaon… -
Page 14
Preface Covidien Spain S.L. Covidien Sverige AB Covidien Switzerland Covidien Thailand C-Mill Gebouw K C-Mill Gebouw K C-Mill Gebouw K 99 Soi Rubia Jan Campertstraat 21-A Jan Campertstraat 21-A Jan Campertstraat 21-A Sukhumvit 42 Road 6416 SG Heerlen, Netherlands 6416 SG Heerlen, Netherlands 6416 SG Heerlen, Netherlands 13-14 Fl., Berli Jucker Building… -
Page 15: Safety Information
1 Safety Information Definitions This manual uses three indicators to highlight critical information: warning, caution, and note. They are defined as follows: WARNING Indicates a condition that can endanger the patient or the ventilator operator. Caution Indicates a condition that can damage the equipment. Note Indicates points of particular emphasis, that make operation of the ventilator more efficient or con- venient.
-
Page 16
Safety Information WARNING: The ventilator must be used according to its intended use. Refer to section 2.1, Indications for Use. WARNING: Be aware this manual describes how to respond to the ventilator, but does not tell you how to respond to the patient. -
Page 17
If the ventilator fails the alarm tests or if you cannot complete the tests, refer to Chapter 3, Alarms and Troubleshooting or call your equipment supplier or Covidien. WARNING: When an alarm condition is triggered, or there is evidence of a patient-ventilator fault or problem, examine the patient first before examining the ventilator. -
Page 18: Warnings Regarding Installation And Environment Of Use
Safety Information WARNING: Do not connect the ventilator to any device other than a PC with a dedicated compatible Puritan Bennett™ software package. WARNING: The ventilator system is not intended to be a comprehensive monitoring device and does not activate alarms for all types of conditions.
-
Page 19
Warnings WARNING: To avoid damage to the ventilator, in particular the batteries or electrical components, fluids must not be allowed to enter the device, particularly through the air inlet filter or the cooling apertures located in the side, rear, and bottom panels of the ventilator. WARNING: To ensure correct and lasting operation of the device, ensure that the ventilator is installed and operated in the environmental conditions recommended in Appendix A, Specifications. -
Page 20
60°C (140°F). This may lead to undesirable side effects for the patient. To avoid injury to the patient move the patient and the ventilator to a cooler location. For more information, contact Covidien. WARNING: The default setting for altitude compensation is YES. Altitude compensation should always be set to YES for accurate volume delivery calculations at all elevations. -
Page 21: Warnings Regarding Electrical Power Supplies
Warnings WARNING: Exercise care to avoid any potential significant risks of reciprocal interference posed by the ventilator and accessories during specific investigations or treatments. Warnings Regarding Electrical Power Supplies 1.2.3 WARNING: The operator should connect the ventilator to an AC power source whenever available, for safer operation.
-
Page 22: Warnings Regarding Hoses And Accessories
Safety Information WARNING: Even if the internal battery charging indicator is off, charging of the battery may sometimes be incomplete if the ambient temperature is above 40°C (104°F) because of the battery’s internal heat safety device. WARNING: When the Low Battery alarm is triggered, immediately connect the ventilator to an AC power supply to maintain ventilation and recharge the internal battery.
-
Page 23
Warnings WARNING: The exhalation block is intended for single use by a single patient . It may periodically be cleaned, but it cannot be disinfected or sterilized. To maintain good measurement quality when used continuously, clean the exhalation block periodically (refer to section 7.3, Cleaning the Exhalation Block). -
Page 24
(Max VTI), and minimum inspired volume (Min VTI) settings—must be periodically adjusted according to changes in the patient circuit resistance—especially when filters are replaced. WARNING: To ensure proper performance of the ventilator, use a patient circuit recommended by Covidien in this manual; refer to Chapter 4, Installation and Assembly… -
Page 25: Warnings Regarding Settings
Ø 22 mm for adult patients, and a corrugated tube of Ø 15 mm for pediatric patients with a tidal volume lower than 200 ml. WARNING: To ensure proper performance of the ventilator, use only accessories (including oxygen accessories) approved and recommended by Covidien. See Appendix F, Parts and Accessories or contact your customer services.
-
Page 26
Safety Information WARNING: Ensure that the I Sens setting is not set to OFF when ventilating patients capable of triggering spontaneous breaths. WARNING: The ventilator offers a variety of breath delivery options. Throughout the patient’s treatment, the clinician should carefully select the ventilation mode and settings to use for that patient, based on clinical judgment, the condition and needs of the patient, and the benefits, limitations, and characteristics of the breath delivery options. -
Page 27
Warnings WARNING: The Apnea alarm should be set to YES for ventilator dependent patients. WARNING: Setting any alarm limits to OFF or extreme high or low values can cause the associated alarm not to activate during ventilation, which reduces its efficacy for monitoring the patient and alerting the clinician to situations that may require intervention. -
Page 28: Warnings Regarding Pc Connection And Usb Memory Devices
WARNING: To ensure proper servicing and avoid the possibility of physical injury to personnel or damage to the ventilator, only personnel authorized and qualified by Covidien should attempt to service or make authorized modifications to the Puritan Bennett™ 560 ventilator.
-
Page 29
Do not attempt to open, repair or otherwise service the ventilator yourself. Doing so might endanger the patient, damage the ventilator, or void your warranty. Only personnel authorized and qualified by Covidien should repair, open or service the ventilator. WARNING:… -
Page 30
Safety Information WARNING: A patient treated by mechanical ventilation is highly vulnerable to the risks of infection. Dirty or contaminated equipment is a potential source of infection. Clean the ventilator and its accessories regularly and systematically before and after each use and following any maintenance procedure to reduce the risks of infection. -
Page 31: Warnings Regarding Oxygen
Warnings WARNING: Connect the external electrical power source by first connecting the power cable to the ventilator and then to the external power source. Follow the reverse procedure to disconnect the device from electrical power sources. Warnings Regarding Oxygen 1.2.8 WARNING: The ventilator must not be used with flammable anesthetic substances.
-
Page 32
Safety Information WARNING: The hose connecting the ventilator to the oxygen source must be designed exclusively for use with medical-grade oxygen. Under no circumstances should the oxygen hose be modified by the user. In addition, the hose must be installed without the use of lubricants. WARNING: Ensure that the only gas supplied to the ventilator through the dedicated oxygen supply connector is medical-grade oxygen. -
Page 33: Warnings Regarding Electromagnetic Interference
The use of any accessory other than those specified, with the exception of the power supplies or cables sold by Covidien, may lead to an increase in electromagnetic emissions or a decrease in the equipment protection against electromagnetic emissions. If the ventilator is used adjacent to such accessories or stacked with such devices, the ventilator’s performance should be monitored to verify normal…
-
Page 34
Safety Information Table 1-1. Ventilator Symbols (Continued) Symbols Descriptions Insulation class II equipment (IEC 60417-5172). A regulatory standard classification for protection against electric shock. Class II equipment relies on double insulation rather than protective earthing. This symbol appears on the ventilator’s back panel; see item 5 in Table 1-2. … -
Page 35
Symbols and Markings Table 1-1. Ventilator Symbols (Continued) Symbols Descriptions Exhalation valve pilot port. This symbol appears on the front right of the ventilator, adjacent to the exhalation valve and TO PATIENT ports, indicating the connection of the tubing between the patient circuit exhalation valve; see Figure 1-1, and item 3 in Figure 1-4. … -
Page 36
Safety Information Table 1-1. Ventilator Symbols (Continued) Symbols Descriptions Inspiratory effort detected. This symbol appears in the front panel display’s Status window when the patient triggers a breath. Parameter adjustment bar. This graphic shows the current setting for parameters such as display contrast and alarm volume in the Pref- erences menu. -
Page 37
Table 1-1. Ventilator Symbols (Continued) Symbols Descriptions PC connection. This symbol indicates a port that can be used by authorized Covidien product service personnel or Covidien service personnel for software maintenance. See item 10 in Figure 1-3. Atmospheric pressure limitations. See section for specifications. -
Page 38: Labels (Identification And Instruction Information)
Safety Information Labels (Identification and Instruction Information) Various labels or specific markings are affixed to the ventilator that describe precautions to be taken for the correct use of the ventilator and contribute to the traceability of the product. See Table and the figures on the following pages for illustrations of these labels and markings and their loca- tions on the ventilator.
-
Page 39: Figure 1-1. Locations Of Labels-Top-Front View
Labels (Identification and Instruction Information) Note: The item number callouts in the following figures correspond to those listed in Table 1-2. Figure 1-1. Locations of Labels—Top-Front View Figure 1-2. Locations of Labels—Front-Left View User Manual 1-25…
-
Page 40: Figure 1-3. Location Of Labels And Markings-Rear View
Safety Information Figure 1-3. Location of Labels and Markings—Rear View Figure 1-4. Location of Labels—Bottom View 1-26 User Manual…
-
Page 41: Ventilator Overview
2 Ventilator Overview Indications for Use The Puritan Bennett™ 560 Ventilator is indicated for the continuous or intermittent mechanical ventilatory support of patients weighing at least 11 lb (5 kg) who require mechanical ventilation. The ventilator is a restricted medical device intended for use by qualified, trained personnel under the direction of a doctor.
-
Page 42: Target Operators
Ventilator Overview Association), International Maritime Dangerous Goods code for sea and the European Agreement concerning the International Carriage of Dangerous Goods by Road (ADR) for Europe. Private individuals who transport the device are excluded from these regulations although for air transport some requirements apply.
-
Page 43: Operational Use
Operational Use Operational Use The Puritan Bennett™ 560 ventilator uses a micro-turbine to provide ventilatory support to patients. Clinicians may use a variety of interfaces to connect patients to the ventilator for continuous or intermittent ventilatory support. Some examples include mouthpieces; nasal masks or full face masks;…
-
Page 44: Device Classification
Ventilator Overview WARNING: Users must always possess an additional breathing circuit and exhalation valve while using the Puritan Bennett™ 560 ventilator. Device Classification The ventilator’s IEC/EN 60601-1classification is as follows: Protection/insulation class (electric shock): Class II • Protection index of enclosure: IP32 •…
-
Page 45: Front Panel
Front Panel Front Panel Figure 2-1. Front Panel LCD display—Shows information about the ventilator, including Exhalation valve port—Nipple for providing piloting patient hours and software version, ventilation modes and settings, pressure to the exhalation valve. Controls the open-closed and monitored and calculated patient data and waveforms. The position of the exhalation valve.
-
Page 46: Back Panel
Ventilator Overview Back Panel Figure 2-2. Back Panel Ergonomic carrying handle. PC cable connector: USB mini-B connector used for Puritan Bennett™ ventilator test software. WARNING: Do not connect the ventilator to any device other than a PC with a dedicated compatible Puritan Bennett™ soft- ware package.
-
Page 47: Control Panel
Control Panel Control Panel Figure 2-3. Control Panel Alarm indicators (two LEDs): DOWN/FREEZE key: Red indicator: • Moves the cursor down and decreases parameter values. • Continuous: Very high priority (VHP) alarm activated. • During ventilation, freezes the waveform shown in the Wave- form menu.
-
Page 48: Ventilation Menu
Ventilator Overview Ventilation Menu Figure 2-4. Ventilation Menu Display (on standby at left; during ventilation at right) 1 General information line: 2 Ventilation settings: 3 Preferences menu access line: Shows the current ventilation mode, Shows the specific ventilation parameter Highlight this line and press the along with the following: values for the currently selected ventilation ENTER…
-
Page 49: Alarm Menu
Alarm Menu Alarm Menu Figure 2-5. Alarm Menu (on standby at left; during ventilation at right) 1 Title line: 2 Alarm settings: 3 Access line to Alarm Logs menu. Shows ventilation mode and the follow- Shows the specific alarm parameter Highlight this line and press the ENTER ing symbols: values for the currently selected ventila- key to show the Alarm Logs menu.
-
Page 50: Waveforms Menu
Ventilator Overview Waveforms Menu 2.10 The display of waveforms (see Figure 2-6) is optional and can be selected using the Menu key. The Waveform menu is only accessible when ventilation is active. Figure 2-6. Waveforms Menu 1 Title line: 2 Graphic zone: 3 Numeric zone: Shows ventilation mode and the follow- Shows the patient’s pressure and flow…
-
Page 51: Usb Memory Device Menu
Keep in mind that troubleshooting information is available in this manual to assist you in the event of a problem. See Chapter 3, Alarms and Troubleshooting. If you cannot determine the cause of a problem, contact your equipment supplier or Covidien. See section 8.7, Service Assistance.
-
Page 52
Ventilator Overview Page Left Intentionally Blank 2-12 User Manual… -
Page 53: Alarms And Troubleshooting
3 Alarms and Troubleshooting Overview The alarms or faults generated by the Puritan Bennett™ 560 ventilator are classified into two cat- egories: Ventilation (or utilization) alarms • Technical faults • Alarms indicate events likely to affect the ventilation in the short term and necessitate rapid inter- vention (see section 3.9, Troubleshooting).
-
Page 54: Alarm Level Of Priority
Alarms and Troubleshooting Note: Default alarm setting preferences should be entered prior to using the ventilator. Note: All configurable alarm settings are recorded in the ventilator’s nonvolatile internal memory, and are retained when powering down or in the event of a total loss of power. Alarm Level of Priority The alarm hierarchy for signaling the level of alarm criticality is listed as follows: Very high priority (VHP): Immediate critical situation;…
-
Page 55: Alarm Display
Alarm Display Alarm Display Note: The alarm indicator LEDs to the left of the ALARM CONTROL key on the Puritan Bennett™ 560 ventilator are designed to be visible to the operator at any position where the ventilator is visible to the operator. Specific alarm detail (shown in the alarm message area) is designed to be readable from up to four meters from the screen, at a viewing angle of up to 30°.
-
Page 56: Alarm Logs Menu
Alarms and Troubleshooting Note: When an alarm is triggered, if the current menu shown is not the Ventilation parameters or Alarm menu, the display automatically switches to one of these menus to show the alarm message. Note: In the event several alarms are activated at the same time, the highest priority audible and visual alarm is highlighted;…
-
Page 57: Figure 3-4. Alarm Logs Screen
Alarm Logs Menu Figure 3-4. Alarm Logs Screen Note: When no alarm has been activated, the message “NO DATA” is shown on the screen (see Figure 3-5). Figure 3-5. Alarm Logs Screen (no alarm activated) For more information on the User’s clear alerts line, see section 3.7, Reactivating Alarms.
-
Page 58: Pausing The Audible Portion Of Alarms
Alarms and Troubleshooting Pausing the Audible Portion of Alarms WARNING: Do not pause, disable, or decrease the volume of the ventilator’s audible alarm if patient safety could be compromised. To pause the audible portion of activated alarms for 60 seconds at a time, press the ALARM CONTROL key.
-
Page 59: Pausing And Resetting Alarms
Pausing and Resetting Alarms Pausing and Resetting Alarms WARNING: Alarm volume should be adjusted with respect to the ventilator’s operating environment and so that the patient’s caretakers can hear the alarms. The audible alarm vents located at the front of the device should never be obstructed.
-
Page 60: Reactivating Alarms
Alarms and Troubleshooting Reactivating Alarms Alarms that have been paused and whose activation conditions continue to exist can be reactivated. To reactivate alarms, proceed as follows: Press the MENU key to access the alarm setting menu, if this is not the menu currently shown. Press the DOWN key to position the cursor on the Alarm Logs line, if this is not already the case.
-
Page 61: Overview Of Alarms
Overview of Alarms The messages of all active alarms are shown in a loop in the Ventilation and Alarm menus. • The audio paused symbol disappears (if it was shown). • The alarm paused symbol disappears. • Overview of Alarms Note: The message: “*IF PERSISTS RESTART/SRVC”…
-
Page 62
Alarms and Troubleshooting Table 3-1. Overview of Alarms (Continued) Alarm message Cause/ventilator response Priority Audio Paused Alarm Paused available available BUZZER FAULT3 Battery charge failure due to incorrect voltage. Contact your service representative for assistance. RESTART/SRVC BUZZER LOW BATTERY Buzzer battery failure. The battery buzzer voltage is too low. -
Page 63
Overview of Alarms Table 3-1. Overview of Alarms (Continued) Alarm message Cause/ventilator response Priority Audio Paused Alarm Paused available available CHECK SETTINGS Alarm activation occurs: • Systematically after software versions have changed. • Loss of memorized parameters Consequence: • Locking key disabled •… -
Page 64
Alarms and Troubleshooting Table 3-1. Overview of Alarms (Continued) Alarm message Cause/ventilator response Priority Audio Paused Alarm Paused available available EMPTY BATTERY Internal battery capacity <10 minutes or 3%. (battery If AC power is voltage <22.5 V) not connected: Consequence: Ventilation comes to a halt. If AC power is connected: LP EXH VALVE LEAKAGE… -
Page 65
Overview of Alarms Table 3-1. Overview of Alarms (Continued) Alarm message Cause/ventilator response Priority Audio Paused Alarm Paused available available INSP FLOW Inspiratory flow is constant (±1 lpm) with normal turbine temperature and speed conditions. Contact RESTART/SRVC your service representative for assistance. INTENTIONAL VENT STOP Ventilation has been stopped voluntarily by the care- giver or patient. -
Page 66
Alarms and Troubleshooting Table 3-1. Overview of Alarms (Continued) Alarm message Cause/ventilator response Priority Audio Paused Alarm Paused available available PATIENT DISCONNECTION* Alarm activation occurs under the following condi- tions (time is in seconds): *IF PERSISTS RESTART/SRVC • Disconnection time or 60/R-Rate, whichever is great- er, in P A/C and V A/C mode •… -
Page 67: Troubleshooting
WARNING: To ensure proper servicing and avoid the possibility of physical injury to personnel or damage to the ventilator, only personnel authorized and qualified by Covidien should attempt to service or make authorized modifications to the Puritan Bennett™ 560 ventilator.
-
Page 68
Alarms and Troubleshooting Table 3-2. Alarms and Corrective Actions Alarm message or Possible reason for the alarm event Corrective action symptom AC POWER DISCONNECTION AC (“mains”) power source cut off. Cancel the alarm, and then check the supply cable and the effective availability of a voltage on the AC power (“mains”) port. -
Page 69
Troubleshooting Table 3-2. Alarms and Corrective Actions (Continued) Alarm message or Possible reason for the alarm event Corrective action symptom CALIBRATION FAIL Too large a difference between a calibration point There may be a leak in the circuit. Ensure an approved and its tolerance range. circuit is in use (see circuit documentation). -
Page 70
Alarms and Troubleshooting Table 3-2. Alarms and Corrective Actions (Continued) Alarm message or Possible reason for the alarm event Corrective action symptom CHECK PROXIMAL LINE1* No connection of the proximal pressure tube Reconnect the proximal pressure line. when ventilation starts. *IF PERSISTS RESTART/SRVC Note: The Check Proximal Proximal pressure line disconnected or obstruct- Reconnect the connection line or replace it if… -
Page 71
Troubleshooting Table 3-2. Alarms and Corrective Actions (Continued) Alarm message or Possible reason for the alarm event Corrective action symptom DEVICE FAULT7 Internal technical problem. Restart ventilator to see if alarm clears. If not, replace the ventilator. Contact your customer service representa- IF PERSISTS RESTART/SRVC tive for assistance. -
Page 72
Alarms and Troubleshooting Table 3-2. Alarms and Corrective Actions (Continued) Alarm message or Possible reason for the alarm event Corrective action symptom SENSOR MISSING There is no FiO sensor, and FiO alarms are active. Contact your customer service representative for assis- tance. HIGH FiO The level of oxygen being delivered to the patient Contact your customer service representative for assis-… -
Page 73
Troubleshooting Table 3-2. Alarms and Corrective Actions (Continued) Alarm message or Possible reason for the alarm event Corrective action symptom HIGH LEAKAGE The leak estimated by the ventilator exceeds the Readjust mask to reduce leakage. Max Leak alarm threshold. Contact your customer service representative for addi- tional assistance. -
Page 74
Alarms and Troubleshooting Table 3-2. Alarms and Corrective Actions (Continued) Alarm message or Possible reason for the alarm event Corrective action symptom HIGH VTI Adjustment of the Max VTI level too low (for PSV, Contact your customer service representative for assis- CPAP, P A/C, P SIMV, and V SIMV modes). tance. -
Page 75
Troubleshooting Table 3-2. Alarms and Corrective Actions (Continued) Alarm message or Possible reason for the alarm event Corrective action symptom LOW VTE Patient circuit obstructed. Clean, unblock, or properly connect the patient circuit. Leak in the patient circuit. Check and properly connect the patient circuit connec- tions. -
Page 76
Alarms and Troubleshooting Table 3-2. Alarms and Corrective Actions (Continued) Alarm message or Possible reason for the alarm event Corrective action symptom PATIENT DISCONNECTION Adjustment of Min PIP too high. Contact your customer service representative for assis- tance. *IF PERSISTS RESTART/SRVC Leak or loose connection in the patient circuit. Check the patient circuit connections to the ventilator;… -
Page 77: Additional Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting Table 3-2. Alarms and Corrective Actions (Continued) Alarm message or Possible reason for the alarm event Corrective action symptom VALVE MISSING CONNECT The ventilation settings are not compatible with Connect exhalation valve. VALVE the type of patient circuit used. VTI NOT REACHED Defective inspiratory flow sensor or internal leak of Restart ventilator to see if alarm clears.
-
Page 78
Alarms and Troubleshooting Table 3-3. Additional Troubleshooting and Corrective Actions (Continued) Conditions Possible causes Corrective actions Unusual display on the Problem with the display unit. Ensure that the ventilator is not exposed to direct screen radiation from the sun. Contact your customer service representative if the problem persists. -
Page 79: Installation And Assembly
4 Installation and Assembly WARNING: Before operating the ventilator, read, understand, and strictly follow the information contained in Chapter 1, Safety Information. WARNING: A patient treated by mechanical ventilation is highly vulnerable to the risks of infection. Dirty or contaminated equipment is a potential source of infection. Clean the ventilator and its accessories regularly and systematically before and after each use and following any maintenance procedure to reduce the risks of infection.
-
Page 80
60°C (140°F). This may lead to undesirable side effects for the patient. To avoid injury to the patient move the patient and the ventilator to a cooler location. For more information, contact Covidien. WARNING: To reduce the risk of a fire hazard, keep matches, lighted cigarettes, and all other sources of ignition (such as flammable anesthetics and/or heaters) away from the ventilator and oxygen hoses. -
Page 81: Connecting To External Ac Power
The use of any accessory other than those specified, with the exception of the power supplies or cables sold by Covidien, may lead to an increase in electromagnetic emissions or a decrease in the equipment protection against electromagnetic emissions. If the ventilator is used adjacent to such accessories or stacked with such devices, the ventilator’s performance should be monitored to verify normal…
-
Page 82: Figure 4-1. The Power Cable Holder
Installation and Assembly WARNING: Do not leave power cables lying on the ground where they may pose a hazard. To prevent accidental disconnection of the AC power cable, use the power cable holder that is inserted into the notch on the battery cover. See Figure 4-1. Figure 4-1. The Power Cable Holder Power cable holder Notch on battery cover…
-
Page 83: Figure 4-3. Power Cable Connected To The Ventilator
Connecting to External AC Power Connect the female end of the ventilator’s AC power cable to the AC connector on the back of the ven- tilator. Figure 4-3. Power Cable Connected to the Ventilator Connect the male end of the AC power cable to the AC power outlet. The AC power indicator on the top left corner of the ventilator illuminates.
-
Page 84: Connecting To An External Dc Power Source
Installation and Assembly To disconnect the AC power cable: Disconnect the AC power cable from the AC power outlet. Disconnect the AC power cable from the ventilator’s AC connector at the rear of the device. Grasp the AC power cable at the level of the power cable holder and turn the cable clockwise while lifting it upwards and out of the holder.
-
Page 85: Figure 4-5. Connecting The Dc Power Cable To The Ventilator
Connecting to an External DC Power Source Figure 4-5. Connecting the DC Power Cable to the Ventilator Red alignment dots Connector locking ring DC power cable connector To connect the DC power cable to the ventilator (see Figure 4-5): Line up the red alignment dots on the ventilator’s DC power receptacle and on the DC power cable. Push the DC power cable into the ventilator’s DC power receptacle.
-
Page 86: Patient Circuit
Installation and Assembly Connect the smaller connector on the DC power cable into the DC power input receptacle on the rear of the ventilator. Connect the larger connector on the DC power cable into the power source’s DC auxiliary receptacle. If connecting the ventilator to the Puritan Bennett™…
-
Page 87: Choosing The Patient Circuit Type
WARNING: To ensure proper performance of the ventilator, use a patient circuit recommended by Covidien in this manual; refer to Chapter 4,…
-
Page 88: Figure 4-7. Single-Limb Patient Circuit With Exhalation Valve (Including Accessories)
Installation and Assembly Single-Limb Circuit (With Exhalation Valve) Figure 4-7. Single-Limb Patient Circuit With Exhalation Valve (including accessories) Inspiratory bacteria filter Exhalation valve tubing Short circuit tubing Proximal pressure tubing Humidifier (optional accessory) Patient proximal pressure port Water trap Exhalation valve port Exhalation valve FROM PATIENT port Note:…
-
Page 89: Figure 4-8. Closeup Of Exhalation Valve Tube And Proximal Pressure Tube
Patient Circuit Connect the exhalation valve tubing to the exhalation valve port on the ventilator. See Figure for a detailed view. Figure 4-8. Closeup of Exhalation Valve Tube and Proximal Pressure Tube TO PATIENT port Proximal pressure tube Exhalation valve tube Connect the inspiratory bacteria filter to the TO PATIENT outlet port on the ventilator. Connect one end of the short circuit tubing to the inspiratory bacteria filter.
-
Page 90: Figure 4-9. Double-Limb Patient Circuit (Including Accessories)
Installation and Assembly Double-Limb Circuit Figure 4-9. Double-Limb Patient Circuit (including accessories) Inspiratory bacteria filter Exhalation valve tubing Humidifier (optional accessory) Exhalation valve assembly Water traps Exhalation (FROM PATIENT) port Short circuit tubing Exhalation bacteria filter Patient wye Patient proximal pressure port Proximal pressure tubing Exhalation valve port Double-limb circuit tubing…
-
Page 91: Figure 4-10. Closeup Of Exhalation Valve Tube And Proximal Pressure Tube
Patient Circuit Connect the proximal pressure tubing to the patient proximal pressure port on the ventilator. See Figure 4-10 for a detailed view. Connect the exhalation valve assembly to the exhaled gas outlet on the left side of the ventilator, near the left front corner.
-
Page 92: Figure 4-11. Close-Up Of Exhalation Bacteria Filter Connection
Installation and Assembly Using a circuit adapter, connect the exhalation bacterial filter to the FROM PATIENT inlet port. See Figure 4-11. Figure 4-11. Close-up of Exhalation Bacteria Filter Connection Single-Limb Circuit (Without Exhalation Valve) Figure 4-12. Single-Limb Patient Circuit Without Exhalation Valve Inspiratory bacteria filter Short circuit tubing Humidifier (optional accessory) Patient circuit tubing…
-
Page 93
Patient Circuit Connect the inspiratory bacteria filter to the TO PATIENT outlet port on the ventilator. Connect one end of the short circuit tubing to the inspiratory bacteria filter. Connect the other end of the short circuit tubing to the inlet port of the humidifier. If it is not already in place, connect a water trap to the outlet port of the humidifier and to the patient circuit tubing. -
Page 94: Filters
Installation and Assembly WARNING: Adding accessories to the ventilator breathing circuit, such as a humidifier and water trap(s), may result in a decrease in tidal volume delivered to the patient due to the added compressible volume of the accessory. Always assure that the patient is receiving the appropriate inspired volume when altering the breathing circuit configuration.
-
Page 95: Bacteria Filter
Filters WARNING: Failing to replace a dirty air inlet filter, or operating the ventilator without a filter, may cause serious damage to the ventilator. Bacteria Filter 4.5.2 It is highly recommended that you install a bacteria filter (see Figure 4-14) on both single- and double-limb circuits.
-
Page 96: Humidifier
Installation and Assembly Humidifier The humidifier (Figure 4-15) adds moisture (water vapor) and warms the gas in the patient circuit. It is inserted into the patient circuit between the TO PATIENT outlet port and the patient (see Figures 4-7, 4-9, and 4-12). Figure 4-15. Humidifier WARNING: During invasive ventilation (when an artificial airway bypasses the patient’s upper respiratory system),…
-
Page 97: Exhalation Block
Exhalation Block See the humidification device’s instructions for information on operating, cleaning, and sterilizing the humidifier. Note: It is the user’s responsibility to verify that any humidification system selected for use is compatible with the Puritan Bennett™ 560 ventilator. Exhalation Block WARNING: The exhalation block is intended for single use by a single patient .
-
Page 98: Oxygen
Installation and Assembly Oxygen Administering Oxygen 4.8.1 WARNING: The ventilator must not be used with flammable anesthetic substances. WARNING: Oxygen therapy for patients with respiratory failure is a common and effective medical prescription. However, be aware that inappropriate oxygen use may potentially lead to serious complications, including, but not limited to, patient injury.
-
Page 99: Connecting The Oxygen Supply
Oxygen Connecting the Oxygen Supply 4.8.2 WARNING: Ensure that the only gas supplied to the ventilator through the dedicated oxygen supply connector is medical-grade oxygen. WARNING: The hose connecting the ventilator to the oxygen source must be designed exclusively for use with medical-grade oxygen.
-
Page 100: Figure 4-18. Connecting The Oxygen Supply
Installation and Assembly WARNING: Before connecting the oxygen supply, ensure that the stud on the oxygen inlet (Figure 4-17, item 3) is protruding outwards. WARNING: Inspect the oxygen coupler (Figure 4-17, item 2) before use to ensure it has its black O-ring (Figure 4-18, item 2) attached and in good condition.
-
Page 101: Figure 4-19. Disconnecting The Oxygen Supply
Oxygen Figure 4-19. Disconnecting the Oxygen Supply Disconnect the oxygen supply by pulling the coupler out from the inlet port. The locking stud on the inlet port (Figure 4-18, item 4) will then extend outwards, which is required before the oxygen connector can be reconnected. WARNING: The coupler must not remain connected to the oxygen connector unless it also connected to a leak- proof, external oxygen gas source.
-
Page 102: Figure 4-20
Installation and Assembly Note: When using a new sensor, allow its temperature to become stable for about 20 minutes in ambient air before installing it, calibrating it, and starting ventilation. Note: A clinician or medical professional should be present when calibrating the FiO sensor.
-
Page 103: Using The Dual Bag
Using the Dual Bag Using the Dual Bag The dual bag accessory allows the patient to carry the Puritan Bennett™ 560 ventilator on his or her back, and also allows it to be secured to the back of a wheelchair or to the seat of a personal vehicle. WARNING: Due to the internal battery’s limited reserve capacity, the ventilator should only be operated on the internal battery when no other power source is available.
-
Page 104: Wearing The Dual Bag As A Backpack
Installation and Assembly Slip the ventilator into the dual bag, front panel first. Push it in completely to ensure a snug fit. Shut the rear panel of the dual bag ensuring that the hook and loop fastener strips are securely fastened. If not mounting the dual bag on a wheelchair or in a personal vehicle, the patient circuit can be reconnected to the ventilator.
-
Page 105: Figure 4-22
Using the Dual Bag Figure 4-22. Using the Dual Bag on a Wheelchair (with double-limb circuit on left; with single-limb circuit on right) To secure the dual bag onto a wheelchair with two push handles (see Figure 4-22): Facing the back of the wheelchair, loop each backpack strap over one of the push handles. Attach the nonadjustable side of the maintaining belt to the side clip of the dual bag.
-
Page 106: Securing The Ventilator In A Personal Vehicle
Installation and Assembly Securing the Ventilator in a Personal Vehicle 4.9.4 Figure 4-23. Using the Dual Bag in a Personal Vehicle To secure the dual bag in a personal vehicle (see Figure 4-23): Unclip the two backpack straps from the side clips. Clip the suspension onto the central ring.
-
Page 107: Mounting The Ventilator On A Utility Cart
Mounting the Ventilator on a Utility Cart Mounting the Ventilator on a Utility Cart 4.10 As an alternative to using the dual bag for patient mobility, the Puritan Bennett™ 560 ventilator can be mounted on a utility cart. To mount the ventilator on the cart: Match the mounting holes on the bottom of the ventilator to the mounting studs on the top of the utility cart platform.
-
Page 108: Figure 4-26. Puritan Bennett™ 560 Ventilator Mounted On Utility Cart
Installation and Assembly Figure 4-26. Puritan Bennett™ 560 Ventilator Mounted on Utility Cart 4-30 User Manual…
-
Page 109: Operating Procedures
5 Operating Procedures Turning on the Ventilator WARNING: Before operating the ventilator, read, understand, and strictly follow the information contained in Chapter 1, Safety Information. WARNING: If the ventilator has been transported or stored at a temperature that differs more than 20°C (36°F) from the temperature in which it will be operating, the ventilator should be allowed to stabilize in its operating environment for at least 2 hours prior to use.
-
Page 110: Figure 5-1. Turning On The Ventilator
If the ventilator fails the alarm tests or if you cannot complete the tests, refer to section 3.9, Troubleshooting or call your equipment supplier or Covidien. WARNING: Due to the internal battery’s limited reserve capacity, the ventilator should only be operated on the internal battery when no other power source is available.
-
Page 111: Figure 5-2. Ventilation On/Off Button And Standby Indicator
Turning on the Ventilator The following events occur: The ventilator is turned on. • A Power On Self Test (POST) is carried out (when plugged in to an AC power source). • The front panel indicators flash (except for the indicator showing the type of power supply in use, which •…
-
Page 112: Usb Menu Parameters
Only one USB memory device may be connected at any time; otherwise, an error message will be shown. To access patient data via a PC, the Puritan Bennett™ Respiratory Insight software package is avail- able for clinicians. Contact Covidien or your product representative for further information. User Manual…
-
Page 113: Usb Memory Device Specifications
USB Menu Parameters USB Memory Device Specifications 5.2.1 Table 5-1. USB Memory Device Specifications Characteristics Supported formats USB compatibility USB flash memory USB 2.0 or USB 1.1, 32 bit format Number of files Maximum 999 (sector size: 512-2048 bytes) USB size 128 MB to 4GB (to guarantee accuracy of transfer time, at least 10% of the USB memory device capacity must be free) USB Memory Device Menu 5.2.2…
-
Page 114: Figure 5-6. Selecting Transfer Continuously
Operating Procedures The following data will be recorded to the USB memory device: Monitoring: Pressure, inspired flow, exhaled flow and leak waveforms • Trends: Leaks, VTI, VTE, Rate, I:E, M. Vol, PIP, and PEEP measurements • The data can be accessed by a doctor or service provider using the Puritan Bennett™ Respiratory Insight software package.
-
Page 115: Figure 5-7. Selecting Transfer Trends
USB Menu Parameters Note: Other functions of the USB memory device are not available during continuous recording. Note: If the memory capacity on the USB memory device is insufficient the message “TRANSFER NOT ALLOWED — USB CAPACITY INSUFFICIENT” is shown and data transfer is not allowed. Delete the data on the USB memory device before restarting data transfer.
-
Page 116
Operating Procedures Press ENTER to confirm the new parameter setting. The new parameter setting is shown continuously. • The cursor is placed at the STOP position. • To manually stop trend transfer, press ENTER. If a parameter change is not confirmed by pressing ENTER before 7 seconds elapse, the ventilator resets the parameter to its previous value. -
Page 117: Starting Ventilation
Starting Ventilation Starting Ventilation Before starting ventilation, see Appendix C, Operational Verification Checklist, and set the parameter values in the Preferences menu. WARNING: Verify the functionality of the alarms before connecting the patient to the ventilator. WARNING: Before starting ventilation, ensure that the device is properly assembled and that the air inlet, cooling vents, and alarm sound diffusion holes are not obstructed.
-
Page 118: Stopping Ventilation
Operating Procedures Figure 5-9. Starting Ventilation Stopping Ventilation WARNING: Do not allow a patient to remain connected to the ventilator when ventilation is stopped, because a substantial quantity of expiratory gas, primarily carbon dioxide, may be inhaled by the patient. In some circumstances, inhaling carbon dioxide may lead to under-ventilation, suffocation, and serious injury or death.
-
Page 119: Turning Off The Ventilator
Turning Off the Ventilator Figure 5-11. Stopping Ventilation (2) A double beep sounds. • Release the VENTILATION ON/OFF button. Press the VENTILATION ON/OFF button again within 5 seconds to confirm stop, otherwise ventilation will continue. Ventilation stops. • The blue LED located to the upper right of the VENTILATION ON/OFF button (Figure 5-9, item 2) illumi- •…
-
Page 120
Operating Procedures Note: A continuous alarm condition will be activated if the ventilator power switch is turned off while ventilation is in progress. When the power switch is turned back on again, the ventilation will resume without having to press the VENTILATION ON/OFF button. -
Page 121: Internal Battery
6 Internal Battery WARNING: Even though the Puritan Bennett™ 560 ventilator meets current safety standards, the internal Lithium-ion battery of the device exceeds the 100Wh threshold and is therefore considered to be Dangerous Goods (DG) Class 9 – Miscellaneous, when transported in commerce. As such, the Puritan Bennett™…
-
Page 122: Battery Capacity
Internal Battery Battery Capacity The reserve capacity offered by the internal battery depends on the level of ventilation parameters, the environmental conditions (primarily in terms of temperature) and the physiological character- istics of the patient. With a fully charged battery at a normal room temperature of 25°C (±5°C), the ventilator can be expected to operate on internal battery power for the average durations shown in Table 6-1. …
-
Page 123: Battery Operation
Battery Operation Battery Operation WARNING: Before using the ventilator’s internal battery, ensure that the battery is fully charged and that the charge holds. Back up ventilators or those in storage should be connected to an AC power source to protect the integrity of the battery. Note: Buzzer and battery alarms may occur when the unit is first powered on after the internal battery has been completely drained.
-
Page 124: Figure 6-2. Battery Reserve Capacity As A Percentage
Internal Battery If ventilation is stopped, the internal battery reserve capacity is shown as a percentage of battery charge. See Figure 6-2. Figure 6-2. Battery Reserve Capacity as a Percentage If the ventilator is running, the internal battery reserve is momentarily shown as a percentage. Then, after the ventilator calculates the battery time remaining (which takes about 2 minutes, depending on the power consumption of the ventilator), the internal battery reserve is then shown in hours and minutes (rounded to the nearest 10 minutes).
-
Page 125: Testing The Battery
Testing the Battery In the final discharge phase, the Empty Battery alarm will become continuous, and ventilation may be interrupted at any time during this phase. Note: The Empty Battery alarm symbol may disappear shortly before the ventilator completely stops, but it always triggers a final, continuous alarm.
-
Page 126: Storage
Internal Battery WARNING: Even if the internal battery indicator is off, charge of the battery may sometimes be incomplete regardless of charge time when the ambient temperature is above 40°C (104°F). This is due to the characteristics of the battery’s internal heat safety device. Although it is not necessary to start the ventilator to charge the battery, charging the battery during operation will increase the time required to fully charge the internal battery.
-
Page 127: Cleaning
7 Cleaning WARNING: A patient treated by mechanical ventilation is highly vulnerable to the risks of infection. Dirty or contaminated equipment is a potential source of infection. Clean the ventilator and its accessories regularly and systematically before and after each use and following any maintenance procedure to reduce the risks of infection.
-
Page 128: Cleaning The Accessories
Cleaning To clean the surface of the ventilator: Dip a clean, soft cloth into a mixture of mild soap and water, or other approved cleaning solution. For a list of approved cleaning solutions, see Table 7-1. Table 7-1. Approved Cleaning Solutions for Exterior Ventilator Surfaces Description Mild dishwashing detergent 70% isopropyl alcohol (rubbing alcohol)
-
Page 129: Cleaning The Exhalation Block
Cleaning the Exhalation Block Cleaning the Exhalation Block WARNING: The exhalation block is intended for single use by a single patient . It may periodically be cleaned, but it cannot be disinfected or sterilized. To maintain good measurement quality when used continuously, clean the exhalation block periodically.
-
Page 130: Pneumatic System
Cleaning Pneumatic System This section describes the components of the pneumatic system. Figure shows a pneumatic block diagram of the Puritan Bennett™ 560 Ventilator, including the patient circuit. The main pneumatic components that can potentially get contaminated during use are the air inlet filter (2); low pressure oxygen inlet /valve (36); oxygen solenoid valve (37); inlet and outlet silencers (not shown);…
-
Page 131
Pneumatic System Humidifier, nebulizer, or additional water traps (not shown) Power supply (located above power management PCBA) Inspiratory tubing Power switch Proximal pressure tube AC input Patient wye DC input Inspiratory pressure sensor PC port Proximal pressure sensor Type A USB ports (2) Exhalation valve pilot tube port (not used) Buzzer PCBA… -
Page 132
Cleaning Page Left Intentionally Blank User Manual… -
Page 133: Routine Maintenance
Do not attempt to open, repair or otherwise service the ventilator yourself. Doing so might endanger the patient, damage the ventilator, and/or void your warranty. Only personnel authorized and qualified by Covidien should repair, open or service the ventilator. WARNING: Ensure that the ventilator is powered off and not in use before performing routine maintenance.
-
Page 134: Calibrating The Exhalation Flow Sensor
Routine Maintenance Calibrating the Exhalation Flow Sensor Each time the exhalation block or circuit is removed and reinstalled or after installing a new exhala- tion block, the exhalation flow sensor must be recalibrated before using the ventilator. This process is automatic and does not require the use of a measurement device. Note: Perform calibration with either an adult or pediatric circuit.
-
Page 135
Calibrating the Exhalation Flow Sensor Figure 8-2. Calibrating the Exhalation Flow Sensor (1) Press the UP or DOWN key. “YES” is shown instead of “OFF”. Figure 8-3. Calibrating the Exhalation Flow Sensor (2) Press the ENTER key to start calibration. The message “…Exp. calib. Processing…” is shown in the window on the right while calibration is in •… -
Page 136: Calibrating The Fio2 Sensor
Routine Maintenance A short beep sounds to confirm the second adjustment. • This process continues until adjustments are complete for all eight calibration points. • Note: The exhalation flow sensor calibration procedure, once initiated, must run to its conclusion. Note: No message is shown when the ventilator passes calibration;…
-
Page 137
Calibrating the FiO2 Sensor Press the ENTER key twice to access the Patient column (central column) of the FiO setup line. “OFF” flashes in the central column. • “OFF” flashes in the window on the right. • The message “FiO Calibration?”… -
Page 138: Replacing The Air Inlet Filter
Routine Maintenance Figure 8-7. Calibrating the FiO Sensor (3) A short beep sounds to confirm that the FiO sensor has been calibrated. • Press the ENTER key to exit the FiO setup line. Note: The FiO sensor calibration procedure, once initiated, must run to its conclusion. In the event of calibration errors, the following events occur: An alarm is activated and the message “FiO CALIBRATION FAIL”…
-
Page 139: Figure 8-8. Replacing The Air Inlet Filter
Replacing the Air Inlet Filter Figure 8-8. Replacing the Air Inlet Filter To replace the air inlet filter (see Figure 8-8): Hold the filter between your fingers (view 1). Remove the filter (view 2) and discard it as instructed by the responsible organization. WARNING: Contact local authorities to determine the proper method to dispose of potentially hazardous parts and accessories.
-
Page 140: Recommended Schedule Of Maintenance
Routine Maintenance Recommended Schedule of Maintenance Preventive Maintenance Intervals 8.6.1 Table lists the periodic maintenance activities required for the Puritan Bennett™ 560 Ventilator. Total machine hours appear on the welcome screen that appears when turning on the ventilator with the power switch, in the Preferences menu during normal operation, and also when entering maintenance mode.
-
Page 141
For all additional accessories not necessarily considered as consumables consult the manufacturer’s recommendations. Note: To prevent any risk of cross contamination, Covidien recommends the use of DAR™ filters (Ref: 351/5856 or equivalent) to protect the patient outlet port and the exhalation block port. User Manual… -
Page 142: Maintenance Of The Internal Battery
Routine Maintenance Failure to observe these recommendations may result in a loss of performance, excessive overheat- ing, a loss of certain functions and, in the long term, compromise the longevity of the ventilator. Maintenance of the Internal Battery 8.6.2 The internal battery does not need to be removed to verify its correct operation. Periodic Test of the Internal Battery 8.6.3 The ventilator continuously and automatically checks the state of the internal battery, even when…
-
Page 143: Service Assistance
In the event of a problem with the ventilator, see Chapter 3, Alarms and Troubleshooting. If you cannot determine the cause of the problem, contact your equipment supplier or Covidien. For more information and local Covidien Technical Service contact details, see Service Centers in the Preface.
-
Page 144
Routine Maintenance Page Left Intentionally Blank 8-12 User Manual… -
Page 145: Specifications
A Specifications Physical Table A-1. Physical Description (excluding accessories) Ventilator weight 9.9 lb. (4.5 kg) Ventilator dimensions 9.25 in wide x 12.40 in deep x 6.0 in high (235 mm wide x 315 mm deep x 154 mm high) Connectors Inspiratory limb connector: ISO 22 mm (OD) conical Exhalation limb connector (on exhalation block): ISO 22 mm (ID) conical Oxygen inlet: female connector with valve Device airway volume…
-
Page 146: Indicators And Alarms
Specifications Table A-3. Internal Lithium Ion Battery Voltage 25.2 VDC Full-load capacity 4.8 Ah On standby: 1.5 Ah Ampere-hour rating During ventilation: 0.5 Ah Watt hour rating 124 Wh to 126 Wh Standby mode: 1.5 A/hr. (duration: <6 hr.) Charging current Ventilation mode: 0.5 A/hr. (duration: <13 hr.) Average operating time at 25°C (±5°C) with a fully charged battery (having less than 50 charge/discharge cycles) at the following displayed values: Vt = 200 ml (±5 ml), PIP = 10 mbar (±2 mbar), Rate = 20 bpm…
-
Page 147: Performance
Performance Performance Note: Performance specifications listed are applicable when dry gases are used in the patient system. Table A-7. Performance Parameter Specifications and Tolerances Settings Range Tolerances Volume 50 to 2000 ml ±(10 ml +15%) Pressure 5 to 55 mbar ±(1 mbar +10%) Time 0.3 to 6.0 s ±10%…
-
Page 148: Range, Resolution, And Accuracy
Specifications Table A-8. Monitored Parameter Tolerances (Continued) Ventilator parameter Tolerances Inspiratory Minute Volume (M VoI) ±(10 mL +15% VTI) ×Rate (with exhalation valve) and ±(20 mL +20% VTI) ×Rate in NIV configuration (without exhalation valve) Vt Sigh ±(20ml +20%) ±(2.5% +2.5% FiO Leak ±(3 lpm +20%) Apnea Index (AI)
-
Page 149
Range, Resolution, and Accuracy Table A-9. Ventilator Range, Resolution, and Accuracy (Continued) Ventilator settings Range, resolution, and accuracy Pressure support Range: OFF or 5 mbar to 55 mbar in valve configuration (P Support) Range: 6 mbar to 30 mbar in leak configuration Resolution: 1 mbar Accuracy: ±(1 mbar +10%) of P Support + PEEP setting Default value: 15 mbar… -
Page 150
Specifications Table A-9. Ventilator Range, Resolution, and Accuracy (Continued) Ventilator settings Range, resolution, and accuracy Ramp Range: Square (SQ), descending ramp (D), sinusoidal (S) (Flow Pattern) Resolution: N/A Default value: Descending ramp (D) In V SIMV, flow pattern is set to square and is not adjustable PEEP Range: OFF (0.5 mbar) to 20 mbar Resolution: 1 mbar… -
Page 151
Range, Resolution, and Accuracy Table A-9. Ventilator Range, Resolution, and Accuracy (Continued) Ventilator settings Range, resolution, and accuracy Maximum Exhaled Tidal Volume Range: 80 mL to 3000 mL (Max VTE) Resolution: 10 mL Default value: 1000 Depends on: Min VTE Maximum Respiratory Rate Range: 10 bpm to 70 bpm in CPAP, P A/C, and V A/C modes and 17 bpm to 70 bpm in P SIMV and V SIMV modes (Max Rtot) -
Page 152: Environmental
Specifications Environmental The following environmental conditions shall be observed: Table A-10. Environmental Conditions for Storage or Transport Temperature Humidity Atmospheric pressure Altitude -40°C to +70°C 10% to 95% RH 500 hPa to 1060 hPa -152 m to 3964 m (-40°F to +158°F) (7.2 psi to 15.4 psi) (500 ft to 13 000 ft) Table A-11. Environmental Conditions for Operation…
-
Page 153: Pneumatic
Pneumatic Pneumatic Table A-14. Airway Resistances Inspiratory Exhalation 1.0 mbar at 30 lpm flow ±0.1 mbar 0.5 mbar at 30 lpm ±0.1 mbar 3.7 mbar at 60 lpm flow ±0.1 mbar 1.1 mbar at 60 lpm ±0.1 mbar Table A-15. Patient Circuit Resistances Adult double limb Pediatric double limb 2 mbar at 30 lpm flow 2 mbar at 60 lpm flow…
-
Page 154: Manufacturer’s Declaration
Specifications Manufacturer’s Declaration A.10 Tables A-19 through A-22 contain the manufacturer’s declarations for the ventilator’s electromagnetic emissions and electromagnetic immunity, as well as a list of compliant cables. WARNING: Portable and mobile RF communications equipment can affect the performance of the Puritan Bennett™…
-
Page 155
Manufacturer’s Declaration Table A-19. Electromagnetic Emissions The ventilator is intended for use in the electromagnetic environment specified below. The customer or the user of the ventilator should ensure that it is used in such an environment. Phenomenon and standard Compliance Electromagnetic environment – guidance Conducted and radiated RF emissions Group 1 The ventilator uses RF energy only for its internal functions. -
Page 156
Specifications Table A-21. Electromagnetic Immunity—Conducted and Radiated RF Phenomenon Basic EMC standard or test Immunity test levels for Home Healthcare method environment Conducted disturbances induced by RF IEC/EN 61000-4-6 fields 0,15 MHz–80 MHz 6 V in ISM and amateur radio bands between 0,15 MHz and 80 MHz 80% AM at 1 kHz Radiated RF EM fields… -
Page 157: Standards Compliance And Iec Classification
Standards Compliance and IEC Classification Table A-22. Compliant Cables and Accessories (Continued) Cable or accessory Maximum length 12V DC car adapter cable 5 m (16.4 ft) Oxygen inlet connector Puritan Bennett™ power pack (4098100) Standards Compliance and IEC Classification A.11 General Standards A.11.1 Medical Electrical Equipment: General Requirements for Safety IEC 60601-1 •…
-
Page 158: Particular Standards
Specifications Particular Standards A.11.3 Particular requirement for basic safety and Essential performance of home healthcare environmental • ventilators for ventilator-dependent patients — EN ISO 80601-2-72. Anesthetic and respiratory equipment — Conical connectors — Part 1: Cones and sockets EN ISO 5356-1. •…
-
Page 159: Modes Of Ventilation
B Modes of Ventilation Overview This chapter is a general description of the various modes of ventilation and breath types available with the Puritan Bennett™ 560 ventilator. Note: The default ventilation mode setting is P A/C; for more information, see below. Assist/Control (A/C) Modes When set to an Assist/Control mode, machine-initiated breaths are delivered at a clinician-set volume or pressure, inspiratory time, and rate.
-
Page 160: Cpap Mode
Modes of Ventilation CPAP Mode In CPAP, the ventilator maintains a constant level of pressure in the patient’s airway. PSV Mode PSV mode maintains a constant level of pressure in the patient’s airway during exhalation. In addi- tion, the ventilator applies a clinician-set pressure (Pressure Support) to each of the patient’s breaths.
-
Page 161
• If the ventilator fails any of the safety checks below, or if you cannot complete these checks, see section 3.9, Troubleshooting or call the equipment supplier or Covidien (see section 8.7, Service Assistance). WARNING: Provide the patient with an alternate means of ventilation before conducting these tests. -
Page 162: Operational Verification Checklist
Operational Verification Checklist Table C-1. Operational Verification Checklist Verify that the preventive maintenance schedule for the ventilator is followed. See Chapter 8, Routine Mainte- Pass nance. Ensure the patient breathing circuit is correctly attached to the ventilator, with all the necessary components, Pass and is free from any signs of damage and leaks.
-
Page 163
D Unpacking and Preparation The Puritan Bennett™ 560 ventilator is delivered with the items listed in Table D-1. Table D-1. Items Included with Ventilator Item Quantity Printed user’s manual Clinician’s manual on CD Patient circuit and valve Set of six combination foam/fine particle air inlet filters Dual bag (carrying bag) Oxygen connector AC power cable… -
Page 164: Unpacking And Preparation
Never use a ventilator or any components or accessories that appear to be damaged. If any signs of damage are evident, contact your equipment supplier or Covidien. Clean the ventilator with a mild soap solution, if necessary (see Chapter 7, Cleaning).
-
Page 165
If the ventilator fails any alarm test or if you cannot complete these tests, see the Troubleshooting section (refer to Chapter 3, Alarms and Troubleshooting) of this manual or call your equipment supplier or Covidien (refer to section 8.7, Service Assistance). WARNING: The Min PIP alarm setting must be adjusted for the patient, but must also be set high enough to allow the Patient Disconnection alarm to trigger properly. -
Page 166: Alarms Tests
Alarms Tests Low Pressure Test WARNING: The Min PIP alarm setting must be adjusted for the patient, but must also be set high enough to allow the Patient Disconnection alarm to trigger properly. Perform the following test to ensure that the Low PIP alarm is properly set.
-
Page 167: Max Leak Test (Only Niv
Max Leak Test (Only NIV) Max Leak Test (Only NIV) WARNING: The Max Leak alarm setting must be adjusted for the patient, but must also be set low enough to allow the High Leakage alarm to trigger properly. Perform the following test to ensure that the alarm is functioning properly.
-
Page 168: Circuit Check
Alarms Tests Press and hold the VENTILATION ON/OFF key for 3 seconds, then release it. Press the VENTILATION ON/OFF key again to confirm stop. Ventilation stops • Circuit Check Perform a circuit check whenever replacing or altering a patient circuit. Ensure the patient is fully disconnected from the ventilator prior to starting this test.
-
Page 169: Performing The Circuit Check
Circuit Check Performing the Circuit Check E.3.2 To perform a circuit check: Verify that the proximal pressure tube of the patient circuit is properly connected to the proximal pres- sure port (see section 4.4, Patient Circuit). Verify that the exhalation valve tube is connected to the exhalation valve port. Block the patient connection port or patient wye of the patient circuit (see Figure E-4).
-
Page 170: Figure E-6. Circuit Check (Complete, Passed)
Alarms Tests Increase pressure to 30 mbar (±10% with no leak) Show flow sensor measurement as Leak in Lpm (updated every 2 seconds) Sound a short beep every time the flow measurement is updated Sound a long audible beep once the check is complete Show PASS (see Figure E-6) or FAIL (see Figure E-7) in the Test Status field Figure E-6. Circuit Check (complete, passed) Figure E-7. Circuit Check (complete, failed)
-
Page 171: Troubleshooting A Failed Check
Power Failure Test Troubleshooting a Failed Check E.3.3 If the circuit check fails, do the following: Ensure an approved circuit is in use. See Table F-2. Check patient circuit connections to the ventilator, examining each for leakage and tightness. Replace the patient circuit if necessary. Rerun the circuit check.
-
Page 172: Occlusion Test
Alarms Tests The AC Power Disconnection alarm is shown • Figure E-8. Ventilator Screen (AC Power Disconnection alarm shown) Press the ALARM CONTROL key twice to reset the alarm. Reconnect the ventilator to its AC power supply. Occlusion Test To perform an occlusion test: Verify that the pressure tube of the patient circuit is properly connected to the appropriate fitting on both the ventilator and the proximal pressure port (see section 4.4, Patient…
-
Page 173: Battery Test
Battery Test After two breaths or after 5 seconds, whichever takes longer, ensure that the following events occur: The high priority indicator (flashing red LED) illuminates • An audible alarm sounds • The Occlusion alarm is shown; the Low VTI alarm may also activate •…
-
Page 174: Involuntary Stop Test
Alarms Tests Figure E-11. Ventilator Screen (AC Power Disconnection alarm shown) Press the ALARM CONTROL key twice to reset the alarm. Ensure that the following events occur: The internal battery indicator to the upper-left of the display illuminates • The battery symbol is shown at the top of the screen (along with its reserve capacity) •…
-
Page 175: Table F-1. List Of Consumables And Accessories
Table provides a list of accessories that are available for the Puritan Bennett™ 560 ventilator. To order parts or accessories, contact your equipment supplier or Covidien representative. For a list of items delivered with the ventilator, see Appendix D, Unpacking and Preparation.
-
Page 176: Parts And Accessories
Adult-pediatric HME (formerly Hygrolife II) Table provides a list of consumable parts available for the ventilator. WARNING: To ensure proper performance of the ventilator, use a patient circuit recommended by Covidien in this manual; see Chapter 4, Installation and Assembly and Appendix F, Parts and Accessories.
-
Page 177
G Glossary AC Power Alternating current. Alarm Pause The audible and visual alarms cease and the alarm paused symbol appears. The symbol will remain until the cause of the alarm is addressed. For example, when the ventilator is running on internal battery, the AC Disconnection alarm may be paused, and the alarm paused symbol will appear until the device is plugged into AC. -
Page 178: Glossary
Glossary Back Up Rate Rate of control cycles in PSV or SIMV modes during apnea phase. Battery Level Display of the remaining battery capacity; located adjacent to the battery symbol. Bias Flow Turbine flow during exhalation phase through the patient circuit to avoid rebreathing. An abbreviation for “breaths per minute,”…
-
Page 179
Exhalation Tidal Volume (VTE) Volume exhaled by the patient at each exhalation phase. Exhaled Tidal Volume (VTE) Exhaled volume measured for all breath types through the exhalation block. Monitored value avail- able only with double-limb patient circuit. Exhaled volume is computed using a five-breath average. Fraction of Inspired Oxygen (FiO Amount of oxygen delivered to the patient. -
Page 180
Glossary Intentional Vent Stop Alarm Ventilation has been switched off by the user/caregiver and the ventilator is in standby. I/T Ratio Inspiratory time versus total breath time ratio. Liters (a unit of volume). Leak When ventilating with a double-limb circuit in leak configuration, it is the average unexpected leak during each cycle and over the past 24-hour period. -
Page 181
Minimum Inspiratory Time Minimum inspiratory time before allowing the patient to exhale. M Vol (Minute Volume) Flow delivered at each breath to the patient is measured by the inspiratory flow sensor and that measurement is used to calculate minute volume (Vt × Rtot). Non-Invasive Ventilation (NIV) Patient ventilation without the use of an endotracheal tube;… -
Page 182
Glossary Pressure Support (P Support) Augmentation of the patient’s ventilation synchronously with inspiratory effort until a preset pres- sure is met. Pressure is maintained until inspiratory flow is reduced to a percentage of peak flow that depends on the exhalation sensitivity setting for the inspiration, when the ventilator cycles into exhalation. -
Page 183
V A/C (Volume Assist/Control) A ventilator mode which provides machine-initiated breaths are delivered at a clinician-set volume inspiratory time, and rate. Vent Time (Ventilation Time) The ventilation duration data is based on the patient counter and shows the total ventilation time in hours and minutes over the previous 24-hour period. -
Page 184
Glossary Page Left Intentionally Blank User Manual… -
Page 185
Index INTENTIONAL VENT STOP ……3-13, 3-22 KEYPAD FAULT ……..3-13, 3-22 AC power LOW BATTERY . -
Page 186
Index Reserve capacity display Check Settings alarm Ventilation running ……..6-4 Cause &… -
Page 187
Index High Internal Temperature alarm Device Fault 7 alarm Cause & response ………3-12 Cause &… -
Page 188
Index Maintenance ……….8-10 Periodic test . -
Page 189
Index Power Supply Loss alarm Single-limb patient circuit Cause & response ……… 3-14 Installing Corrective action . -
Page 190
Index USB menu VTI Not Reached alarm Transfer continuously ……..5-5 Cause &… -
Page 192
Part No. PT00106571 Rev A 2019-07 © 2019 Covidien. All rights reserved. Covidien llc 15 Hampshire Street, Mansfield, MA 02048 USA Covidien Ireland Limited, IDA Business and Technology Park, Tullamore, Ireland. www.Medtronic.com [T] 1 800 635 5267…
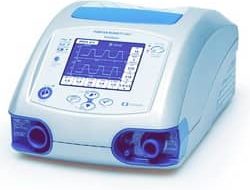
Аппарат искусственной вентиляции легких Puritan Bennett 560 предназначен для постоянной или периодической механической вентиляционной поддержки пациентов с весом тела не ниже 5 кг, которым требуется проведение механической вентиляции. Аппарат ИВЛ Puritan Bennett 560 представляет собой медицинский прибор ограниченного применения, который должен использоваться квалифицированным и обученным персоналом под руководством врача.
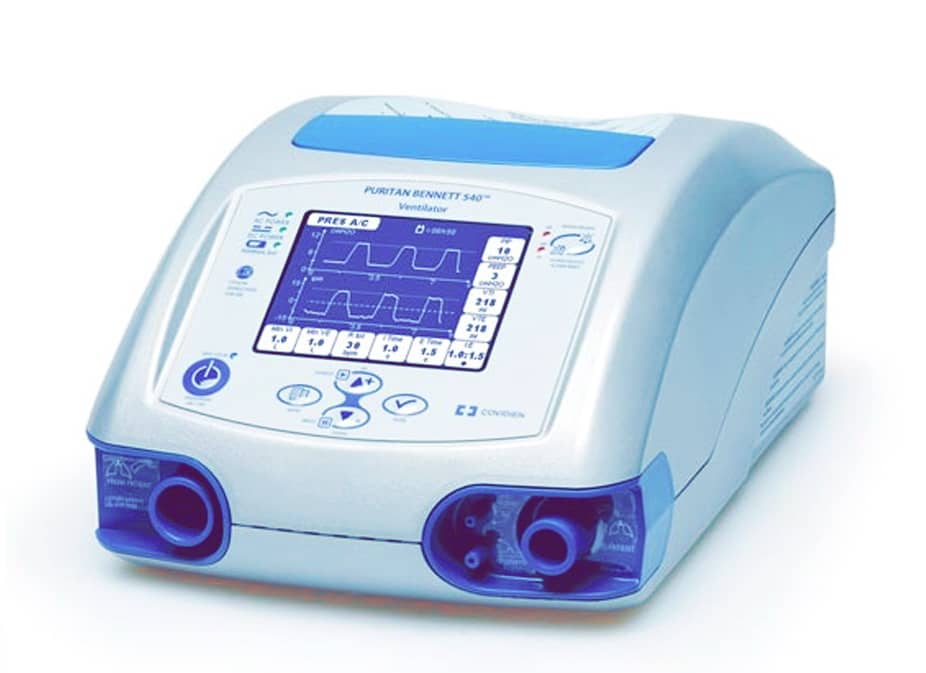
Данный вентилятор специально предназначен для взрослых и детей, которым необходимо проведение следующих видов инвазивной или неинвазивной вентиляции легких, как предписано наблюдающим врачом:
- Вентиляция с положительным давлением.
- Вспомогательная вентиляция с поддержкой/управлением, режимы SIMV или CPAP.
- Дыхание с управлением по давлению, объему или с поддержкой по давлению.
Вентилятор Puritan Bennett 560 рассчитан на использование в условиях медицинского учреждения, дома и в качестве переносного устройства. Не предполагается использовать его в качестве аппарата ИВЛ для машин скорой помощи.
Использование Puritan Bennett 560 COVIDIEN
Аппаратом искусственной вентиляции легких могут управлять:
- Врачи – специалисты в области заболеваний органов дыхания;
- Врачи;
- Медсестры;
- Персонал, ухаживающий за больными на дому (сиделки);
- Сам пациент и его родственники.
Переносной аппарат ИВЛ Puritan Bennett 560 использует микро-турбину для осуществления респираторной поддержки пациентов. Практикующее врачи могут пользоваться различными способами для подключения пациентов к этому аппарату: носовыми масками или лицевыми масками, эндотрахеальными или трахеотомическими
трубками. Пользователь может выбирать следующие режимы вентиляции:
- С поддержкой/управлением по объему (V A/C).
- С поддержкой/управлением по давлению (Р A/C).
- Синхронизированная перемежающаяся принудительная вентиляция (СППВ) с поддержкой по объему (V SIMV).
- Синхронизированная перемежающаяся принудительная вентиляция (СППВ) с поддержкой по давлению (Р SIMV).
- Самостоятельное дыхание с созданием постоянного положительного давления (СДППД) в дыхательных путях (СРАР).
- Вентиляция с поддержкой давлением и вентиляцией при отсутствии дыхания ВПД/ОД) (PSV/ST).
Система безопасности
В вентилятор встроена система сигнализации, которая постоянно отслеживает состояние пациента и машины на предмет сигналов о конкретных ошибках или неполадках, которые могут вызвать опасную ситуацию. Если такие ошибки или неполадки замечены, система сигнализации подает характерный сигнал тревоги, как зрительный, так и звуковой. Параметры срабатывания сигнализации по неполадкам прибора заданы на производстве, в то время как параметры срабатывания, связанные с пациентом, задаются пороговыми значениями величин, которые выбирают операторы (врачи в клинике или сиделки/медперсонал).
Настройки аппарата ИВЛ
Программная клавиша, так называемая клавиша блокировки, предотвращает доступ к настройкам параметров вентиляции, чтобы разграничить «врачебное» использование и «личное» использование самим пациентом.
Обогащение кислородом
Кислород может подаваться из внешнего источника низкого давления, но его расход должен быть не выше 15 л/мин, давление – 50 кПа, 7 PSI. Аппараты искусственной вентиляции легких (ИВЛ) Puritan Bennett 560 автоматически компенсирует избыточный расход, создаваемый при подаче кислорода извне.
Дыхательный контур
Вентилятор можно использовать с контуром пациента, снабженным одним или двумя патрубками (отводами). Если нужно контролировать объем выдыхаемого воздуха (как в случае с пациентами, которые самостоятельно дышать не могут), следует использовать контур с двумя патрубками для контроля дыхательного объема на выдохе.
Производитель Puritan Bennett 560
Производитель аппарата искусственной вентиляции легких Puritan Bennett 560 – Medtonic (COVIDIEN), страна производитель США.
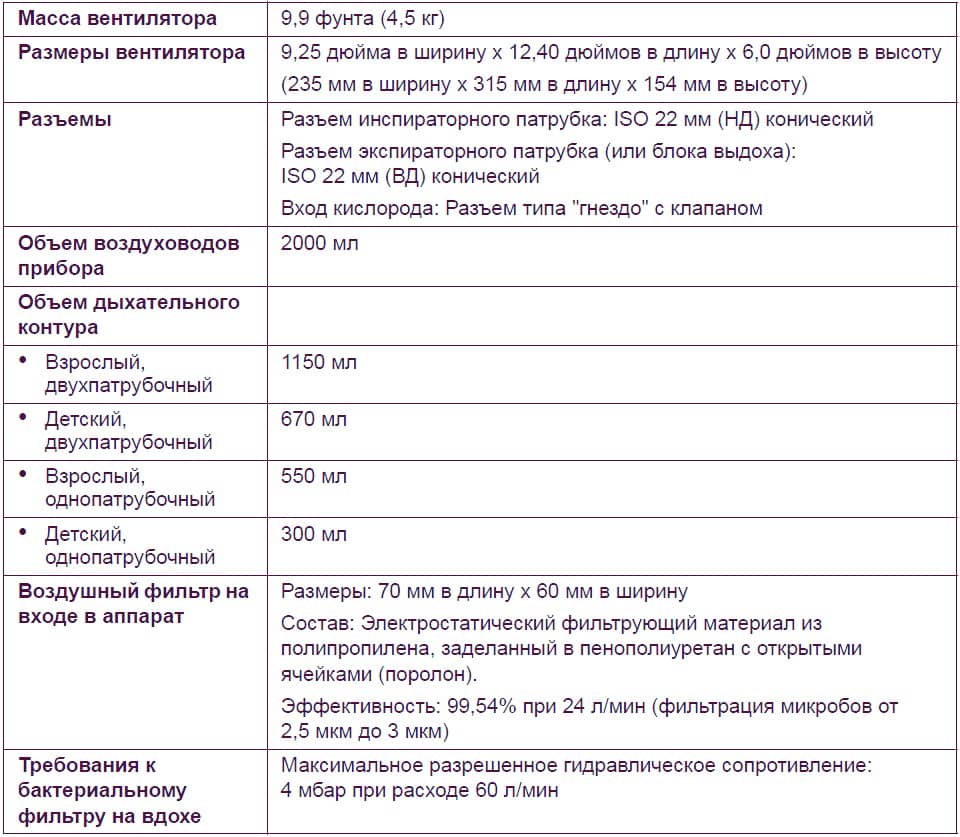
Технические характеристики Puritan Bennett 560
Ниже указаны технические характеристики аппарата Puritan Bennett 560. Физическое описание (включая дополнительные приспособления).
Полный перечень технических характеристик можно найти в инструкции. Скачать инструкцию на аппарат ИВЛ Puritan Bennett 560 COVIDIEN можно в конце статьи.
Видео обзор аппарата ИВЛ Puritan Bennett 560
Ниже представлено видео с обзором на аппарат ИВЛ Puritan Bennett 560 (Covidien, Medtronic).
Передняя панель Puritan Bennett 560
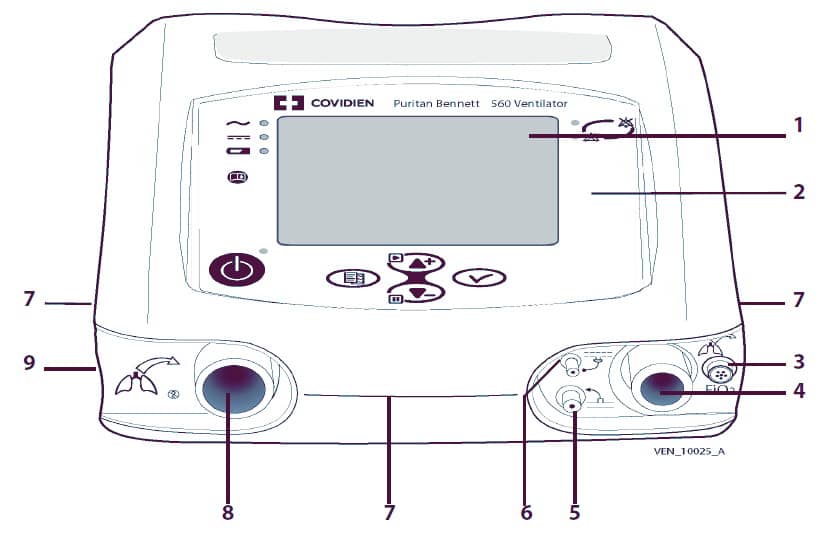
- ЖК- дисплей – отображает информацию о вентиляторе, в том числе время, проведенное пациентом на вентиляторе, версию ПО, режимы и настройки вентиляции, контролируемые и расчетные данные пациента и формы сигналов. Также при помощи дисплея пользователь может просматривать рабочие параметры и параметры системы сигнализации вентилятора и менять их, пользуясь панелью управления.
- Панель управления – предоставляет возможность управления настройками и работой вентилятора, а также светодиодную индикацию источника питания вентилятора, состояния «вкл/выкл» и приоритета сигналов тревоги. Функции управления включают в себя выключение и включение вентилятора, настройку режимов работы вентилятора, заглушение и отмену сигналов тревоги и установку параметров срабатывания системы сигнализации и рабочих параметров аппарата.
- Подключение датчика FiO2 – для датчика FiO2, который измеряет концентрацию кислорода в контуре пациента.
- Порт подключения пациента – предоставляет возможность поступления газа к пациенту через дыхательный контур.
- Разъем контроля давления пациента – Патрубок для контроля проксимального давления у пациента.
- Порт клапана выдоха – патрубок для подачи управляющего давления на клапан выдоха. Управляет открытием и закрытием клапана выдоха.
- Боковые и передние отверстия – вентиляционные отверстия, благодаря которым осуществляется охлаждение внутренних узлов вентилятора. Кроме того, они служат для распространения звукового сигнала тревоги.
- Порт «от пациента» – через него осуществляется измерение выдыхаемого объема, т.к. часть выдыхаемого газа через этот порт направляется на датчик расхода. Путем измерения этого расхода вычисляется величина VTE (Дыхательный объем на выдохе).
- Выход выдыхаемого газа – сюда подключается клапан выдоха.
Задняя панель
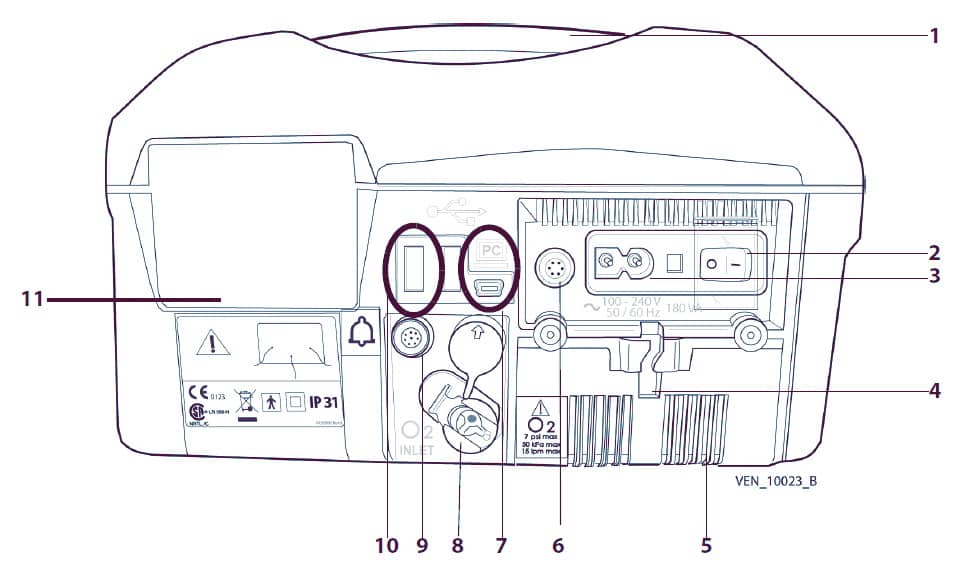
- Эргономичная ручка для переноски.
- Выключатель питания «Вкл/Выкл» (I/O) с защитной крышкой: В положении I прибор включен, в положении О — выключен.
- Разъем шнура электропитания переменного тока («Сетевой»).
- Система крепления шнура электропитания переменного тока («Сетевого»): Закрепляет шнур электропитания переменного тока во избежание случайного отсоединения.
- Крышка аккумуляторного отсека.
- Разъем для подключения шнура электропитания постоянного тока с направляющим ключом.
- Разъем для подключения ПК Мини- USB разъем для подключения тестирующего ПО вентилятора Puritan Bennett 560.
- Порт подвода O2: Соединяет вентилятор с источником кислорода низкого давления через переходник, надетый на патрубок ввода O2.
- Разъем вывода сигнала на устройство вызова медсестры: Используется для подключения вентилятора к системе вызова медсестры.
- Разъем устройства памяти USB: Разъем USB, который используется с программным обеспечением Puritan Bennett по поддержанию работы вентилятора. Имеются два порта USB типа А.
- Воздушный фильтр на входе в аппарат: Фильтрует воздух, поступающий в аппарат.
Панель управления
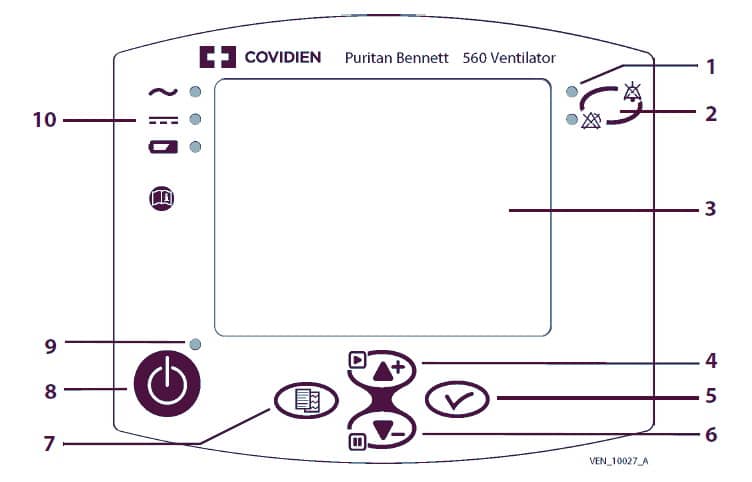
- Световые сигналы (два СДИ). Красные: (Непрерывный) Сработал сигнал тревоги ОВУ (очень высокого уровня); Сработал сигнал тревоги ВУ (высокого уровня). Желтый: Сработал сигнал тревоги СУ (среднего уровня).
- Клавиша УПРАВЛЕНИЕ СИГНАЛИЗАЦИЕЙ. Однократное нажатие заглушает звуковой сигнал тревоги на 60 секунд. Двойное нажатие останавливает звуковой и световой сигнал тревоги. Если ситуация, вызвавшая сигнал тревоги, исправлена, то сигнализация отменяется (за исключением сигнала по высокому давлению).
- Дисплей. Отображает режимы, настройки вентиляции, данные пациента и формы сигналов расхода или давления газа, конфигурацию вентилятора, а также позволяет управлять сигналами тревоги.
- Клавиша ВВЕРХ/ВОЗОБНОВИТЬ. Перемещает курсор вверх и увеличивает значение параметра. В ходе вентиляции возобновляет отслеживание форм сигналов расхода или давления в меню форм кривых.
- Клавиша ВВОД. Дает доступ к величинам настроек и проверке настроек в случае их изменения. Доступ в подменю.
- Клавиша ВНИЗ/ОСТАНОВИТЬ. Перемещает курсор вниз и уменьшает значение параметра. В ходе вентиляции останавливает отображение форм сигналов в меню форм кривых.
- Клавиша МЕНЮ. Изменяет отображаемое меню. Нажатием этой клавиши из меню вентиляции можно вызвать экран меню сигнализации. Когда к вентилятору подключается USB-карта памяти, нажатием этой клавиши можно вызвать экран меню устройства USB.
- Клавиша ВКЛ/ВЫКЛ ВЕНТИЛЯЦИЮ. Кратковременное нажатие на эту клавишу запускает вентиляцию. Для остановки вентиляции нажатие нужно удерживать в течение трех (3) секунд.
- Индикатор состояния вентиляции. Горит голубой индикатор: прибор включен и находится в состоянии готовности (вентиляция отключена). Голубой индикатор отключен: вентиляция включена.
- Индикаторы источников электропитания. Горит индикатор ПЕРЕМЕННЫЙ ТОК: подключен источник питания переменного тока. Горит индикатор ПОСТОЯННЫЙ ТОК: подключен источник питания постоянного тока. Индикатор ВСТРОЕННЫЙ АККУМУЛЯТОР горит постоянно: используется встроенный аккумулятор (никакой внешний источник не подключен). Индикатор ВСТРОЕННЫЙ АККУМУЛЯТОР мигает: аккумулятор заряжается.
Сигналы тревоги или неисправности
Сигналы тревоги или неисправности, создаваемые аппаратом Вентилятор Puritan Bennett 560, классифицируются по двум категориям:
- тревоги вентиляции (или те, что возникают в ходе работы);
- технические неисправности.
Некоторые из сигналов тревоги вентилятора могут регулироваться в зависимости от режима работы вентилятора. Также существуют нерегулируемые сигналы тревоги, предназначенные для создания сети безопасности и более безопасной вентиляции пациента.
Сигналы тревоги указывают на события, которые могут оказать влияние на ход вентиляции и требуют быстрого вмешательства.
Технические неисправности не влияют непосредственно на работу аппарата. Соответственно, пользователь не ставится в известность о технических неисправностях. Меню технического обслуживания доступно только для обученных техников с правом допуска.
Уровень приоритетности сигналов тревоги
Ниже перечислена иерархия сигналов тревоги в зависимости от того, насколько они критичны:
ОВУ, очень высокий уровень: Наступила критическая ситуация; вентиляция невозможна.
Постоянный звуковой сигнал / с постоянно горящим красным СДИ или без него / с выдачей сообщения или без него / с освещением дисплея или без него (возможны такие аварийные ситуации, при которых не будет как сообщения, так и освещения дисплея).
ВУ – высокий уровень: Критическая ситуация вскоре наступит; потенциальная угроза проведению вентиляции.
Высокочастотный прерывистый звуковой сигнал / мигающий красный СД-индикатор / сообщение / освещение дисплея.
СУ – средний уровень: До начала критической ситуации может пройти значительное время; в ближайшее время вентиляция не прервется.
Прерывистый звуковой сигнал, подаваемый со средней частотой / мигающий желтый СД-индикатор / сообщение / освещение дисплея.
Если не будут приняты какие-либо меры и если звуковой сигнал не будет прерван (заглушением звукового сигнала) или сброшен (путем сброса сигнализации) в течение 60 секунд, то сигнал ВУ будет подаваться на максимальной громкости.
Фильтры Puritan Bennett 560
Аппарат искусственной вентиляции легких Puritan Bennett 560 использует два типа фильтров:
- воздушный фильтр на входе в аппарат;
- бактериальный фильтр.
Воздушный фильтр на входе в аппарат
Этот фильтр, состоящий из поролона и специального наполнителя для удаления мелких частиц, расположенный в задней части вентилятора, фильтрует воздух по мере его поступления в прибор.
Бактериальный фильтр
Настоятельно рекомендуется устанавливать бактериальный фильтр как с однопатрубочными, так и с двухпатрубочными контурами. В двухпатрубочном контуре используются два бактериальных фильтра: один в порте К ПАЦИЕНТУ, другой — в порте ОТ ПАЦИЕНТА.
Увлажнитель Puritan Bennett 560
Увлажнитель добавляет влагу (водяной пар) и согревает газ в контуре пациента. Он вставляется в контур пациента между главным выходным патрубком и собственно пациентом.
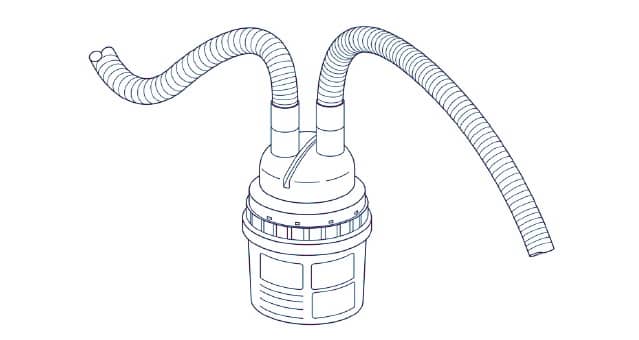
При использовании увлажнителя весь конденсат, образующийся в контуре пациента, собирается в водяной ловушке. При обнаружении любой влаги в контуре пациента влажные его части нужно заменить сухими.
Подключение датчика FIO2 (концентрации кислорода)
При назначении кислорода рекомендуется использовать датчик концентрации кислорода FiO2, который можно присоединить спереди к аппарату при помощи комплекта для определения FiO2 (концентрации кислорода).
Датчик кислорода требует калибровки, снимать и чистить его разрешается только квалифицированным сотрудникам. Если используется новый датчик, то его нужно выдержать при температуре окружающей среды в течение примерно 20 минут прежде чем устанавливать, калибровать и начинать вентиляцию.
Чтобы установить датчик FiO2 (концентрации кислорода):
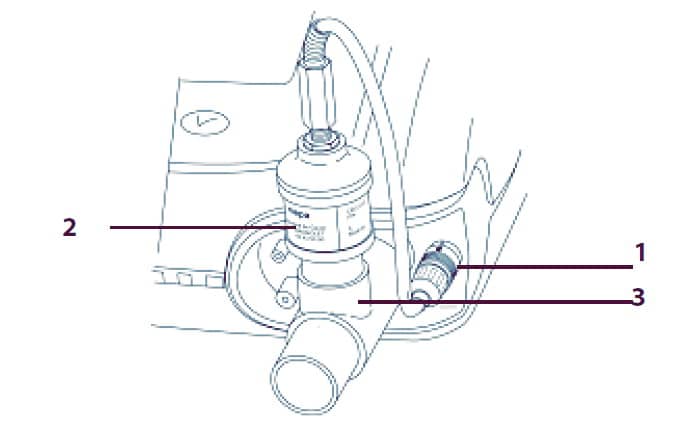
- Выньте устройство из герметичной упаковки.
- Установите переходник FiO2 (концентрации кислорода) в разъем FiO2 на вентиляторе (поз. 1).
- Соедините датчик FiO2 (концентрации кислорода) (поз.2) с переходником диаметром 15 мм (поз.3).
- Установите переходник на выходной порт К ПАЦИЕНТУ, как показано. Закрепите контур пациента за переходником.
Калибровка датчика кислорода FiO2
В видео представлена последовательность действий при калибровке датчика кислорода (FiO2) аппарата ИВЛ Puritan Bennett 560 и для чего это нужно.
Аккумулятор Puritan Bennett 560
Вентилятор Puritan Bennett 560 удовлетворяет всем условиям электробезопасности, внутренний аккумулятор литий-ионная батарея. Максимальный рекомендуемый срок хранения встроенного аккумулятора два года. Не следует брать в работу аккумулятор, который пролежал на складе два года и ни разу не использовался.
Для продления срока службы аккумулятора важно, чтобы его периодически перезаряжали. Не следует хранить аккумуляторы длительное время без перезарядки, это сокращает срок их службы.
Емкость аккумулятора Puritan Bennett 560
Резервная емкость встроенного аккумулятора зависит от уровня заданных параметров вентиляции, от условий окружающей среды (в основном, от температуры) и от физиологических характеристик пациента.
Проверка уровня заряда аккумулятора подразумевает, что на момент проверки вентилятор находится в работе и работает от аккумулятора. Чтобы проверить уровень заряда аккумулятора, следует временно отключить вентилятор от источника переменного тока (либо в режиме готовности, либо в ходе вентиляции) и прочесть значение уровня заряда в процентах, которое показывается рядом с символом аккумулятора, отображаемым в верхней части экрана дисплея.
Работа аккумулятора Puritan Bennett 560
Перед тем, как пользоваться встроенным аккумулятором вентилятора, следует убедиться, что он полностью заряжен и удерживает заряд. Запасные вентиляторы или вентиляторы, находящиеся на хранении, должны быть подключены к источнику переменного тока, чтобы защитить целостность аккумулятора.
Когда прибор впервые запускается после полной перезарядки встроенного аккумулятора, возможно срабатывание сигнального устройства и сигнализации по состоянию аккумулятора. В этом случае нужно подключить прибор к сети переменного тока и перезапустить питание прибора.
В случае прекращения подачи переменного тока или отсоединения от внешнего источника переменного или постоянного тока вентилятор автоматически переключается на встроенный аккумулятор и происходит следующее:
- Символ аккумулятора отображается в верхней части строки общих сведений.
- Остаток емкости аккумулятора отображается справа от соответствующего символа.
- Индикатор «ВСТРОЕННЫЙ АККУМУЛЯТОР» в левой верхней части передней панели индикатора горит постоянно.
- Срабатывает сигнализация по прекращению подачи электропитания от внешнего источника.
Если вентиляция останавливается, остаток емкости аккумулятора отображается в виде процента заряда аккумулятора.
Если вентилятор работает, то остаток емкости встроенного аккумулятора кратковременно показывается в виде процента. Затем, после того, как вентилятор рассчитает срок работы от аккумулятора (что может занять до двух минут, в зависимости от энергопотребления вентилятора) остаток заряда аккумулятора отображается в часах и минутах (с округлением до пятнадцати минут).
С момента срабатывания сигнала «БАТАРЕЯ РАЗРЯЖЕНА», если не подключить прибор к внешнему источнику тока, могут сработать другие сигналы тревоги в связи с недостаточным уровнем напряжения. В последней стадии разрядки сигнал «БАТАРЕЯ РАЗРЯЖЕНА» становится постоянным, и вентиляция в любой момент может быть прекращена.
Проверка аккумулятора Puritan Bennett 560
Вентилятор постоянно автоматически проверяет состояние встроенного аккумулятора, даже когда он не используется в качестве основного источника энергии. Сигнал «СБОЙ БАТАРЕИ 1» срабатывает в случае обнаружения любой проблемы с аккумулятором или зарядным устройством.
Раз в месяц нужно отсоединять вентилятор от внешнего источника энергии, чтобы проверить целостность соединений между встроенным аккумулятором и другими узлами вентилятора.
Перезарядка аккумулятора Puritan Bennett 560
Когда уровень заряда в аккумуляторе недостаточен, если судить по показателям остаточной емкости, необходимо выполнить перезарядку аккумулятора. В общем рекомендуется ставить вентилятор на зарядку, когда уровень заряда в аккумуляторе падает ниже 80%, а также систематически перезаряжать вентилятор после хранения и перед повторным использованием.
Во избежание перехода с одного источника питания на другой и для продления срока службы аккумулятора, он при присоединении к источнику переменного тока не будет заряжаться до тех пор, пока заряд не упадет ниже 85 — 90%.
Чтобы перезарядить встроенный аккумулятор, нужно подсоединить вентилятор к источнику переменного тока. Когда аккумулятор полностью заряжается, индикатор ВСТРОЕННЫЙ АККУМУЛЯТОР гаснет.
Нет необходимости запускать вентилятор в работу при зарядке аккумулятора, пополнение заряда при работающем вентиляторе приводит к увеличению времени, необходимого для полной зарядки встроенного аккумулятора.
При перезарядке истощенного аккумулятора может понадобиться оставить вентилятор на зарядке на протяжении 6 (шести) часов в режиме готовности или около 13 часов при работающем вентиляторе.
Хранение аккумулятора
Если вентилятор необходимо сдать на хранение на длительный срок, не обязательно вынимать из него аккумулятор. Однако хранить вентилятор следует в сухом прохладном месте, хорошо вентилируемом, при следующих условиях:
- Температура: около 21 °C (70 °F);
- Влажность: менее 80% относительной влажности.
Если аккумулятор хранится более месяца при температуре выше 21 °C (70 °F) или более двух недель — при температуре свыше 45 °C (113 °F), то это может сказаться на остаточной емкости аккумулятора. Перед повторным использованием такой аккумулятор следует перезарядить.
Если вентилятор в течение более чем 30 дней хранился подключенным к источнику переменного тока, перед началом вентиляции включите его выключателем I/O (вкл/выкл) в задней части аппарата и дайте ему зарядиться в течение 15 минут.
Очистка Puritan Bennett 560
Протирайте все внешние панели и поверхности перед и после работы с каждым из пациентов, а также по мере надобности, чтобы вентилятор всегда был чистым. Загрязненные или испачканные участки вентилятора нужно очищать перед выполнением технического обслуживания, а также перед отправкой на хранение.
Чтобы почистить поверхность вентилятора, нужно:
- Намочить чистую мягкую ткань в некрепком мыльно-водном растворе или в другом разрешенном моющем растворе.
- Тщательно отжать ткань, чтобы удалить избыток жидкости.
- Слегка протереть наружный корпус вентилятора, следя за тем, чтобы жидкость не попала в какие-либо из отверстий на его поверхности. См. предупреждение выше.
- Вытереть насухо поверхность вентилятора чистой мягкой безворсовой тканью.
Растворы, которыми разрешено пользоваться для чистки внешних
поверхностей вентилятора:
- Слабый раствор средства для мытья посуды;
- 70% изопропиловый спирт (для протирки);
- 10% хлорный отбеливатель (90% — вода из крана);
- Глутаральдегид;
- Больничные дезинфектанты в форме раствора;
- Перекись водорода;
- 15% р-р аммиака (85% — вода из-под крана);
- Домашние чистящие средства, содержащие аммиак;
- Домашние чистящие средства.
Техническое обслуживание Puritan Bennett 560
Необходимо регулярно проверять чистоту воздушного фильтра на входе в аппарат,который расположен в задней части вентилятора. При необходимости фильтр заменяют до истечения рекомендованного периода замены. Если вовремя не заменить воздушный фильтр на входе в аппарат или допустить работу вентилятора «без» — Yulia фильтра, это может привести к серьезной поломке аппарата. Воздушные фильтры являются одноразовыми изделиями. Запрещается мыть, чистить или повторно использовать их.
При использовании вентилятора в помещении проверку состояния воздушного фильтра следует проводить раз в месяц. При использовании аппарата на открытом воздухе или в запыленном помещении проверку воздушного фильтра следует выполнять еженедельно и заменять фильтр по необходимости.
Рекомендуемый график технического обслуживания
При использовании в нормальных условиях — относительно незапыленной атмосфере и без повреждений аппарата и его узлов (толчки, трещины, сильная загрязненность) — сроки замены расходных материалов вентилятора приведены ниже.
Расходные материалы и сроки их замены
Воздушный фильтр на входе в аппарат (Поролон + мелкие частицы).
Раз в месяц или чаще, в зависимости от степени загрязнения.
Инспираторный бактериальный фильтр.
Смотреть рекомендации производителя.
Контур пациента.
Смотреть рекомендации производителя. Одноразовый однопользовательский (для одного пациента).
Датчик FiO2.
От 14 до 18 месяцев или чаще в случае постоянных сбоев в калибровке.
Блок выдоха.
Раз в 4 месяца и для каждого нового пациента.
Замена встроенного аккумулятора
Встроенный аккумулятор нужно заменять, когда его емкость падает ниже 3450 мАh. Следует иметь в виду, что по соображениям экологического характера вентилятор и его узлы — включая встроенный аккумулятор — нельзя утилизировать как бытовые отходы. Вентилятор и его узлы следует отправлять на раздельный сбор вторсырья для возможной утилизации и повторного использования с соблюдением всех применимых законодательных норм.
Режимы вентиляции Puritan Bennett 560
Ниже представлено общее описание различных режимов вентиляции и типов дыхания, которые может обеспечивать Вентилятор Puritan Bennett 560. По умолчанию в приборе установлен режим P A/C.
Режимы с поддержкой/управлением (A/C)
При задании режимов с поддержкой/управлением такие параметры аппаратно инициируемых вдохов, как объем, давление, время вдоха и частота дыхания задаются лечащим врачом. Если у пациента между аппаратными вдохами случается самопроизвольный вдох, то вентилятор подает ему воздух в объеме или под давлением, заданными соответствующими установками, а также в течение заданного времени.
Вне зависимости от того, спонтанные это дыхания или аппаратные, каждое дыхание совершается в том же самом заданном объеме (или при том же заданном давлении) и за одно и то же заданное время вдоха.
Режимы с поддержкой/управлением бывают:
- V A/C (с поддержкой/управлением по объему), если заданным параметром дыхания является объем;
- P A/C (с поддержкой/управлением по давлению), если заданным параметром дыхания является давление.
Режимы SIMV
При задании режима SIMV (Синхронизированная перемежающаяся принудительная вентиляция, СППВ) такие параметры аппаратно инициируемых вдохов, как объем, давление, время вдоха и частота дыхания задаются лечащим врачом. Эти принудительные вдохи синхронизированы с дыхательными усилиями пациента. Если между аппаратными вдохами пациент делает вдох самостоятельно, вентилятор осуществляет самостоятельное дыхание с поддержкой давлением.
Самостоятельное дыхание с постоянным положительным давлением в дыхательных путях (CPAP) недоступно в режимах СППВ.
Режимы SIMV бывают:
- V SIMV (СППВ с поддержкой по объему), если заданным параметром принудительного дыхания является объем;
- P SIMV (СППВ с поддержкой по давлению), если заданным параметром принудительного дыхания является давление.
Режим CPAP
В режиме CPAP вентилятор поддерживает постоянный уровень давления в дыхательных путях пациента.
Режим PSV
В режиме PSV постоянный уровень давления поддерживается в дыхательных путях пациента во время выдоха. Кроме того, каждое из дыханий пациента вентилятор поддерживает заданным врачом давлением поддержки — Pressure Support. Это дает те же преимущества, что и метод CPAP, дополнительно помогая пациенту в поступлении газа в легкие.
Запчасти и расходные материалы
Ниже указан перечень приспособлений для Вентилятор Puritan Bennett 560. Чтобы заказать запчасти или приспособления, свяжитесь с поставщиком оборудования или с представителем компании Covidien.
Вентилятор поставляется в следующей комплектации: отпечатанное Руководство для пользователя, компакт-диск с Руководством для практикующего врача (печатный экземпляр можно заказать отдельно); Один контур пациента с клапаном; один комплект из 6 (шести) комбинированных воздушных фильтров для входного патрубка (поролоновый фильтр/фильтр мелких частиц); одна сумка для переноски; один кислородный переходник; и один шнур электропитания переменного тока.
Перечень расходных материалов
- Сумка для переноски (серая).
- Впускной патрубок для кислорода.
- Тележка для вентилятора.
- Двойная сумка (синяя или розовая).
- Шнур электропитания переменного тока (сетевой).
- Шнур электропитания постоянного тока (для подключения к внешнему источнику постоянного тока, например, к автомобильному разъему постоянного тока напряжением 12 В).
- Кабель вызова медсестры (5 метров).
- Блок выдоха, одно пользовательский (голубой).
- Комбинированный воздушный фильтр, мелкопористый (6 штук в комплекте).
- Встроенный аккумулятор.
- Внешний аккумулятор.
- Комплект для измерения концентрации кислорода.
- Датчик FIO2 (концентрации кислорода).
Скачать инструкцию на Puritan Bennett 560
Скачать инструкцию по применению и другую документацию на аппарат искусственной вентиляции легких Medtonic (COVIDIEN) Puritan Bennett 560 можно здесь.
Руководство пользователя ( user manual ) на русском языке Puritan Bennett 560 скачать.
Декларация соответсвия Puritan Bennett 560 скачать.
Регистрационное удостоверение Puritan Bennett 560 скачать.
Респираторное обеспечение — каталог скачать.
Трахеостомические трубки и принадлежности — каталог скачать.
Кислородная и аэрозольная терапия — каталог скачать.
Также смотрите Puritan Bennett 840 аппарат ИВЛ.
-
Contents
-
Table of Contents
-
Troubleshooting
-
Bookmarks
Quick Links
Clinician’s Manual
Puritan Bennett
TM
560 Ventilator
Related Manuals for Covidien Puritan Bennett 560
Summary of Contents for Covidien Puritan Bennett 560
-
Page 1
Clinician’s Manual Puritan Bennett 560 Ventilator… -
Page 2
Nothing in this manual shall limit or restrict in any way Covidien’s right to revise or otherwise change or modify the equipment (including its software) described herein, without notice. In the absence of… -
Page 3: Table Of Contents
Table of Contents Preface Purpose of this Manual …………xv Qualification of Personnel .
-
Page 4
P A/C Mode Parameters and Setting Ranges ……. . . 3-11 V A/C Mode Parameters and Setting Ranges . -
Page 5
Table of Contents 6.11 Connecting the Nurse Call Cable ……….6-26 Operating Procedures Turning on the Ventilator . -
Page 6
Battery Operation …………8-2 Testing the Battery . -
Page 7
Table of Contents Modes and Breath Types Modes of Ventilation …………D-1 D.1.1 Assist/Control (A/C) Modes . -
Page 8
Page Left Intentionally Blank viii… -
Page 9
List of Figures Figure 1-1. Locations of Labels—Top-Front View ……….. . 1-25 Figure 1-2. … -
Page 10
Figure 5-5. Pausing the Audible Portion of Alarms ……….. . 5-6 Figure 5-6. … -
Page 11
Puritan Bennett 560 Ventilator …….. -
Page 12
Page Left Intentionally Blank… -
Page 13
List of Tables Table 1-1. Ventilator Symbols …………..1-19 Table 1-2. … -
Page 14
Table B-19. Performance Specifications …………. . B-10 Table B-20. … -
Page 15: Purpose Of This Manual
Information regarding your product warranty is available from your sales representative or Covi- dien. Extended Service The Puritan Bennett 560 Ventilator offers extended service contracts/warranties for purchase when the ventilator is purchased. Please contact your local Covidien sales or service represen- tative for additional information.
-
Page 16: Technical Support
Here, you will find answers to frequently asked questions about the product and other Covidien products 24 hours a day, 7 days a week. If you require further assistance, contact your local Covidien represen- tative.
-
Page 17
Fax: +358 9 725 192 89 Tel: +33 1 57 32 35 10 Fax: +33 1 57 32 70 10 Covidien Hellas SA Covidien Hungary Covidien Ireland Commercial Ltd 8 Fragoklisias Street 1095 Budapest Block G, Ground Floor, Maroussi, 151 25 Mariassy u. -
Page 18
Fax: + 46 8 502 521 10 Tel: +34 91 275 48 54 (option 3) Fax: +34 91 276 89 33 Covidien Switzerland Covidien UK & Ireland Covidien Singapore Roosstr. 53 Unit 2, Talisman Business Park Singapore Regional Service Centre… -
Page 19: Safety Information
1 Safety Information Definitions This manual uses three indicators to highlight critical information: warning, caution, and note. They are defined as follows: WARNING Indicates a condition that can endanger the patient or the ventilator operator. Caution Indicates a condition that can damage the equipment. Note Indicates points of particular emphasis, that make operation of the ventilator more efficient or convenient.
-
Page 20
Safety Information WARNING: Be aware this manual describes how to respond to ventilator, but it does NOT tell you how to respond to the patient. WARNING: While the ventilator is in use, an alternative means of ventilation should always be available in the event of a ventilator problem. -
Page 21: Warnings Regarding Installation And Environment Of Use
WARNING: If the ventilator fails the alarm tests or if you cannot complete the tests, refer to Chapter 5.8, “Troubleshooting” or call your equipment supplier or Covidien. WARNING: When an alarm condition is triggered, or there is evidence of a patient-ventilator fault or problem, examine the patient first before examining the ventilator.
-
Page 22
Safety Information Dangerous Goods (DG) Class 9 – Miscellaneous, when transported in commerce. As such, the Puritan Bennett 560 Ventilator and/or the associated Lithium-ion battery are subject to strict transport conditions under the Dangerous Goods Regulation for air transport (IATA: International… -
Page 23
41°C (106°F). This may lead to undesirable side effects for the patient. To avoid injury to the patient move the patient and the ventilator to a cooler location. For more information, contact Covidien. … -
Page 24: Warnings Regarding Electrical Power Supplies
Safety Information WARNING: Handle the ventilator with care during and after use, particularly when ambient temperatures are high. Some ventilator surfaces may become hot, even if safety specifications are not exceeded. Warnings Regarding Electrical Power Supplies 1.2.3 WARNING: Never connect your ventilator to an electrical outlet controlled by a wall switch because the power may be inadvertently turned off.
-
Page 25: Warnings Regarding Hoses And Accessories
Warnings WARNING: Due to its limited internal battery’s reserve capacity, the ventilator should only be operated on the internal battery when no other power source is available. Ensure that the internal battery never becomes fully discharged. WARNING: When using a car auxiliary adapter (cigarette lighter) ensure the car has been started prior to plugging in the ventilator’s DC adapter.
-
Page 26
Safety Information WARNING: Before opening the packaging for the Patient Circuit, ensure that no damage is evident to the packaging or its contents. Do not use if evidence of damage exists. WARNING: The patient circuit should not be changed during ventilation. … -
Page 27
Warnings WARNING: If the ventilator is used indoors, the condition of the air inlet filter should be checked monthly. If the ventilator is used outdoors or in a dusty environment, the filter should be checked weekly and replaced as necessary. … -
Page 28
– especially when filters are replaced. WARNING: To ensure proper performance of the ventilator, use a patient circuit recommended by Covidien in this manual; refer to Chapter 6, “Installation and Assembly” and Appendix H, “Parts and… -
Page 29: Warnings Regarding Settings
Warnings WARNING: Do not use Nurse Call devices that operate based on the closure of an electrical circuit, because the devices often do not take into account possible cable disconnection or a total loss of power. Ensure that the Nurse Call device is always connected to the ventilator. Warnings Regarding Settings 1.2.5 …
-
Page 30
Safety Information WARNING: In adult or pediatric use ensure that the adjusted tidal volume is compatible with the needs of the patient. WARNING: When changing the mode during ventilation, significant transitions of pressure, flow or cycling rate might occur, depending on the difference between the modes. Before setting the new mode, first ensure that the settings between the different modes are compatible. -
Page 31: Warnings Regarding Usb Memory Device
WARNING: To ensure proper servicing and avoid the possibility of physical injury to personnel or damage to the ventilator, only personnel authorized and qualified by Covidien should attempt to service or make authorized modifications to the Puritan Bennett™ 560 Ventilator.
-
Page 32
Do not attempt to open, repair or otherwise service the ventilator yourself. Doing so might endanger the patient, damage the ventilator, and/or void your warranty. Only personnel authorized and qualified by Covidien should repair, open or service the ventilator. … -
Page 33
Warnings WARNING: The exhalation block is intended for single use by a single patient . It may periodically be cleaned, but it cannot be disinfected or sterilized. To maintain good measurement quality when used continuously, clean the exhalation block periodically (refer to section 9.3, “Cleaning the Exhalation Block”). -
Page 34: Warnings Regarding Oxygen
Safety Information during the start-up procedure), the oxygen and power supplies should be disconnected and use of the device stopped immediately. WARNING: Before using the ventilator’s internal battery, ensure that the battery is fully charged and that the charge holds. Back up ventilators or those in storage should be connected to an AC power source to protect the integrity of the battery.
-
Page 35
WARNING: The Puritan Bennett 560 Ventilator is designed to deliver a percentage of oxygen equal or lower than 50%. Do not exceed this value as this may cause the ventilator to malfunction and put the patient at risk. -
Page 36: Warnings Regarding Electromagnetic Interference
To prevent any interference with the internal sensors of the ventilator, do not install a humidifier upstream of the ventilator. WARNING: To ensure stability, when the Puritan Bennett 560 Ventilator is mounted on a cart, the weight of the oxygen bottle should not exceed 14 kg (30 lbs). WARNING: The oxygen supply hose ages even when it is not in use and should be replaced periodically.
-
Page 37: Symbols And Markings
Table 1-1. Ventilator Symbols Symbols Descriptions It is essential to read, understand, and follow these instructions before using the Puritan Bennett 560 Ventila- tor (ISO 7000-0434A). This symbol appears on the ventilator’s back panel, see Table 1-2. , item 5. Type BF applied part (IEC 60417-5333).
-
Page 38
Safety Information Table 1-1. Ventilator Symbols (Continued) Symbols Descriptions This symbol appears on the ventilator’s front panel DOWN/FREEZE key; see Figure 2-3. on page 2-6, item 6. This key is used to: move the LCD display’s cursor downwards, line-by-line; decrease the value of displayed and selected parameter settings;… -
Page 39
Symbols and Markings Table 1-1. Ventilator Symbols (Continued) Symbols Descriptions Software lock enabled. This symbol appears on the upper-left of the ventilator’s LCD display when the keyboard Locking key is enabled; see section 7.8, “Locking the Control Panel.” Internal battery. This symbol appears on the top-center of ventilator’s LCD display to indicate that the ventilator is being powered by its internal battery. -
Page 40
This symbol indicates a communications port for interfacing with a USB connector. See Figure 2-2. , item 11. PC connector. This symbol indicates a port that can be used by authorized Covidien product service personnel or Covidien service personnel for software maintenance. See Figure 2-2. , item 10. -
Page 41: Labels / Identification And Instruction Information
Labels / Identification and Instruction Information Table 1-1. Ventilator Symbols (Continued) Symbols Descriptions Fragile. Keep dry. Keep away from direct sunlight. This side up. Labels / Identification and Instruction Information Various labels or specific markings are affixed to the ventilator that describe precautions to be taken for the correct use of the ventilator and contribute to the traceability of the product.
-
Page 42
Safety Information Table 1-2. Ventilator Labels and Markings (Continued) 7. Identification label (Figure 1-4. ) 1 Location of AC power cable connector 1 Location of DC power cable connector 8. AC power (mains) cable connector marking 9. External cable connector marking (Figure 1-3. ) (Figure 1-3. ) 10. PC connection marking (Figure 1-3. ) 11. -
Page 43: Figure 1-1. Locations Of Labels-Top-Front View
Labels / Identification and Instruction Information Figure 1-1. Locations of Labels—Top-Front View Figure 1-2. Locations of Labels—Front-Left View Clinician’s Manual 1-25…
-
Page 44: Figure 1-3. Location Of Labels And Markings-Rear View
Safety Information Figure 1-3. Location of Labels and Markings—Rear View Figure 1-4. Location of Labels—Bottom View 1-26 Clinician’s Manual…
-
Page 45: Ventilator Overview
The ventilator is suitable for use in institutional, home, and portable settings. It is not intended for use as an emergency transport ventilator. The Puritan Bennett 560 Ventilator is suitable for use on commercial aircraft, per FAA require- ments. See section B.11, “Standards Compliance and IEC…
-
Page 46: Contraindications
Nurses • Homecare providers • Patient and patient’s families • For more details on the knowledge and skill requirements for operating the Puritan Bennett 560 Ventilator, see Appendix A, “Patient/Caregiver Checklist.” WARNING: This ventilator must be used only under the responsibility and on the prescription of a doctor.
-
Page 47: Device Classification
Device Classification Pressure Support Ventilation with apnea ventilation (PSV/ST) • Safety Net Incorporated in the ventilator design is an alarm system that continuously monitors both patient and machine for signs of specific errors or faults that could lead to an unsafe condition. Should any of these errors or faults be detected, the alarm system announces the specific alarm condition both audibly and visually.
-
Page 48: Front Panel
Ventilator Overview Front Panel Figure 2-1. Front Panel LCD display—Shows information about the ventilator, Exhalation valve port—Nipple for providing piloting pres- including patient hours and software version, ventilation sure to the exhalation valve. Controls the open-closed posi- modes and settings, and monitored and calculated patient tion of the exhalation valve.
-
Page 49: Back Panel
Back Panel Back Panel Figure 2-2. Back Panel Ergonomic carrying handle. PC cable connector: USB mini-B connector used for Puritan Bennett Ventilator test software. On/Off (I/O) switch with protective cover: inlet port: Device powered on in position I; device Connects the ventilator to a low pressure oxygen switched off in position 0.
-
Page 50: Control Panel
Ventilator Overview Control Panel Figure 2-3. Control Panel Alarm indicators (two LEDs): DOWN/FREEZE key: Red indicator: • Moves the cursor down and decreases parameter values. • Continuous: very high priority (VHP) alarm activated • During ventilation, freezes displayed waveform in the Wave- form menu.
-
Page 51: Ventilation Menu
Ventilation Menu Ventilation Menu Figure 2-4. Ventilation Menu Display Ventilation menu with ventilation on standby. Ventilation menu during ventilation. General information line: Ventilation settings: Preferences menu access line: Shows the current ventilation mode, Shows the specific ventilation parame- Highlight this line and press the ENTER along with the following: ter values for the currently selected key to show the Preferences…
-
Page 52: Alarm Menu
Ventilator Overview Alarm Menu Figure 2-5. Alarm Menu Alarm menu with ventilation on standby. Alarm menu when not in standby. Title line: Alarm settings: Access line to Alarm Logs menu. Shows ventilation mode and the fol- Shows the specific alarm parameter Highlight this line and press the ENTER lowing symbols: values for the currently selected venti- key to show the Alarm Logs…
-
Page 53: Waveforms Menu
Waveforms Menu Waveforms Menu 2.10 The display of waveforms (Figure 2-6. ) is optional and can be selected using the Menu (see Chapter 4, “Monitored Parameters”). The Waveform menu is only accessible when ventilation is active. Figure 2-6. Waveforms Menu Title line: Graphic zone: Numeric zone: •…
-
Page 54: Usb Memory Device Menu
Keep in mind that troubleshooting information is available in this manual to assist you in the event of a problem. See Chapter 5, “Alarms and Troubleshooting.” If you cannot determine the cause of a problem, contact your equipment supplier or Covidien. See section 10.5, “Service Assistance.”…
-
Page 55: Operating Parameters
3 Operating Parameters This chapter describes ventilation and alarm parameters and their setting ranges for each ven- tilation mode. For a listing of operating parameters and monitored patient data, see Table B- 11. on page B-8. For further information about the different ventilation modes and breath types provided by the Puritan Bennett™…
-
Page 56: Figure 3-2. Menus In Psv Mode With Leakage Configuration
Operating Parameters Figure 3-2. Menus in PSV Mode with Leakage Configuration The ventilation parameters and setting ranges available in PSV mode are listed in Table 3-1. Table 3-1. Ventilation Parameters in PSV Menu Name Units Min. value Max. value Adjustment Default Linked resolution value parameters P Support Standby: 2 Standby: 55…
-
Page 57: Table 3-2. Alarm Parameters In Psv Mode
PSV Mode Parameters and Setting Ranges Table 3-2. lists the available alarm settings in PSV mode. Table 3-2. Alarm Parameters in PSV Mode Name Units Min. Max. Adjustment Default Linked value value resolution value parameters Min VTI 2000 Max VTI Max VTI 3000 2,000 Min VTI Min VTE (with exhalation…
-
Page 58
Operating Parameters The different levels available are as follows: Rise time = 200 ms Rise time = 400 ms Rise time = 600 ms Rise time = 800 ms These time ranges are determined by the pressure setting required, the breath rate and the phys- iological condition of the patient. -
Page 59: Figure 3-3. Exhalation Trigger Sensitivity
PSV Mode Parameters and Setting Ranges Figure 3-3. Exhalation Trigger Sensitivity Seconds Exhalation Inspiration Note: See section 7.2.2, “Changing the Setup Menu Parameters” for positive and negative E Sens settings. Backup R Backup R allows you to determine the frequency of ventilation breaths to be applied in the event of prolonged apnea –…
-
Page 60
Operating Parameters Note: During apnea ventilation, the ventilator delivers machine controlled breaths according to a backup rate (Backup R)—as long as no inspiratory trigger has been detected. Note: The Backup R value applied depends on the Rate setting. … -
Page 61
PSV Mode Parameters and Setting Ranges Max I Time defines the maximum duration of time during which the inspiratory phase is main- tained. The switch-over to exhalation occurs at the latest after this time has expired. By default, if no parameter is set, the maximum time (Max I Time = AUTO) is the shortest time between a fixed time of 3 seconds and half the duration of the patient’s inspiratory breaths expressed in seconds. -
Page 62: Cpap Mode Parameters And Setting Ranges
Operating Parameters Max Rtot (Max Alarm Setting)—TOTAL BREATH RATE The maximum rate threshold set is used to warn of hyperventilation or ventilator autotriggering. The alarm setting is used to trigger the HIGH RATE alarm. See Chapter 5, “Alarms and Troubleshoot- ing.”…
-
Page 63: Table 3-3. Ventilation Parameters In Cpap Menu
CPAP Mode Parameters and Setting Ranges Table 3-3. Ventilation Parameters in CPAP Menu Name Units Min. Max. Adjustment Default Linked value value resolution value parameters PEEP mbar or Auto Backup R Apnea Time Not available if Apnea alarm is set to OFF in Preferences menu. Table 3-4. …
-
Page 64
Operating Parameters VTI (Min and/or Max Alarm Settings)—INSPIRATORY TIDAL VOLUME It is possible to set a Min, Max, or both Tidal Volume alarm threshold for the patient’s inspired tidal volume during a cycle. This setting is used to trigger an alarm if the tidal volume inspired by the patient is lower than the minimum threshold set (LOW VTI alarm) or greater than the maximum threshold set (HIGH VTI alarm). -
Page 65: P A/C Mode Parameters And Setting Ranges
P A/C Mode Parameters and Setting Ranges Min FiO and Max FiO thresholds are related and their settings must maintain a minimum differ- ence of 10% between the two. Min and Max FiO settings can be set to OFF if an FiO sensor is not connected.
-
Page 66: Table 3-5. Ventilation Parameters In Pa/C Mode Menu
Operating Parameters Table 3-5. Ventilation Parameters in PA/C Mode Menu Name Units Min. value Max. value Adjustment Default Linked resolution parameters value Standby: 2 Standby: 55 PEEP mbar, or Valve configuration: 5 Valve configuration: 55 Leak configuration: 6 Leak configuration: 30 PEEP Standby: OFF mbar, or Valve configuration: OFF…
-
Page 67
P A/C Mode Parameters and Setting Ranges Pi—Inspiratory Pressure When Relative pressure is set to YES in the Setup menu, Pi allows you to determine inspiratory pressure added to PEEP during the inspiratory phase. In this configuration, the sum of Pi and PEEP must not exceed 55 mbar. When Relative pressure is set to OFF in the Setup menu, Pi allows you to determine inspiratory absolute pressure. -
Page 68
Operating Parameters Rise Time is established only if Insp Time ≥0.9 seconds • Rise Time is established only if Insp Time ≥1.1 seconds. • Rate—RESPIRATORY RATE Rate allows you to define the minimal frequency of mandatory ventilator breaths. If the patient actuates the inspiration trigger, total Rate may increase. Insp Time—INSPIRATORY TIME This parameter allows the user to set the inspiratory time to 0.3-6.0 s. -
Page 69
P A/C Mode Parameters and Setting Ranges VTI (Min and/or Max Alarm Settings)—INSPIRATORY TIDAL VOLUME It is possible to set a Min, Max, or both Tidal Volume alarm threshold for the patient’s inspired tidal volume during a cycle. This setting is used to trigger an alarm if the tidal volume inspired by the patient is lower than the minimum threshold set (LOW VTI alarm) or greater than the maximum threshold set (HIGH VTI alarm). -
Page 70: A/C Mode Parameters And Setting Ranges
Operating Parameters Min and Max FiO thresholds are related and their settings must maintain a minimum difference of 10% between the two. Min and Max FiO settings can be set to OFF if an FiO sensor is not connected. Settings are auto- matically restored once a sensor is reconnected.
-
Page 71
V A/C Mode Parameters and Setting Ranges Table 3-7. Ventilation Parameters in V A/C Ventilation Mode (Continued) Name Units Min. Max. Adjustment Default Linked value resolution parameters value value Insp Time Rate Apnea Time I Sens – – – Sigh Rate Sigh Vt –… -
Page 72
Operating Parameters Ramp Pattern—FLOW SHAPE This parameter is used to adjust the flow distribution shape (or ramp pattern) during the inspira- tory phase. The three flow patterns available are: Ramp Pattern: (square waveform) or constant flow • Ramp Pattern: Decelerated (sawtooth waveform) or decreasing flow. •… -
Page 73
V A/C Mode Parameters and Setting Ranges The Min PIP (or Low Pressure) setting determines the trigger threshold for the PATIENT DISCON- NECTION alarm. See Chapter 5, “Alarms and Troubleshooting.” If this pressure level is not reached during a fixed time, the alarm is triggered. … -
Page 74: P Simv Mode Parameters And Setting Ranges
Operating Parameters (Min and/or Max Alarm Settings)—FRACTION OF INSPIRED OXYGEN An FiO sensor connected to the patient circuit allows you to determine that the correct level of oxygen is being delivered to the patient. Min and Max FiO thresholds can be set to trigger LOW FiO or HIGH FiO alarms.
-
Page 75: Table 3-10. Alarm Parameters In P Simv Ventilation Mode
P SIMV Mode Parameters and Setting Ranges Table 3-9. Ventilation Parameters in P SIMV Ventilation Mode (Continued) Name Units Min. Max. Adjustment Default Linked resolution parameters value value value Rate Max Rtot Insp Time Insp Time Rate Apnea Time E Sens 5 (-95) 95 (-5) –…
-
Page 76
Operating Parameters When Relative pressure is set to OFF in the Setup menu, P Support allows you to determine inspi- ratory absolute pressure of spontaneous breaths. In this configuration, P Support and PEEP are related and their settings must maintain a minimum difference between the two of 2 mbar in leak configuration and 5 mbar in valve configuration. -
Page 77
P SIMV Mode Parameters and Setting Ranges The sensitivity levels are 0P, 1P, 2, 3, 4, and 5 (P denotes pediatric use); the lower the number, the more sensitive the trigger sensitivity. I Sens can be set to OFF. WARNING: The inspiration trigger threshold should be carefully modified in order to avoid the risk of false triggering or “autotriggering”… -
Page 78: Figure 3-9. Exhalation Trigger Sensitivity
Operating Parameters The exhalation trigger is only taken into account after the Rise Time (which constitutes a default minimum inspiratory time) has elapsed. If the flow drop is insufficient, exhalation is automatically triggered independently of the E Sens, which is defined as a percentage of peak inspiratory flow. Exhalation may be triggered if the maximum inspiratory time has elapsed.
-
Page 79: Simv Mode Parameters And Setting Ranges
V SIMV Mode Parameters and Setting Ranges These thresholds can be set to trigger an alarm if the tidal volume expired by the patient is lower than the minimum threshold set (LOW VTE alarm) or greater than the maximum threshold set (HIGH VTE alarm).
-
Page 80: Figure 3-10. Menus In V Simv Ventilation Mode
Operating Parameters Figure 3-10. Menus in V SIMV Ventilation Mode Table 3-11. shows the adjustments and limits in V SIMV mode. Table 3-11. Ventilation Parameters in V SIMV Mode Name Units Min. Max. Adjustment Default Links resolution value value value 2000 Min VTE Max VTE Insp Time P Support PEEP…
-
Page 81: Table 3-12. Alarm Parameters In The V Simv Mode Menu
V SIMV Mode Parameters and Setting Ranges Table 3-12. Alarm Parameters in the V SIMV Mode Menu Name Units Min. Max. Adjustment Default Links resolution value value value Min PIP mbar, or PEEP Max PIP Max PIP mbar, or PEEP Min PIP Min VTE 1990 Max VTE…
-
Page 82
Operating Parameters In this configuration, P Support and PEEP are related and their settings must maintain a minimum difference between the two of 2 mbar in leak configuration and 5 mbar in valve configuration. PEEP—POSITIVE END EXPIRATORY PRESSURE PEEP allows you to determine the level of pressure maintained during the exhalation phase. When Relative pressure is set to YES in the Setup menu, the sum of P Support and PEEP must not exceed 55 mbar. -
Page 83
V SIMV Mode Parameters and Setting Ranges The sensitivity levels are 0P, 1P, 2, 3, 4, and 5 (P denotes pediatric use); the lower the number, the more sensitive the trigger sensitivity. WARNING: The inspiration trigger threshold should be carefully modified in order to avoid the risk of false triggering or “autotriggering”… -
Page 84: Figure 3-11. Exhalation Trigger Sensitivity
Operating Parameters The end of inspiration will occur when inspiratory flow has decreased to the preset E Sens setting. The exhalation trigger is only taken into account after the Rise Time (which constitutes a default minimum inspiratory time) has elapsed. If the flow drop is insufficient, exhalation is automatically triggered independently of the E Sens, which is defined as a percentage of peak inspiratory flow.
-
Page 85
V SIMV Mode Parameters and Setting Ranges The difference between the Min PIP and Max PIP settings is limited to a minimum of 8 mbar. Their settings are also limited by that of PEEP; thus, Min PIP must be greater than PEEP by at least 2 mbar and Max PIP must be greater than PEEP by at least 10 mbar. -
Page 86: Fio2 For Various Oxygen And Ventilator Settings
Operating Parameters (Min and/or Max Alarm Settings)—FRACTION OF INSPIRED OXYGEN An FiO sensor connected to the patient circuit allows you to determine that the correct level of oxygen is being delivered to the patient. Min and Max FiO thresholds can be set to trigger LOW FiO or HIGH FiO alarms.
-
Page 87: Monitored Parameters
4 Monitored Parameters During ventilation, ventilator parameters measured or calculated are highlighted in the menus used for setting the ventilation parameters, the alarms, and the waveforms. In addition to showing monitored ventilation parameters, ventilation is shown graphically, as follows: Pressure bar chart, in the Ventilation parameters setting menu •…
-
Page 88: Figure 4-2. Ventilation Menu: Pressure Valve Configuration Modes (Psv S, Psv St, Pcv, P A/C)
Monitored Parameters Figure 4-2. Ventilation Menu: Pressure Valve Configuration Modes (PSV S, PSV ST, PCV, P A/C) Figure 4-3. Ventilation Menu: Volume Mode (CV, V A/C, SIMV) Figure 4-4. Alarm Menu: Pressure Leakage Modes (CPAP, PSV S, PSV ST, PCV, P A/C) Clinician’s Manual…
-
Page 89: Figure 4-5. Alarm Menu: Pressure Valve Modes (Psv S, Psv St, Pcv, P A/C)
Digital Monitoring Figure 4-5. Alarm Menu: Pressure Valve Modes (PSV S, PSV ST, PCV, P A/C) Figure 4-6. Alarm Menu: Volume Modes (CV, V A/C, SIMV) Figure 4-7. Waveform Menu: Pressure Leakage Modes (CPAP, PSV S, PSV ST, PCV, P A/C) Clinician’s Manual…
-
Page 90: Figure 4-8. Waveform Menu: Pressure Valve Modes (Psv S, Psv St, Pcv, P A/C)
Monitored Parameters Figure 4-8. Waveform Menu: Pressure Valve Modes (PSV S, PSV ST, PCV, P A/C) Figure 4-9. Waveform Menu: Volume Mode (CV, V A/C, SIMV) Monitored parameter values are updated every two breath cycles and are shown in the form of inserts, as shown in Figure 4-10. …
-
Page 91: Figure 4-11. Display Showing Unavailable Parameter Values
Digital Monitoring If the monitored value for a parameter is not applicable or unavailable, the value is replaced by a hyphen “–”, as shown in Figure 4-11. Figure 4-11. Display Showing Unavailable Parameter Values Inspiratory Trigger During each inspiration phase triggered by the patient, the Inspiratory effort detected symbol is shown beside the cycling I:E ratio in the Ventilation, Alarm, or Waveform menus (see Figure 4-…
-
Page 92: Table 4-1. Displayed Monitored Parameters
Monitored Parameters Displayed Monitored Parameters Table 4-1. Displayed Monitored Parameters Monitored parameters Display Description Exhaled Tidal Volume Patient exhaled flow is measured by the exhalation flow transducer and that measure- ment is used to calculate volume (the flow transducers do not directly measure vol- ume).
-
Page 93: Bargraph Display
Bargraph Display Bargraph Display In the ventilation menu, the highlighted bargraph dynamically shows pressures established throughout the breath cycle (Figure 4-13. ). Figure 4-13. Bargraph Display The Pi value reached during a cycle is represented by a line at the top of the bargraph (Figure 4- 13. , item 1) which remains shown until the maximum value of the following cycle has been reached.
-
Page 94: Figure 4-14. Waveform Screen
Monitored Parameters Figure 4-14. Waveform Screen Ventilation mode Frozen waveform symbol Inspiratory trigger symbol Pressure over last two cycles Maximum flow over last two cycles Pressure and flow scales are adjusted over three cycles, but only two cycles are displayed Waveform tracing can be frozen at any time, which enables the analysis of pressure and flow waveforms, while continuing patient ventilation.
-
Page 95: Ventilation Report
Ventilation Report The waveform screen is automatically dismissed: When a high priority alarm is triggered. • When you press the VENTILATION ON/OFF key to stop ventilation. • Ventilation Report The Ventilation Report is available in the Preferences menu (see Chapter 7, “Operating Procedures”).
-
Page 96
Monitored Parameters VTE—Exhaled Tidal Volume When ventilating with a double-limb circuit configuration and an exhalation valve, the VTE is the average exhaled volume during each ventilation cycle over the previous 24-hour period. In a single-limb circuit configuration this value is not measured. Paw—Peak Airway Pressure The peak airway pressure is the average peak pressure during the inspiratory phase, measured by each cycle and over the previous 24-hour period. -
Page 97: Alarms And Troubleshooting
Technical faults do not directly affect machine operation. Therefore, the user is not alerted to technical faults. Only authorized and trained technicians may consult the Maintenance menu (see the Puritan Bennett 560 service manual).
-
Page 98: Alarm Level Of Priority
Alarms and Troubleshooting Alarm Level of Priority The alarm hierarchy for signaling the level of alarm criticality is listed as follows: Very high priority (VHP): Immediate critical situation; ventilation is impossible: • Continuous sound signaling / with or without continuous red LED illumination / with or without message / with or without display lighting (it is possible for an alarm condition to occur that may not have both a message and lighting).
-
Page 99: Figure 5-1. Alarm Displays
Alarm Display Figure 5-1. Alarm Displays Alarm Control key Alarm messages Note: There are currently no low priority (LP) alarms. When an alarm is triggered, if the current menu shown is not the Ventilation parameters or Alarm menu, the display automatically switches to one of these menus to show the alarm message. In the event several alarms are activated at the same time, the highest priority audible and visual alarm is highlighted;…
-
Page 100: Alarm Logs Menu
Alarms and Troubleshooting Alarm Logs Menu All alarms are recorded in the ventilator’s nonvolatile internal memory at the time they are acti- vated, and are retained when powering down or in the event of a total loss of power. The Alarm Logs menu is used to show the last eight alarms activated, along with their date and time of activation.
-
Page 101: Pausing The Audible Portion Of Alarms
Note: Only qualified service personnel may access all alarms and events recorded by the ventilator. Qualified personnel should see the Puritan Bennett 560 service manual for further information. Pausing the Audible Portion of Alarms You may pause the audible portion of alarms for 60 seconds at a time.
-
Page 102: Pausing/Resetting Alarms
Alarms and Troubleshooting Figure 5-5. Pausing the Audible Portion of Alarms If several alarms are activated at the same time, pressing the ALARM CONTROL key affects all current alarms. The audible portion of activated alarms is automatically reactivated if the following occurs: After 60 seconds, if the cause or causes of the alarm or alarms persist •…
-
Page 103: Reactivating Alarms
Reactivating Alarms To manually pause an alarm, proceed as follows: Press the ALARM CONTROL key twice. The alarm is paused until the alarm condition is corrected and the condition reoccurs: the audible por- • tion, light indicator, and message are all halted (for the alarms that can be paused manually). The Alarm Paused symbol is shown at the top right of the Ventilation, Alarms, and Waveforms •…
-
Page 104: Figure 5-7. Reactivating Alarms
Alarms and Troubleshooting Figure 5-7. Reactivating Alarms Press the ENTER key, to confirm access to the Alarm Logs menu. Press the UP key to position the cursor on the User’s clear alerts line. See Figure 5-8. Figure 5-8. Alarm Logs Press the ENTER key for at least 3 seconds. The following events occur: A “beep”…
-
Page 105: Overview Of Alarms
Overview of Alarms Overview of Alarms Note: The message: “*IF PERSISTS RESTART/SRVC” will occur only if the alarm condition continues for longer than 30 seconds. Table 5-1. Overview of Alarms Alarm message Cause/ventilator response Priority Audio Alarm Paused Paused available available Cut-off of the AC (mains) power supply.
-
Page 106
Alarms and Troubleshooting Table 5-1. Overview of Alarms (Continued) Alarm message Cause/ventilator response Priority Audio Alarm Paused Paused available available CHECK BATTERY Internal battery charging failure. CHARGE Consequence: charging of the internal battery impossi- ble. IF PERSISTS RESTART/ SRVC Inspired tidal volume during exhalation CHECK EXH VALVE* <20% of Inspired tidal volume and Inspired tidal volume *IF PERSISTS… -
Page 107
Overview of Alarms Table 5-1. Overview of Alarms (Continued) Alarm message Cause/ventilator response Priority Audio Alarm Paused Paused available available Cut-off of the external DC power supply. DC POWER DISCONNECTION Consequence: switch-over to the internal battery. DEVICE FAULT3 Failure in the 24 V power supply. RESTART/SRVC Detection of a fault in the electrical power supply system. -
Page 108
Alarms and Troubleshooting Table 5-1. Overview of Alarms (Continued) Alarm message Cause/ventilator response Priority Audio Alarm Paused Paused available available HIGH INT TEMP Device internal ambient temperature out of tolerance COOL VENT* range. *IF PERSISTS RESTART/SRVC The leak estimated by the ventilator exceeds the Max leak HIGH LEAKAGE alarm threshold. -
Page 109
Overview of Alarms Table 5-1. Overview of Alarms (Continued) Alarm message Cause/ventilator response Priority Audio Alarm Paused Paused available available LOW BATTERY Internal battery capacity <30 minutes or 8%. The level of oxygen delivered by the ventilator is below LOW FiO the Min FiO level set. -
Page 110
Alarms and Troubleshooting Table 5-1. Overview of Alarms (Continued) Alarm message Cause/ventilator response Priority Audio Alarm Paused Paused available available POWER FAULT Detection of a fault in the electrical power supply system. RESTART/SRVC 1. Electrical power supply to the machine is interrupted with the I/O switch when ventilation is in progress No—… -
Page 111: Troubleshooting
WARNING: To ensure proper servicing and avoid the possibility of physical injury to personnel or damage to the ventilator, only personnel authorized and qualified by Covidien should attempt to service or make authorized modifications to the Puritan Bennett 560 Ventilator.
-
Page 112
2 hours. BATTERY alarm. If alarm persists, restart ventilator to see if alarm clears. If not, contact Covidien or a local Covidien representa- tive. An FiO sensor is detected and has not been calibrat- CALIBRATE FiO Calibrate FiO sensor. -
Page 113
Troubleshooting Table 5-2. Alarms and Corrective Actions (Continued) Alarm message or Possible reason for the alarm event Corrective action symptom CALIBRATION FAIL Restart calibration. Too large a difference between a calibration point There may be a leak in the circuit. Ensure an approved and its tolerance range. -
Page 114
Alarms and Troubleshooting Table 5-2. Alarms and Corrective Actions (Continued) Alarm message or Possible reason for the alarm event Corrective action symptom No connection of the proximal pressure tube when Reconnect the proximal pressure line. ventilation starts. CHECK PROXIMAL Reconnect the connection line or replace it if obstructed. LINE1* Check for moisture or occlusion of the proximal line. -
Page 115
Troubleshooting Table 5-2. Alarms and Corrective Actions (Continued) Alarm message or Possible reason for the alarm event Corrective action symptom If patient has been disconnected, reconnect patient to DEVICE FAULT9 reset the fault. POST RAM error. RAM read/write does not match IF PERSISTS RESTART/ If persists restart ventilator to see if alarm clears. -
Page 116
Alarms and Troubleshooting Table 5-2. Alarms and Corrective Actions (Continued) Alarm message or Possible reason for the alarm event Corrective action symptom Large leakage detected on the patient circuit return Replace the exhalation valve, its control tube, or both. limb during the inspiratory phase. EXH VALVE LEAKAGE Restart ventilator to see if alarm clears. -
Page 117
Troubleshooting Table 5-2. Alarms and Corrective Actions (Continued) Alarm message or Possible reason for the alarm event Corrective action symptom Note: Ensure that you are operating the ventilator within the proper temperature range (refer to Appendix B, “Specifications”). Put the device in a warmer environment (if the ambient temperature is too low) or in a cooler environment (if the ambient temperature is too high). -
Page 118
Alarms and Troubleshooting Table 5-2. Alarms and Corrective Actions (Continued) Alarm message or Possible reason for the alarm event Corrective action symptom Caution: Ensure that ventilator is being used according to the operating instructions found in Appendix B, “Specifications.” If the ambient temperature is too low, place the device in a warmer environment. -
Page 119
Troubleshooting Table 5-2. Alarms and Corrective Actions (Continued) Alarm message or Possible reason for the alarm event Corrective action symptom Note: Adjustment of the Max VTE level too low. Always consult the clinician before changing PEEP, FiO , pressure, volume, or Rate settings. Modify the Max VTE level. -
Page 120
Alarms and Troubleshooting Table 5-2. Alarms and Corrective Actions (Continued) Alarm message or Possible reason for the alarm event Corrective action symptom Note: Adjustment of Max PIP too low (only for V A/C and Always consult the clinician before changing V SIMV modes). PEEP, FiO , pressure, volume, or Rate settings. -
Page 121
Troubleshooting Table 5-2. Alarms and Corrective Actions (Continued) Alarm message or Possible reason for the alarm event Corrective action symptom Note: Always consult the clinician before changing The level of oxygen being delivered to the patient is LOW FiO PEEP, FiO , pressure, volume, or Rate settings. -
Page 122
Alarms and Troubleshooting Table 5-2. Alarms and Corrective Actions (Continued) Alarm message or Possible reason for the alarm event Corrective action symptom NO PROXIMAL LINE2 The proximal pressure line is disconnected. Connect proximal pressure line. Adjustment of Min PIP too high. Decrease the Min PIP threshold. Check the patient circuit connections to the ventilator;… -
Page 123: Additional Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting Table 5-2. Alarms and Corrective Actions (Continued) Alarm message or Possible reason for the alarm event Corrective action symptom SOFTWARE VERSION Incorrect software version detected. Call your customer service representative. ERROR Ensure lateral and front openings are not obstructed. TURB OVERHEAT Turbine overheated because of blockage during Check air inlet filter.
-
Page 124
Alarms and Troubleshooting Table 5-3. Additional Troubleshooting and Corrective Actions (Continued) Conditions Possible causes Corrective actions Adjustment of the alarm sound level is Alarm sound level too Readjust sound level (see section 7.3, “Preferences Menu incompatible with the patient’s environ- low or too high Parameters”). -
Page 125: Installation And Assembly
6 Installation and Assembly WARNING: Before operating the ventilator, read, understand, and strictly follow the information contained in Chapter 1, “Safety Information.” WARNING: A patient treated by mechanical ventilation is highly vulnerable to the risks of infection. Dirty or contaminated equipment is a potential source of infection.
-
Page 126
The use of any accessory other than those specified, with the exception of the power supplies or cables sold by Covidien, may lead to an increase in electromagnetic emissions or a decrease in the equipment protection against electromagnetic emissions. If the ventilator is used adjacent to such accessories or stacked with such devices, the ventilator’s performance should be monitored to… -
Page 127: Connecting To External Ac Power
Connecting to External AC Power WARNING: The ventilator must not use, nor be connected to, any anti-static or electrically conductive hoses, tubing, or conduits. Connecting to External AC Power Any of four power sources: AC power, 12–30 VDC power, internal battery power, or auxiliary DC car adapter (cigarette lighter) can be used to power the ventilator.
-
Page 128: Figure 6-1. The Power Cable Holder
Installation and Assembly To prevent accidental disconnection of the AC power cable, use the power cable holder (Figure 6- , item 1) that is inserted into the notch (Figure 6-1. , item 2) of the battery cover. Figure 6-1. The Power Cable Holder To secure the AC power cable: Insert the power cable holder (Figure 6-2. , item 1) into the notch of the battery cover.
-
Page 129: Figure 6-3. Power Cable Connected To The Ventilator
Connecting to External AC Power Figure 6-3. Power Cable Connected to the Ventilator Connect the male end of the AC power cable to the AC power outlet. The AC POWER indicator on the top left corner of the ventilator illuminates. • The indicator flashes while the battery charges and then turns off when the battery is fully •…
-
Page 130: Connecting To An External Dc Power Source
Installation and Assembly Figure 6-4. Power Indicators To disconnect the AC power cable: Disconnect the AC power cable from the AC power outlet. Disconnect the AC power cable from the ventilator’s AC connector at the rear of the device. Grasp the AC power cable at the level of the power cable holder and turn the cable clockwise while lifting it upwards and out of the holder.
-
Page 131: Figure 6-5. Connecting The Ventilator To An External Dc Power Source
Connecting to an External DC Power Source Note: When AC power is not available use an external DC power prior to using internal battery power. To connect the ventilator to an external power source, do the following: Ensure the car’s engine is started prior to connecting the ventilator. Connect the DC power cable into the ventilator.
-
Page 132: Patient Circuit
Installation and Assembly Figure 6-6. Connecting the DC Power Cable to the Ventilator Align the red markers Disconnect the cable by (dots or lines) before sliding the locking ring connecting the cable. back and pulling the plug away from ventilator Push in to connect the DC power cable Push the DC power cable onto the ventilator’s DC power connector (Figure 6-6. , item 2).
-
Page 133
WARNING: To ensure proper performance of the ventilator, use a patient circuit recommended by Covidien in this manual; refer to Chapter 6, “Installation and Assembly” and Appendix H, “Parts and… -
Page 134: Choosing The Patient Circuit Type
“Parts and Acces- sories”). For information regarding validated circuits, visit the SolvIT Center Knowledge Base by clicking the link at www.medtronic.com/covidien/support/solvit-center-knowledge-base/ or contact your customer representative. Installing the Patient Circuit 6.4.2 The patient circuit is mounted depending on the setup of the circuit used and the accessories used.
-
Page 135: Figure 6-7. Single-Limb Patient Circuit With Exhalation Valve
Patient Circuit Connect one end of the proximal pressure tubing (item 7) to the proximal pressure port on the exha- lation valve (item 5) and the other end onto the ventilator patient pressure port (item 8). Connect one end of the exhalation valve tubing (item 6) to the exhalation valve port on the exhalation valve (item 5) and the other end onto the ventilator exhalation valve port (item 9).
-
Page 136: Figure 6-8. Double-Limb Patient Circuit
Installation and Assembly Attach one end of the short circuit tubing (item 4) to the filter (item 1). Attach the other end of the circuit tubing to the inlet port of the humidifier (item 2). Place a water trap (item 3) between the outlet port of the humidifier and the patient wye (item 5) on the double-limb circuit.
-
Page 137: Figure 6-9. Close-Up Of Exhalation Valve Tube And Proximal Pressure Tube
Patient Circuit See also Figure 6-9. on page 6-13. Note: Although shown here, the humidifier (item 2), water traps (item 3), and their connecting tubes are not included with the patient circuit or ventilator. Contact your supplier for more information. Figure 6-9. Close-up of Exhalation Valve Tube and Proximal Pressure Tube Inhalation port Proximal pressure tube Exhalation valve tube…
-
Page 138: Figure 6-10. Single-Limb Patient Circuit Without Exhalation Valve
Installation and Assembly Figure 6-10. Single-limb Patient Circuit Without Exhalation Valve For both types of circuits, shown previously, you should connect the end of the proximal pressure tube as close as possible to the patient (at the mouthpiece, mask or cannula entry, if possible) so that the ventilator can account for all load losses due to the circuit and its potential accessories.
-
Page 139: Filters
Filters WARNING: The exhalation valve must allow rapid discharge of the circuit pressure. Ensure that the exhalation valve is always clean and its evacuation aperture (exhaust port) is never obstructed. WARNING: Do not start ventilation until you ensure that the device is suitably assembled, that the air inlet filter is properly installed and is not obstructed, and that there is proper clearance all around the unit.
-
Page 140: Figure 6-11. Air Inlet Filter
Installation and Assembly Figure 6-11. Air Inlet Filter WARNING: The air inlet filter is not reusable; do not attempt to wash, clean, or reuse it. WARNING: Failing to replace a dirty air inlet filter, or operating the ventilator without a filter, may cause serious damage to the ventilator.
-
Page 141: Humidifier
Humidifier Figure 6-12. Bacteria Filter See the manufacturer’s instructions for more information about the use and maintenance of bac- teria filters. Humidifier The humidifier (Figure 6-13. ) adds moisture (water vapor) and warms the gas in the patient circuit. It is inserted into the patient circuit between the main outlet and the patient (see Figure 6-7. and Figure 6-8. ).
-
Page 142: Exhalation Block
Installation and Assembly Figure 6-13. Humidifier When a humidification device is used, any condensation that forms in the patient circuit is collect- ed in the water trap. If you notice any moisture in the patient circuit, you need to replace the wet circuit components with dry ones.
-
Page 143: Oxygen
Oxygen Figure 6-14. Removing the Exhalation Block After removal, the exhalation block can either be cleaned or, if required, replaced with a new one. For information on cleaning, see section 9.3, “Cleaning the Exhalation Block.” To install either a cleaned or a new exhalation block: Figure 6-14. …
-
Page 144: Connecting The Oxygen Supply
Installation and Assembly volume of delivered gas. Remove the oxygen inlet connector from the back of the ventilator when external oxygen is not in use. The specific oxygen flow to the patient depends on the physiological characteristics of the patient and the ventilator settings. The oxygen flow setting should be adjusted for each patient and established in relation to a cali- brated oxygen monitor measurement.
-
Page 145: Figure 6-15. Rear Panel Oxygen Connector
Oxygen Figure 6-15. Rear Panel Oxygen Connector WARNING: Before connecting the oxygen supply, ensure that the stud on the oxygen connector (Figure 6-15. , item 3) is protruding outwards. WARNING: Inspect the oxygen coupler (Figure 6-16. , item 2) before use to ensure it has its black O-ring attached and in good condition.
-
Page 146: Figure 6-16. Connecting The Oxygen Supply System
Installation and Assembly Figure 6-16. Connecting the Oxygen Supply System To disconnect the oxygen supply system from the ventilator: Note: Ensure the oxygen source is turned off prior to placing the ventilator in standby or turning off the ventilator. Stop the oxygen flow from the oxygen supply. Press the locking tab of the ventilator’s oxygen connector, as shown in Figure 6-17. , to unlock the oxygen connection.
-
Page 147: Figure 6-18
Oxygen The ventilator’s oxygen connector’s locking stud (Figure 6-16. , item 4) will then extend outwards, which is required before the oxygen connector can be reconnected. WARNING: The coupler must not remain connected to the oxygen connector unless it also connected to a leak-proof, external oxygen gas source.
-
Page 148: Mounting The Ventilator On A Wheelchair
Back up ventilators or those in storage should be connected to an AC power source to protect the integrity of the battery. The dual bag accessory consists of a carrying bag that allows the Puritan Bennett 560 Ventilator to be both mounted onto a wheelchair or carried as a backpack (see Figure 6-19. ).
-
Page 149: Mounting The Ventilator On The Utility Cart
Figure 6-19. Using the Dual Bag Accessory Mounting the Ventilator on the Utility Cart 6.10 Match the mounting holes (item 1) on the bottom of the Puritan Bennett 560 Ventilator to the mounting studs (item 2) on the top of the utility cart platform. Clinician’s Manual…
-
Page 150: Connecting The Nurse Call Cable
Installation and Assembly Connecting the Nurse Call Cable 6.11 Connect the nurse call cable (Figure 6-20. , item 1) to the nurse call monitor connector (item 2). Figure 6-20. Connecting the Nurse Call Cable 6-26 Clinician’s Manual…
-
Page 151
If the system performance is not as expected, contact Technical Support for assistance troubleshooting the setup. Do not use the Puritan Bennett 560 Ventilator with a nurse call/ monitoring system until the functionality of the ventilator/system combination has been confirmed. -
Page 152
Installation and Assembly Page Left Intentionally Blank 6-28 Clinician’s Manual… -
Page 153: Operating Procedures
7 Operating Procedures Turning on the Ventilator WARNING: Before operating the ventilator, read, understand, and strictly follow the information contained in Chapter 1, “Safety Information.” WARNING: If the ventilator has been transported or stored at a temperature that differs more than ±20 °C (±68 °F) from the temperature in which it will be operating, the ventilator should be allowed to stabilize in its operating environment for at least two (2) hours prior to use.
-
Page 154: Figure 7-1. Turning On The Ventilator
WARNING: If the ventilator fails the alarm tests or if you cannot complete the tests, refer to Chapter 5.8, “Troubleshooting” or call your equipment supplier or Covidien. WARNING: Due to its limited internal battery’s reserve capacity, the ventilator should only be operated on the internal battery when no other power source is available.
-
Page 155: Figure 7-2. Welcome Menu Screen
Turning on the Ventilator The following events occur: The ventilator is turned on. • A Power On Self Test (POST) is carried out (when plugged in to an AC power source). • The front panel indicators flash (except for the indicator showing the type of power supply in use, •…
-
Page 156: Setup Menu Parameters
Operating Procedures Figure 7-3. Ventilation Menu Parameters By default, the starting ventilation mode is the last one used, the settings being those that were active when the machine was last stopped. If the ventilator’s memory of the settings is faulty, a CHECK SETTINGS alarm is activated. If this occurs, the desired parameters should be reset and saved;…
-
Page 157: Changing The Setup Menu Parameters
Setup Menu Parameters Figure 7-4. Setup Menu Release the ALARM CONTROL key. Changing the Setup Menu Parameters 7.2.2 To change the Setup menu settings: Press UP or DOWN to position the cursor beside the parameter to be modified. Press ENTER The cursor changes to: •…
-
Page 158: Table 7-1. Languages
Operating Procedures The parameters in this menu include the following: Machine Hours • Language • Date • Time • Intentional Vent Stop • Pressure Unit • Alarm Tone • Patient Hours • Restore Defaults • Maintenance • Next • Machine Hours The counter records the total ventilation time in hours (to the nearest hour) since manufacture.
-
Page 159
Setup Menu Parameters Intentional Vent Stop Alarm Intentional Ventilation Stop alarm is an alarm to warn that ventilation has been switched off by the user / caregiver and the ventilator is in standby. To set the Intentional Vent Stop Alarm: Use the UP or DOWN arrows to place the cursor at the Intentional Vent Stop alarm position. -
Page 160: Figure 7-5. Resetting Patient Hours To Zero (1)
Operating Procedures Figure 7-5. Resetting Patient Hours to Zero (1) Press ENTER The cursor is placed on the Reset Hours line: OFF. • Press ENTER OFF flashes. • Press UP or DOWN to change the OFF message to YES, as shown in the following graphic: Figure 7-6. Resetting Patient Hours to Zero (2) Press ENTER YES is shown continuously.
-
Page 161: Figure 7-7. Resetting Patient Hours To Zero (3)
Setup Menu Parameters Figure 7-7. Resetting Patient Hours to Zero (3) Press UP or DOWN The screen indicates Reset Hours: OFF, as shown in Figure 7-8. • Figure 7-8. Resetting Patient Hours to Zero (4) Restore Defaults This allows the user to reset all settings back to the original manufacturer defaults except for the Language, Date, and Time.
-
Page 162: Figure 7-9. Restoring Default Settings (1)
Operating Procedures Figure 7-9. Restoring Default Settings (1) Press ENTER . OFF flashes. Press UP or DOWN to change OFF to YES, as shown in Figure 7-10. Figure 7-10. Restoring Default Settings (2) Press ENTER to reset all settings back to the manufacturer defaults except for Language, Date, and Time.
-
Page 163: Entering Setup 2 Menu
Figure 7-11. Restoring Default Settings (3) Maintenance This option is reserved for maintenance operators qualified by Covidien to ensure correct main- tenance and operation of the device. For information on using the Maintenance option, refer to the Puritan Bennett 560 Ventilator service manual.
-
Page 164
Operating Procedures The parameters in this menu include the following: Cycling mode • Relative pressure • E Sens Setting • Back • Cycling Mode The cycling mode is used to set which calculated value (I:E or I/T) appears in the parameter zoom window when changing Insp Time or Rate settings. -
Page 165: Figure 7-13. Absolute And Relative Pressure
Setup Menu Parameters Figure 7-13. Absolute and Relative Pressure E Sens Settings E Sens enables the operator to adjust the sensitivity of the expiratory trigger in Pressure Support breaths in PSV, P SIMV and V SIMV modes which will cycle the breath into the expiratory phase. During a Pressure Support inspiration the delivered flow will reach a peak value and then begin to decelerate toward zero.
-
Page 166: Exiting The Setup Menu
Operating Procedures Back Allows the user to return to the Setup menu. Exiting the Setup Menu 7.2.4 To exit the Setup menu, you must cycle the ventilator’s power. Set the ventilator’s rear panel I/O switch to OFF (O). Wait 30 seconds. Set the ventilator’s I/O switch ON (I).
-
Page 167: Figure 7-15. Selecting The Preferences Menu
Preferences Menu Parameters Figure 7-15. Selecting the Preferences Menu Press ENTER . The Preferences menu is shown. Figure 7-16. Changing Settings in the Preferences Menu To change the settings in the Preferences menu: Press UP to place the cursor on the parameter line to be modified. Press ENTER The cursor changes to the plus/minus symbol.
-
Page 168
Operating Procedures Cursor: plus/minus symbol indicator triangle: filled Parameter value: flashing Press UP or DOWN to change the selected parameter’s value. Press ENTER to confirm the new parameter setting. The new parameter setting is shown. • The cursor returns to its initial form. •… -
Page 169: Backlight
Preferences Menu Parameters A high priority alarm is triggered. • Backlight 7.3.2 To set the Backlight: Select the Backlight parameter on the screen. Set the backlight: To set the backlight to standby, select OFF. • The effect of this setting is that if no keyboard action occurs before 1 minute elapses, the display’s backlight fades almost to off.
-
Page 170: Alarm Volume
Operating Procedures To decrease the contrast, press DOWN . This change can be observe as the cursor moves to • the left: The display contrast progressively decreases. Press ENTER to confirm the new Contrast setting. When ventilation is stopped, the contrast can also be changed directly from the currently shown menu by pressing ALARM CONTROL continuously, while repeatedly pressing UP DOWN…
-
Page 171: Key Sound
Preferences Menu Parameters The buzzer activates and decreases in sound level as the setting decreases. Press ENTER to confirm the new Alarm Volume. Current hospital standards require a minimum sound level of 55 dB(A) at a distance of 3 meters (9.84 feet), which corresponds to the lowest possible volume setting.
-
Page 172: Disconnection Alarm
Operating Procedures Press UP or DOWN to set the message to YES. Setting the key to OFF means the Apnea alarm will not sound when the ventilator is stopped. Press ENTER to confirm the selection. WARNING: The Apnea Alarm should be set to YES for ventilator dependent patients. Figure 7-17. Setting the Apnea Alarm …
-
Page 173: Waveforms Display
Preferences Menu Parameters Waveforms Display 7.3.8 To set Waveforms Display: Select the Waveforms Display parameter on the display. Select either: YES—Shows pressure and flow waveforms as a function of time (refer to section 4.3, “Waveform • Display”). OFF—Results in no waveform display; hence, no Waveform menu. •…
-
Page 174: Setting The Ventilation Mode
Operating Procedures Figure 7-18. Accessing the Ventilation Report Note: The menu is shown for 5 minutes then screen reverts to the Preferences menu. To exit the Ventilation Report: Press ENTER Setting the Ventilation Mode The ventilation mode can be changed from the Ventilation parameters menu or the Alarm param- eters menu, as long as the Locking key is not enabled (refer to section 7.8, “Locking the Control Panel”…
-
Page 175: Changing Modes While Ventilation Is On Standby
Setting the Ventilation Mode Changing Modes While Ventilation is on Standby 7.4.1 To change ventilation modes while on standby: Place the cursor on the first line of the menu (general information line) using the UP key. Figure 7-19. Changing Ventilation Modes While on Standby Press ENTER The cursor changes to: •…
-
Page 176: Figure 7-20. Changing Ventilation Modes During Ventilation (1)
Operating Procedures Changing ventilation modes during ventilation: Place the cursor on the first line of the menu (general information line) using the UP key. Figure 7-20. Changing Ventilation Modes During Ventilation (1) Press ENTER The cursor changes to: • The mode name flashes. •…
-
Page 177: Figure 7-21. Changing Ventilation Modes During Ventilation (2)
Setting the Ventilation Mode Figure 7-21. Changing Ventilation Modes During Ventilation (2) The Alarm menu screen in Figure 7-22. indicates the same active and inactive mode information being shown, along with the Accept Mode: Yes line, alarm parameter settings, and patient values. Figure 7-22. Changing Ventilation Modes During Ventilation (3) Change the settings of the new mode, including alarms, if necessary.
-
Page 178: Setting Ventilation Parameters
Operating Procedures When changing the value of a parameter in this inactive mode, the monitoring data displayed in the window on the right side of the screen are temporarily hidden by the display of the value cur- rently being changed. This is shown in the following figure, as the I Sens setting is adjusted in the inactive V A/C mode.
-
Page 179: Links Between Ventilation Parameters
Setting Ventilation Parameters Validate your intention to modify the parameters using the ENTER button. Refer to Figure 7-24. The cursor changes to: . (Figure 7-24. , item 1) • The parameter value flashes (Figure 7-24. , item 2) • A zoom of the parameter value is shown in the right-side of the window (Figure 7-24. , item 3). •…
-
Page 180: Links Between Ventilation And Alarm Parameters
Operating Procedures Figure 7-25. , item 1, shows that P Support cannot be set above 35 when PEEP is set to 20 and rel- ative pressure is set to YES; this value is limited by PEEP because their sum cannot exceed 55 mbar. Figure 7-25. Setting Links Between Ventilation Parameters Two possibilities exist in this case: Allow the PEEP setting to remain at 20, but the P Support cannot be increased.
-
Page 181: Figure 7-26. Modifying Alarm Parameters-Min Value
Setting Alarm Parameters To modify an alarm parameter: Ensure that the Alarm menu is shown, with a list of alarm parameters and columns for the minimum, current, and maximum alarm parameter values (Figure 7-26. ). Put the cursor next to the alarm parameter to be modified using the UP or DOWN key.
-
Page 182: Figure 7-27. Modifying Alarm Parameters-Max Value
Operating Procedures Figure 7-27. Modifying Alarm Parameters—Max Value Press UP or DOWN to modify the value of the parameter. Press ENTER to confirm the value selected. The new value is continuously shown. • The zoom disappears. • The cursor returns to normal. •…
-
Page 183: Usb Menu Parameters
The USB menu is not accessible from the Setup menu or Maintenance menu. To access patent data via a PC, a dedicated software package, Puritan Bennett respiratory insight software, is available for clinicians. Contact Covidien or your Puritan Bennett product representa- tive for further information.
-
Page 184: Usb Menu
Operating Procedures USB Menu 7.7.2 To access the USB menu when a USB memory device is connected: Press the MENU key several times, until the USB menu appears: Figure 7-28. Selecting the USB Menu In case of high priority alarm activation the ventilator will automatically show the alarm page. To return to the USB menu, press the MENU key.
-
Page 185: Figure 7-29. Selecting Transfer Continuously
USB Menu Parameters Figure 7-29. Selecting Transfer Continuously To transfer continuous data from a ventilator to a USB memory device: Use the UP or DOWN arrow keys to place the cursor at the Transfer Continuously position. Press ENTER The cursor changes to the plus/minus symbol. •…
-
Page 186: Transfer Trends
Operating Procedures Note: If the memory capacity on the USB memory device is insufficient the message “TRANSFER NOT ALLOWED — USB CAPACITY INSUFFICIENT” is shown and data transfer is not allowed. Delete the data on the USB memory device before restarting data transfer. Refer to deletion process. (Refer to section 7.7.5, “Erase Data from the USB Memory Device.”)
-
Page 187: Erase Data From The Usb Memory Device
USB Menu Parameters Press ENTER to confirm the new parameter setting. The new parameter setting is shown continuously. • The cursor is placed at the STOP position. • To manually stop trend transfer, press ENTER Note: If a parameter change is not confirmed by pressing ENTER before 7 seconds elapse, the ventilator resets the parameter to its previous value.
-
Page 188: Figure 7-31. Erasing Data From The Usb Memory Device
Operating Procedures Press ENTER The cursor changes to the plus/minus symbol. • The parameter selected to be modified flashes. • Press UP or DOWN to change the selected parameter’s value. Press ENTER to confirm the new parameter setting. The new parameter setting is shown continuously. •…
-
Page 189: Locking The Control Panel
Locking the Control Panel Note: In case of USB memory device disconnection or deletion error, the message “TRANSFER ERROR — USB DISCONNECTION” or “ERASE ERROR — TECHNICAL PROBLEM” is shown. In this case, restart the erase process. If the problem persists, contact your technical service. Locking the Control Panel When the machine is in service at a patient’s home, it is strongly recommended that you prevent accidental or unauthorized ventilator adjustments from occurring by enabling the Locking key.
-
Page 190: Starting Ventilation
Operating Procedures The initial line access symbol is shown in front of each line. • Starting Ventilation 7.10 Before starting ventilation, refer to Appendix E, “Operational Verification Checklist,” and set the parameter values in the Preferences menu (refer to section 7.3, “Preferences Menu Parameters”…
-
Page 191: Stopping Ventilation
Stopping Ventilation Figure 7-34. Starting Ventilation Stopping Ventilation 7.11 WARNING: Do not allow a patient to remain connected to the ventilator when ventilation is stopped, because a substantial quantity of expiratory gas, primarily carbon dioxide, may be inhaled by the patient. In some circumstances, inhaling carbon dioxide may lead to under-ventilation, suffocation, and serious injury or death.
-
Page 192: Figure 7-35. Stopping Ventilation (1)
Operating Procedures Figure 7-35. Stopping Ventilation (1) While keeping the VENTILATION ON/OFF key pressed: A new message appears that directs the user to press the key again to confirm ventilation stop as • shown in Figure 7-36. Figure 7-36. Stopping Ventilation (2) A double “beep“ sounds. •…
-
Page 193: Turning Off The Ventilator
Turning Off the Ventilator Turning Off the Ventilator 7.12 WARNING: When the ventilator is switched back on after it was switched off while ventilation was in progress, it will immediately begin ventilating—without the user first having to press the VENTILATION ON/ key.
-
Page 194
Operating Procedures Page Left Intentionally Blank 7-42 Clinician’s Manual… -
Page 195: Internal Battery
Lithium-ion battery of the device exceeds the 100Wh threshold and is therefore considered to be Dangerous Goods (DG) Class 9 – Miscellaneous, when transported in commerce. As such, the Puritan Bennett 560 Ventilator and/or the associated Lithium-ion battery are subject to strict transport conditions under the Dangerous Goods Regulation for air transport (IATA:…
-
Page 196: Battery Operation
Internal Battery With a fully charged battery at a normal room temperature of 25 °C (± 5 °C), the ventilator can be expected to operate on internal battery power for the average durations shown in Table 8-1. Checking the battery charge level requires that the ventilator be running on battery power at the time of the battery check.
-
Page 197: Figure 8-1. Internal Battery Indicator
Battery Operation The internal battery indicator at the top left of the ventilator’s front panel is continuously lit (Figure 8- • 1. ). Figure 8-1. Internal Battery Indicator A loss of external supply alarm is activated. • If ventilation is stopped, the internal battery reserve capacity is shown as a percentage of battery charge.
-
Page 198: Testing The Battery
Internal Battery Figure 8-3. Battery Reserve Capacity in Hours and Minutes The LOW BATTERY and EMPTY BATTERY alarms (see Chapter 5, “Alarms and Troubleshooting”) are triggered when the internal battery reserve is reduced. WARNING: Due to its limited internal battery’s reserve capacity, the ventilator should only be operated on the internal battery when no other power source is available.
-
Page 199: Recharging The Battery
Recharging the Battery Recharging the Battery In the event that the battery charge level is considered insufficient, as per the reserve capacity dis- play, recharge of the internal battery is necessary. In general, it is recommended that the ventilator be allowed to charge when the battery drops below 80%, and that the ventilator be recharged systematically after storage and before using it again.
-
Page 200: Storage
Internal Battery Although it is not necessary to start the ventilator to charge the battery, charging the battery during operation will increase the time required to fully charge the internal battery. When recharging a depleted internal battery, it may be necessary to leave the ventilator on charge for up to 6 hours if the ventilator is on standby and about 13 hours if ventilation is operat- ing.
-
Page 201: Cleaning
9 Cleaning WARNING: A patient treated by mechanical ventilation is highly vulnerable to the risks of infection. Dirty or contaminated equipment is a potential source of infection. Clean the ventilator and its accessories regularly and systematically before and after each use and following any maintenance procedure to reduce the risks of infection.
-
Page 202: Cleaning The Accessories
Cleaning To clean the surface of the ventilator: Dip a clean, soft cloth into a mixture of mild soap and water, or other approved cleaning solution. See Table 9-1. for a list of approved cleaning solutions. Table 9-1. Approved Cleaning Solutions for Exterior Ventilator Surfaces Description Mild dishwashing detergent 70% isopropyl alcohol (rubbing alcohol)
-
Page 203: Cleaning The Exhalation Block
Cleaning the Exhalation Block Cleaning the Exhalation Block WARNING: The exhalation block is intended for single use by a single patient . It may periodically be cleaned, but it cannot be disinfected or sterilized. To maintain good measurement quality when used continuously, clean the exhalation block periodically.
-
Page 204
Cleaning Page Left Intentionally Blank Clinician’s Manual… -
Page 205: 10 Routine Maintenance
Do not attempt to open, repair or otherwise service the ventilator yourself. Doing so might endanger the patient, damage the ventilator, and/or void your warranty. Only personnel authorized and qualified by Covidien should repair, open or service the ventilator. Calibrating the Exhalation Flow Sensor 10.1…
-
Page 206: Figure 10-1. Blocking The Patient Wye (Double-Limb Circuit Shown)
Routine Maintenance Figure 10-1. Blocking the Patient Wye (Double-Limb Circuit Shown) Obstruct the patient wye’s open connector using the fleshy portion of your palm to make a good seal as shown in Figure 10-1. Press the MENU key to access the alarm settings menu—if this is not the menu currently shown. Press the UP or DOWN key to place the cursor on the VTE setup line.
-
Page 207: Figure 10-3
Calibrating the Exhalation Flow Sensor Figure 10-3. Calibrating the Exhalation Flow Sensor (2) Press the ENTER key to start calibration. The message “… Exp. calib. Processing …“ is shown in the window on the right, while calibration is • in progress. Figure 10-4. Calibrating the Exhalation Flow Sensor (3) The ventilator adjusts the speed of the blower to reach the initial calibration point.
-
Page 208: Calibrating The Fio2 Sensor
Routine Maintenance In the event of calibration errors, the following events occur: The ventilator sounds a long beep at each point that fails calibration. • An alarm is activated, and the message “CALIBRATION FAIL“ is shown. • The ventilator takes the previously saved value as the default and automatically switches to the next •…
-
Page 209
Calibrating the FiO2 sensor Figure 10-5. Calibrating the FiO Sensor (1) Ensure the ventilator is on and in standby mode. Ensure the Locking key is disabled (see section 7.9, “Unlocking the Control Panel” on page 7-37). Connect the FiO sensor to the ventilator (see section 6.8.3, “Connecting the FiO2 sensor”… -
Page 210: Figure 10-6
Routine Maintenance Figure 10-6. Calibrating the FiO Sensor (2) Press the UP or DOWN key. YES is shown instead of OFF. Figure 10-7. Calibrating the FiO Sensor (3) Press the ENTER key to start calibration. The message “FiO calib. Processing…” is shown in the window on the right while calibration is in •…
-
Page 211: Replacing The Air Inlet Filter
Replacing the Air Inlet Filter Press the ENTER key to exit the FiO setup line. Note: The FiO sensor calibration procedure, once initiated, must run to its conclusion. In the event of calibration errors, the following events occur: An alarm is activated and the message “FiO CALIBRATION FAIL”…
-
Page 212: Recommended Schedule Of Maintenance
Routine Maintenance Figure 10-9. Replacing the Air Inlet filter Recommended Schedule of Maintenance 10.4 Consumables and Replacement Intervals When used under normal circumstances—a relatively dust-free atmosphere, and without damage to the device and its components (shocks, cracks, significant dirt)—the intervals for replacing the ventilator’s consumable elements are as follows: Table 10-1. Consumables and Replacement Intervals Elements Recommended replacement intervals…
-
Page 213
Recommended Schedule of Maintenance report results show that no condensation or drops of water that would affect flow measurement were found in the exhalation block or the Piezzo valve. Note: For all additional accessories not necessarily considered as consumables consult the manufacturer’s recommendations. -
Page 214: Service Assistance
In the event of a problem with the ventilator, see Chapter 5, “Alarms and Troubleshooting.” If you cannot determine the cause of the problem, contact your equipment supplier or Covidien. For more information and local Covidien Technical Service Contact details, see the Technical Support section in Preface chapter.
-
Page 215
A Patient/Caregiver Checklist What the Patient and Caregiver Must Understand Table A-1. presents a summary of the topics that patients and caregivers must understand in order to use the ventilator successfully. Some topics may not apply to some patients, while other patients may require additional information. The Clinician’s Responsibility It is the responsibility of the clinician or clinical educator to ensure that both the patient and the caregiver fully understand the topics listed below. -
Page 216: Patient/Caregiver Checklist
Patient/Caregiver Checklist Table A-1. Patient/Caregiver Checklist (Continued) List of topics References Whom to contact for medical emergencies, equip- Clinician; section 5.8, “Troubleshooting;” ment emergencies, or power emergencies. section 10.5, “Service Assistance” Equipment and phone numbers to have available Clinician; Section 10.5, “Service Assistance”…
-
Page 217
Table A-1. Patient/Caregiver Checklist (Continued) List of topics References What to do if the ventilator alarms inappropriately. Section 5.8, “Troubleshooting” The oxygen setting, and why it is required. Clinician How to connect the oxygen source to the ventila- Clinician; section 6.8, “Oxygen” How to determine the quantity of oxygen being Clinician;… -
Page 218
Patient/Caregiver Checklist Page Left Intentionally Blank Clinician’s Manual… -
Page 219: Specifications
B Specifications Physical Table B-1. Physical Description (Excluding Accessories) Ventilator weight 9.9 lb. (4.5 kg) Ventilator dimensions 9.25 in wide x 12.40 in deep x 6.0 in high (235 mm wide x 315 mm deep x 154 mm high) Connectors Inspiratory limb connector: ISO 22 mm (OD) conical Exhalation limb connector (on exhalation block): ISO 22 mm (ID) conical Oxygen inlet: female connector with valve Device airway volume…
-
Page 220
Specifications Table B-3. Internal Lithium Ion Battery Voltage 25.2 VDC Full-load capacity 4.8 Ah Ampere-hour rating On standby: 1.5 Ah During ventilation: 0.5 Ah Watt hour rating 124Wh to 126Wh Charging current 1.5 A/hr. (duration: < 6 hr.) • Standby mode 0.5 A/hr. (duration: < 13 hr.) •… -
Page 221: Indicators And Alarms
Indicators and Alarms Indicators and Alarms Table B-5. Power Indicators Ventilation ON/OFF AC power DC power Internal battery • Blue in standby mode Green Green • Flashing if the battery charge is in progress • Not lit if ventilation is in progress •…
-
Page 222: Monitored Parameters
± 1 s % Spontaneous (Spont) ± 1 % Peak Airway Pressure (Paw) ± (2 mbar + 8%) The Puritan Bennett 560 Ventilator does not have the capability to reduce pressure below the PEEP pressure during the exhalation phase. Clinician’s Manual…
-
Page 223: Range, Resolution, And Accuracy
Range, Resolution, and Accuracy Range, Resolution, and Accuracy Table B-10. lists the ranges, resolutions, and accuracies for ventilator settings, alarm settings, and patient data. Table B-10. Ventilator Range, Resolution, and Accuracy Ventilator Settings Range, resolution, and accuracy Mode Range: V A/C, P A/C, V SIMV, P SIMV, PSV, CPAP Resolution: N/A Accuracy: N/A Default value: P A/C…
-
Page 224
Specifications Table B-10. Ventilator Range, Resolution, and Accuracy (Continued) Ventilator Settings Range, resolution, and accuracy Inspiratory time (Insp Time) Range: 0.3 s to 6.0 s in P A/C and V A/C modes; 0.3 s to 2.4 s in P SIMV and V SIMV modes Resolution: 0.1 s Accuracy: ±10%… -
Page 225
Range, Resolution, and Accuracy Table B-10. Ventilator Range, Resolution, and Accuracy (Continued) Ventilator Settings Range, resolution, and accuracy Backup rate Range: OFF or 4-40 bpm Resolution: 1 bpm Default value: 13 Depends on: Min I time In P SIMV and V SIMV, Backup rate = Max (8, R-Rate) Apnea time Range: AUTO or 1-60 s Resolution: 1 s… -
Page 226: Environmental
Specifications Table B-10. Ventilator Range, Resolution, and Accuracy (Continued) Ventilator Settings Range, resolution, and accuracy Minimum inspiratory time Range: 0.1 to 2.8 s (Min I time) Resolution: 0.1 s Default value: AUTO (Rise time + 300 ms) Depends on: Max I Time, Backup R, Rise time Maximum inspiratory time Range: 0.8 to 3 s (Max I time)
-
Page 227: Usb
Table B-13. USB Memory Device Specifications Characteristics Supported formats USB compatibility USB flash memory USB 2.0 or USB 1.1 Memory file format USB 32 bit format (sector size: 512–2048 bytes) Number of files Maximum 999 USB size 128 MB to 4 GB Table B-14. Data Transfer Characteristics Ventilator data description Capacity…
-
Page 228: Manufacturer’s Declaration
Table B-20. Electromagnetic Emissions The Puritan Bennett 560 Ventilator is intended for use in the electromagnetic environment specified below. The cus- tomer or the user of the ventilator should assure that it is used in such an environment.
-
Page 229
Manufacturer’s Declaration Table B-21. Electromagnetic Immunity The ventilator is intended for use in the electromagnetic environment specified below. The customer or the user of the ventilator should ensure that it is used in such an environment. Immunity test IEC / EN 60601 test level Compliance level Electromagnetic environment—… -
Page 230
Specifications Table B-22. Electromagnetic Immunity—Conducted and Radiated RF The ventilator is intended for use in the electromagnetic environment specified below. The customer or the user of the venti- lator should assure that it is used in such an environment. Immunity test IEC/EN60601 -1-2 test Compliance level Electromagnetic environment—… -
Page 231
If the measured field strength in the location in which the ventilator is used exceeds the applicable RF compliance level above, the Puritan Bennett 560 Ventilator should be observed to verify normal operation. If abnormal performance is observed, additional measures may be necessary, such as reorienting or relocating the Puritan Bennett 560 Ventilator. -
Page 232
Specifications Table B-23. Recommended Separation Distances (Continued) The ventilator is intended for use in an electromagnetic environment in which radiated RF disturbances are con- trolled. The customer or the user of the ventilator can help prevent electromagnetic interference by maintaining a minimum distance between portable and mobile RF communications equipment (transmitters) and the ventilator as recommended below, according to the maximum output power of the communications equipment. -
Page 233: Standards Compliance And Iec Classification
Standards Compliance and IEC Classification Table B-24. Compliant Cables and Accessories Cable or accessory Maximum length UK AC power cable assembly 1.8 m (5.9 ft) Japan AC power cable assembly 1.8 m (5.9 ft) China AC power cable assembly 1.8 m (5.9 ft) South Africa AC power cable assembly 1.8 m (5.9 ft) India AC power cable assembly…
-
Page 234
Specifications Collateral Standards Medical Electrical Equipment — Part 1: General Requirements for Safety -2- Collateral standard Electro- • Magnetic Compatibility requirements and tests IEC 60601-1-2:2007 and EN 60601-1-2: 2007. Medical Electrical Equipment — Part 1: General Requirements for Safety -2- Collateral standard: Pro- •… -
Page 235: Theory Of Operation
C Theory of Operation Architecture The Puritan Bennett™ 560 Ventilator’s gas delivery system is primarily composed of an airflow generator and a three-way valve to control the patient circuit exhalation valve. The flow gener- ator is a low-inertia, micro-turbine driven by a brushless DC electric motor, while the three-way valve is a proportional solenoid valve.
-
Page 236
Body Temperature Pressure Saturated (BTPS) conditions. This necessitates that periodic inspec- tions for calibrating the sensors be performed by maintenance technicians authorized by Covid- ien (see the Puritan Bennett 560 Ventilator service manual). If the Altitude Compensation feature is active, a corrective algorithm is applied to the inspiration and exhalation flow for volume calculation and the flow set point in volume breath. -
Page 237
Operation Not shown with humidifier, nebulizer, or AC input additional water traps Inspiratory filter DC input Exhalation valve pilot tube Mini type B PC port Expiratory filter Type A USB ports (2) Water trap Nurse call port Exhalation valve Low pressure O inlet Exhaust port Air inlet… -
Page 238
Theory of Operation Page Left Intentionally Blank Clinician’s Manual… -
Page 239: D Modes And Breath Types
D Modes and Breath Types Modes of Ventilation This chapter is a general description of the various modes of ventilation and breath types avail- able with the Puritan Bennett™ 560 Ventilator. Note: The default ventilation mode setting is P A/C; for more information, see below. Assist/Control (A/C) Modes D.1.1 When set to an Assist/Control mode, machine-initiated breaths are delivered at a clinician-set…
-
Page 240: Cpap Mode
Modes and Breath Types CPAP Mode D.1.3 In CPAP, the ventilator maintains a constant level of pressure in the patient’s airway. PSV Mode D.1.4 PSV mode maintains a constant level of pressure in the patient’s airway during exhalation. In addi- tion, the ventilator applies a clinician-set pressure (Pressure Support) to each of the patient’s breaths.
-
Page 241
Breath Types Time Volume Airway pressure Start of inspiration Flow End of inspiration A/C mode guarantees a maximum period between breaths, as determined by the Breath Rate set- ting. In the waveform below, the ventilator delivers a controlled (machine) breath, and calculates the time before another controlled breath must be delivered. -
Page 242: Pressure Control Breaths In Assist/Control Mode
Modes and Breath Types Time Machine breath Airway pressure Patient-initiated breath Period Pressure Control Breaths in Assist/Control Mode D.2.2 In Assist/Control mode (P A/C), each delivered breath will maintain the selected pressure (Pi) maintained over the selected inspiratory time. Inspiration is triggered by patient-generated flow (for assisted breaths) or by the ventilator (for controlled breaths;…
-
Page 243
Breath Types Time Start of inspiration Airway pressure End of inspiration Flow P A/C mode guarantees a maximum period between breaths, as determined by the Breath Rate setting. In the next waveform (shown on the following page), the ventilator delivers a controlled (machine) breath, and calculates the time before another controlled breath must be delivered. -
Page 244: Volume Breaths In V Simv Mode
Modes and Breath Types Time Machine breath Airway pressure Patient-initiated breath Period Volume Breaths in V SIMV Mode D.2.3 In V SIMV the mandatory volume breaths deliver the selected volume (Vt) over the selected inspi- ratory time (Insp Time). Inspiration is triggered by patient-generated flow (for assisted breaths) or by the ventilator (for controlled breaths;…
-
Page 245
Breath Types Time Volume Airway pressure Start of inspiration Flow End of inspiration SIMV mode will also deliver pressure supported breaths (see the description for Pressure support- ed breaths). The SIMV mode is a combination of mandatory volume breaths and pressure sup- ported breaths. -
Page 246: Pressure Supported Breaths In Simv And Psv Modes
Modes and Breath Types trolled“ cycles following an apnea event will be volume cycles. These cycles end as soon as a new inspiration trigger is detected. When the patient triggers a breathing effort, the volume and pressure cycles alternate between each other according to the breath rate setting (R-Rate).
-
Page 247: Cpap
Breath Types Time Airway pressure Flow End of inspiration CPAP D.2.5 In Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) the ventilator maintains pressure at the selected PEEP over the entire breath cycle. Inspiration is triggered by patient-generated flow. Inspiration is limited by the pressure and is cycled by the patient when inspiratory flow drops to the Exhalation Sensitivity threshold (E Sens = 25%).
-
Page 248: Ventilation Modes And Apnea
Modes and Breath Types Airway pressure Start of inspiration Flow End of inspiration Ventilation Modes and Apnea In SIMV mode with apnea time (Apnea Time) settings, the ventilator will sound an APNEA alarm if no patient effort occurs during the apnea time. During an APNEA alarm, the ventilator delivers breaths at a breath rate (backup rate) equal to the maximum of eight and the breath rate setting (R-Rate).
-
Page 249: E Operational Verification Checklist
Following maintenance or changes in ventilator settings • If the ventilator fails any of the safety checks below, or if you cannot complete these checks, see section 5.8, “Troubleshooting” or call the equipment supplier or Covidien (see section 10.5, “Ser- vice Assistance”…
-
Page 250
Operational Verification Checklist Table E-1. Operational Verification Checklist (Continued) Verify the alarm volume is adapted to the patient environment. See section 7.3, “Pref- erences Menu Parameters” on page 7-14 for instructions on changing the alarm Pass volume setting. Verify that the preventive maintenance schedule for the ventilator is followed. See Pass Chapter 10, “Routine… -
Page 251: F Alarms Tests
If the ventilator fails any alarm test or if you cannot complete these tests, see the Troubleshooting section (refer to Chapter 5, “Alarms and Troubleshooting”) of this manual or call your equipment supplier or Covidien (refer to section 10.5, “Service Assistance” on page 10-10). …
-
Page 252: Circuit Check Test
Alarms Tests Wait for (Apnea time + 2 seconds; Apnea time is not always 5 seconds), then ensure that: The high priority indicator (red color) lights up • The PATIENT DISCONNECTION alarm is shown • The audible alarm sounds • Press the ALARM CONTROL key once to pause the audible alarm.
-
Page 253
Circuit Check Test Block the patient connection port of the patient circuit (see Figure F-2. ) Figure F-2. Blocking the Patient End of a Single-Limb Circuit Activate the circuit test by pressing the ENTER key. During the circuit check (which typically takes about 10 seconds to complete), the ventilator will do the following: Sound a short beep Close the exhalation valve… -
Page 254: Troubleshooting A Failed Check
Alarms Tests Figure F-4. Circuit Check (Complete, Passed) Figure F-5. Circuit Check (Complete, Failed) Review the results. A FAIL result indicates leak(s) of greater than 1 L/min exist. To rerun circuit check test, press the ENTER key again. To cancel the circuit check while it is run- ning, press the UP, DOWN, ENTER, VENTILATION ON/OFF, or MENU key.
-
Page 255: Apnea Test
Apnea Test Apnea Test Apnea breaths only apply in PSV, CPAP, and SIMV modes. Connect the patient end of the patient circuit to a test lung. Verify that the pressure tube of the patient circuit is properly connected to the appropriate fitting on both the ventilator and the proximal pressure port (see section 6.4, “Patient Circuit”…
-
Page 256: Occlusion Test
Alarms Tests Occlusion Test Note: Occlusion testing can only be done in pressure modes. When using a single-limb circuit, do the following: Verify that the pressure tube of the patient circuit is properly connected to the appropriate fitting on both the ventilator and the proximal pressure port (see section 6.4, “Patient Circuit”…
-
Page 257: High Pressure Test
High Pressure Test High Pressure Test Set the ventilator to V A/C mode and set the following parameter values: Vt: 250 ml • PEEP: OFF • Flow Pattern: D • R-Rate: 30 bpm • I:E: 1/4 or I/T: 20% • Insp Sens: 3 •…
-
Page 258: Battery Test
Alarms Tests Battery Test The ventilator is capable of testing the power of the battery (see Chapter 8, “Internal Battery”). You can determine which power source the ventilator is using by checking the power indicator, located on the top panel. The indicator light will be lit to indicate which power source is currently available.
-
Page 259: G Unpacking And Preparation
Users must always possess an additional circuit and valve while using the Puritan Bennett 560 Ventilator. WARNING: To minimize the risk of damage, you must use the Dual Bag to transport the Puritan Bennett 560 Ventilator. Refer to Figure G-2. To unpack and prepare the ventilator, follow the steps below: From the plastic bag, remove the following: Plastic pocket containing the clinician’s manual.
-
Page 260
Never use a ventilator or any components or accessories that appear to be damaged. If any signs of damage are evident, contact your equipment supplier or Covidien. Clean the ventilator with a mild soap solution, if necessary (see Chapter 9, “Cleaning”). -
Page 261
Figure G-2. Dual Bag Clinician’s Manual… -
Page 262
Unpacking and Preparation Page Left Intentionally Blank Clinician’s Manual… -
Page 263: H Parts And Accessories
Table H-1. provides a list of accessories that are available for the Puritan Bennett™ 560 Ventila- tor. To order parts or accessories, contact your equipment supplier or Covidien representative. Note: The ventilator is delivered with the following items: a printed user’s manual, a CD with clinician’s manual…
-
Page 264
Table H-2. provides a list of consumable parts available for the ventilator. WARNING: To ensure proper performance of the ventilator, use a patient circuit recommended by Covidien in this manual; refer to Chapter 6, “Installation and Assembly” and Appendix H, “Parts and… -
Page 265
DAR™ Single-limb patient circuit without exhalation valve, 180 cm, PVC, ADULT 5093300 DAR™ Single-limb patient circuit without exhalation valve, 180 cm, PVC, PEDIATRIC 5093100 For more information regarding parts and accessories for the Puritan Bennett 560 Ventilator contact your service representative or www.covidien.com/rms/products. Clinician’s Manual… -
Page 266
Parts and Accessories Page Left Intentionally Blank Clinician’s Manual… -
Page 267
I Glossary AC Power Alternating current. Alarm Pause The audible and visual alarms cease and the symbol appears. The symbol will remain until the cause of the alarm is addressed. For example, when the ventilator is running on internal bat- tery, the AC Disconnection alarm may be paused, and the alarm paused symbol will appear until the device is plugged into AC. -
Page 268: Glossary
Glossary Back Up Rate Rate of control cycles in PSV or SIMV modes during apnea phase. Battery Level Display of the remaining battery capacity; located adjacent to the battery symbol. Bias flow Turbine flow during exhalation phase through the patient circuit to avoid rebreathing. An abbreviation for “breaths per minute,”…
-
Page 269
Exhalation Sensitivity The exhalation sensitivity (E Sens) level is a percentage of peak flow at which a pressure-support- ed breath will be terminated. Exhalation Tidal Volume (VTE) Volume exhaled by the patient at each exhalation phase. Fraction of Inspired Oxygen (FiO Amount of oxygen delivered to the patient. -
Page 270
Glossary I Time (Inspiratory Time) Inspiratory time measure. Intentional Vent Stop Alarm Ventilation has been switched off by the user/caregiver and the ventilator is in standby. I/T Ratio Inspiratory time versus total breath time ratio. liters (a unit of volume). Leak When ventilating with a double-limb circuit in leak configuration, it is the average parasitic leak during each cycle and over the past 24-hour period. -
Page 271
Minimum Exhalation Time Minimum exhalation time before allowing the patient inspiratory trigger. Minimum Inspiratory Time Minimum inspiratory time before allowing the patient to exhale. M Vol (Minute Volume) Flow delivered at each breath to the patient is measured by the inspiratory flow sensor and that measurement is used to calculate minute volume (Vt x Rtot) P A/C (Pressure Assist /Control) A ventilator mode which provides machine-initiated breaths delivered at a clinician-set pressure,… -
Page 272
Glossary that depends on the exhalation sensitivity setting for the inspiration, when the ventilator cycles into exhalation. Available in SIMV mode. Pounds per square inch. PSV (Pressure Support Ventilation) Pressure support ventilation. Rebreathing The patient breathes his/her exhaled gas. Respiratory rate The number of breath cycles (inspiration + expiration) completed within one minute. -
Page 273
Unfreeze Resumption of the waveform plot tracing on the ventilator’s display. V A/C (Volume Assist / Control) A ventilator mode which provides machine-initiated breaths are delivered at a clinician-set volume inspiratory time, and rate. Vent Time (Ventilation Time) The ventilation duration data is based on the patient counter and shows the total ventilation time in hours and minutes over the previous 24-hour period. -
Page 274
Glossary Page Left Intentionally Blank Clinician’s Manual… -
Page 275
Index HIGH PRESSURE ……..3-13, 3-25 HIGH RATE . -
Page 276
Breathing Circuit ……….4-8 Electromagnetic compatibility and moble/portable communications BUZZER FAULT1 alarm message . -
Page 277
Index KEYPAD FAULT alarm message ……3-13, 3-26 Placing the ventilator (installing) ……. 4-1 Pneumatic specifications . -
Page 278
Transfer continuously, USB Memory Device ….. 5-5 Transfer Trends USB Memory Device ……5-7 Transport, emergency, ventilator not intended for . -
Page 280
Part No. 10071962 Rev D 2017-05 © 2011 Covidien. Covidien llc 15 Hampshire Street, Mansfield, MA 02048 USA Covidien Ireland Limited, IDA Business and Technology ParkTullamore. www.covidien.com [T] 1 800 635 5267…
- Главная страница
- Каталог
- Медицинское оборудование
- Анестезиология, ИВЛ и Реаниматология
- Аппараты ИВЛ
- Стационарные аппараты ИВЛ
Портативный аппарат ИВЛ Puritan Bennett 560 для инвазивной и неинвазивной вентиляционной поддержки дыхания.
Вес и возраст пациентов: от 5 кг, взрослые, дети.
Преимущества: универсальность, высокая чувствительность потокового триггера к снижению усилия вдоха, доступность для пациентов, безопасность, период автономной работы 11 часов, лёгкость и портативность (вес 4,5 кг), низкий уровень шума.
Функционально: выбор режимов и типа вентиляции лёгких, блокировка клавиатуры, совместимость с автономным оборудованием подачи кислорода низкого давления, выбор специфических конфигураций для детей и взрослых.
Использование ИВЛ Puritan Bennett 560: в лечебных учреждениях, на дому, при транспортировке.
Варьирование уровня тревог позволяет с высокой точностью контролировать параметры вентиляции и минимизировать риски.
Программное обеспечение: просмотр отчётов и диаграмм за сутки на экране, анализ и архивирование данных о пациенте за год, перенос данных с помощью USB на ПК врача, подробные диаграммы за 2 суток.
Оборудование отвечает российским стандартам, имеет РУ, а также Сертификат RTCA/DO-160F (позволяет использовать его на борту коммерческих рейсов).
В избранное
В сравнение
Доставка по всей России
Сроки уточняйте у оператора
- Описание
Портативный аппарат искусственной вентиляции легких Puritan Bennett 560 предназначен для механической вентиляционной поддержки дыхания взрослых и детей при оказании экстренной помощи на месте, во время перевозки, в условиях ЛПУ, а также для продолжительного жизнеобеспечения в медучреждениях и на дому.
К его основным достоинствам относятся:
- Универсальность (может применяться при большинстве патологических состояний, сопровождаемых дыхательной недостаточностью, и вызванных нервно-мышечными поражениями);
- Простота и скорость запуска, доступность для использования пациентами без помощи медперсонала;
- Чувствительность, безопасность, большой объём предоставляемых данных, которые можно перенести на ПК врача с помощью USB.
ИВЛ Puritan Bennett 560 – разработка известного американского производителя медоборудования Medtronic и отвечает всем современным стандартам и нормам, в том числе он имеет Сертификат RTCA/DO-160F, благодаря чему может применяться на борту коммерческих рейсов.
Он применим и для взрослых, и для детей (весом от 5 кг), при этом допускается домашнее использование, так как оборудование максимально просто и безопасно в эксплуатации.
Преимущества аппарата ИВЛ Puritan Bennett 560
- До 11 часов автономной работы на внутренней литий-ионной батарее – можно использовать вдали от источника тока, при транспортировке (в оптимальных условиях, без отягощающих обстоятельств).
- Контроль заряда батареи – специальный индикатор показывает оставшееся время в часах и минутах на основе ситуационного режима.
- Универсальность – применение при большинстве патологических состояний с хронической недостаточностью дыхания и дыхательных патологиях, вызванных нервно-мышечными заболеваниями (ХОБЛ, боковой амиотрофический склероз, спинальная мышечная атрофия и проч.).
- Варьирование уровня тревог повышает точность контроля параметров вентиляции и сводит к минимуму риски клинических нарушений.
- Соответствие стандартам РФ: Puritan Bennett 560 имеет Регистрационное удостоверение и отвечает всем требованиям к оборудованию этого типа в России.
- Портативность, небольшой вес (4,5 кг) и наличие в комплекте сумки для переноски позволяют безопасно переносить и перевозить оборудование.
- Высокий уровень самостоятельности больных обеспечивает безопасность в отсутствие рядом медработников.
- Уровень шума – менее 30 дБА на расстоянии 1 метра.
Технические характеристики Puritan Bennett 560
|
Общие |
Вес аппарата – 4,5 кг. Вес пациентов – от 5 кг. Диапазон дыхательного объёма – 50-2000 мл. Уровень шума – менее 30 дБА на расстоянии 1 метра. |
|
Настройки |
Типы вентиляции – инвазивный и неинвазивный. Режимы – P AC, V AC, P SIMV, V SIMV, PSV, CPAP. Выбор специфических конфигураций для детей и взрослых. |
|
Безопасность |
Блокировка клавиатуры. Регулируемость потокового триггера на снижение усилия вдоха. Автоматическое определение клапана при выборе режима в соответствии с конфигурацией контура. |
|
Совместимость |
С автономным оборудованием подачи кислорода низкого давления извне. |
|
Анализ и управление информацией |
Создание и хранение диаграмм состояния пациента за 2 суток. Просмотр отчётов и диаграмм за 1 сутки на экране. Хранение информации о пациенте до 1 года. Перенос информации и диаграмм на ПК с помощью USB. |
Инструкция производителя по эксплуатации Puritan Bennett 560
Разработчик аппарата рекомендует не пренебрегать дополнительной техникой безопасности при эксплуатации:
- Вести тщательное наблюдение в соответствии с тяжестью состояния больного;
- Иметь в ближайшем доступе другие средства вентиляции лёгких для работы с пациентами, не способными дышать самостоятельно;
- Иметь в наличии альтернативные источники питания (переменного тока, запасные аккумуляторы, вспомогательные автомобильные переходники постоянного тока).
Приобрести Puritan Bennett 560 на оптимальных условиях и по выгодной цене вы можете в Тиара-Медикал: специалисты проконсультируют вас, помогут оформить заказ и проследят за его оперативной доставкой. Кроме того, компания способна обеспечить техническое гарантийное и постгарантийное обслуживание аппаратов ИВЛ и их ремонт квалифицированными мастерами.
Мы гарантируем
Гарантия производителя и продавца
Профессиональные консультации и поддержка на каждом этапе
Собственный сервисный центр
Демократичная цена и лизинг
Быстрая и бережная доставка
Частые вопросы
Стоимость-
Вопрос: Почему на многие товары не указана цена?
Ответ: Итоговая стоимость оборудования зависит от множества факторов:1) Конфигурация. Многие модели медицинского оборудования являются модульными системами. По желанию клиента некоторые модули могут быть добавлены или исключены из поставки. Яркий пример – ультразвуковые сканеры, каждый из которых может комплектоваться различными наборами датчиков (на выбор из нескольких десятков) и дополнительными модулями (например, для расчетов и 4d-исследований). Таким образом, один и тот же УЗ-сканер может иметь несколько десятков конфигураций, значительно различающихся по цене.
2) Стоимость доставки. Мы предлагаем несколько вариантов доставки, из которых наши клиенты могут выбрать наиболее приемлемый по скорости и цене. Подробнее…
3) Установка и наладка. Многие виды оборудования требуют обязательной установки и наладки с помощью сертифицированного специалиста, выдающего акт ввода в эксплуатацию, что так же сказывается на стоимости.
4) Курс валюты, сроки поставки и прочие менее значимые факторы.
Совет: Если вы видите в каталоге какой-либо компании точную цену на медицинское оборудование – обязательно уточняйте, что входит в эту сумму!
Скидки! У нас действует гибкая система скидок, постоянно проводятся специальные акции и действуют другие привлекательные предложения. Следите за новостями!
Доставка-
Территория доставки?
ТИАРА-МЕДИКАЛ осуществляет доставку медицинского оборудования в пределах Таможенного Союза (ЕврАзЭС) транспортными компаниями. За 10 лет работы мы установили тесные партнерские отношения с различными транспортными компаниями и предлагаем нашим покупателям наиболее выгодные варианты доставки.
В каких случаях бесплатная доставка?
Доставка по Санкт-Петербургу – БЕСПЛАТНО.
Доставка до транспортных компаний – БЕСПЛАТНО.
Лизинг-
Компания ТИАРА-МЕДИКАЛ имеет многолетний опыт продажи медицинского оборудования в лизинг. Мы сотрудничаем с лизинговыми компаниями, выбранными покупателем, или можем порекомендовать наших проверенных партнеров.
Какое оборудование можно купить в лизинг?
В лизинг предоставляется оборудование для УЗИ, томографии, рентгенологии, эндоскопии, офтальмологии, косметологии. А также любое медицинское оборудование стоимостью от 1 000 000 рублей. Обратитесь за расчетом выгодного приобретения в лизинг к нашим специалистам по телефону: 8 (800) 500-26-76
Как быстро принимаем решение?
Срок рассмотрения от 1 дня.
С какими лизинговыми компаниями мы сотрудничаем?
В основном с «Элемент лизинг» и «Балтийский лизинг», также готовы работать с другими компаниями, которые выгодны и удобны для Вас.
Сервис-
Мы создали лучшую систему сервисной поддержки медицинского оборудования, на протяжении всего срока службы. В нашей команде работают высококвалифицированные инженеры, систематически совершенствующие свои навыки на заводах производителей мед. оборудования. Мы оказываем исчерпывающий спектр услуг по поддержке и ремонту оборудования.
При поставке мы предлагаем
Установку, настройку, ввод в эксплуатацию (по всей территории РФ).
Обслуживание после поставки
Наш собственный лицензированный сервисный центр производит:
— Гарантийное и пост-гарантийное комплексное обслуживание медицинской техники.
— Гарантийный и пост-гарантийный ремонт.
— Выездной инструктаж пользователей.
— Поддержку документацией и учебными материалами.
— Консультации на любом этапе использования.Отдел запчастей медицинского оборудования
Подбор и продажа оригинальных запчастей для медицинской техники.
Гарантии-
ТИАРА-МЕДИКАЛ осуществляет продажу медицинского оборудования, инструментов и материалов в соответствии с законодательством РФ. Наше оборудование имеет всю необходимую разрешительную документацию, гарантию производителя и продавца.
Гарантийный срок на медицинское оборудование
Срок базовой гарантии на мед. оборудование составляет 12 месяцев со дня покупки и может быть увеличен в зависимости от индивидуальных гарантийных условий производителя!
Как заказать гарантийное обслуживание
Гарантийное сервисное обслуживание осуществляется по запросу в сервисный центр ТИАРА-МЕДИКАЛ. Звоните по тел.: 8 (800) 500-26-76 или оставьте заявку на странице сервисного центра
Кто проводит обслуживание медицинского оборудования
Мы имеем собственный лицензированный сервисный центр для обслуживания и устранения неисправностей и команду сертифицированных специалистов выездного обслуживания техники. Работы проводятся согласно стандартам производителя. Доставляем оборудование в сервисный центр — бесплатно!
Наши специалисты готовы на них ответить, рассказать об оборудовании и помочь с выбором.
- About
- Blog
- Projects
- Help
-
Donate
Donate icon
An illustration of a heart shape - Contact
- Jobs
- Volunteer
- People
Bookreader Item Preview
texts
Puritan Bennett 560 Service Manual
Puritan Bennett 560 Service Manual
- Addeddate
- 2020-05-19 23:37:00
- Classification
- Clinical;Ventilator;Puritan Bennett Ventilator;Puritan Bennett 560
- Identifier
- manual_Puritan_Bennett_560_Service_Manual
- Identifier-ark
- ark:/13960/t5q90375k
- Ocr
- ABBYY FineReader 11.0 (Extended OCR)
- Ppi
- 300
- Scanner
- Internet Archive Python library 1.9.0
comment
Reviews
There are no reviews yet. Be the first one to
write a review.
SIMILAR ITEMS (based on metadata)