- Systematic review
- Open Access
- Published: 02 January 2014
- Andrea Juliana Sanabria1,
- Ivan Solà1,
- Pablo Alonso-Coello1 &
- …
- Laura Martínez García1
Implementation Science
volume 9, Article number: 3 (2014)
Cite this article
-
17k Accesses
-
106 Citations
-
46 Altmetric
-
Metrics details
Abstract
Background
Updating clinical practice guidelines (CPGs) is a crucial process for maintaining the validity of recommendations. Methodological handbooks should provide guidance on both developing and updating CPGs. However, little is known about the updating guidance provided by these handbooks.
Methods
We conducted a systematic review to identify and describe the updating guidance provided by CPG methodological handbooks and included handbooks that provide updating guidance for CPGs. We searched in the Guidelines International Network library, US National Guidelines Clearinghouse and MEDLINE (PubMed) from 1966 to September 2013. Two authors independently selected the handbooks and extracted the data. We used descriptive statistics to analyze the extracted data and conducted a narrative synthesis.
Results
We included 35 handbooks. Most handbooks (97.1%) focus mainly on developing CPGs, including variable degrees of information about updating. Guidance on identifying new evidence and the methodology of assessing the need for an update is described in 11 (31.4%) and eight handbooks (22.8%), respectively. The period of time between two updates is described in 25 handbooks (71.4%), two to three years being the most frequent (40.0%). The majority of handbooks do not provide guidance for the literature search, evidence selection, assessment, synthesis, and external review of the updating process.
Conclusions
Guidance for updating CPGs is poorly described in methodological handbooks. This guidance should be more rigorous and explicit. This could lead to a more optimal updating process, and, ultimately to valid trustworthy guidelines.
Peer Review reports
Background
Clinical practice guidelines (CPGs) intend to patient care by providing recommendations about the benefits and downsides of best practice in healthcare [1]. If adequately implemented, CPGs have the potential of reducing variability and translating scientific research into clinical practice and consequently improve the quality and safety of healthcare [2–4].
However, scientific knowledge is in constant change; therefore CPGs need to be updated regularly to maintain validity [5]. The obsolescence of a CPG might occur because of new scientific research, including the development of new technologies in treatment and diagnosis alternatives, economic differences, or changes in values and preferences [6, 7]. Generally, an updating process consists of three components: the identification of new evidence, the assessment of the need to update, and the formulation of new or modified recommendations [5, 8–11]. Some authors suggest that an update is generally required after three to five years; however, little research has been undertaken so far [8, 12, 13].
Several institutions responsible for developing CPGs drafted their own methodological handbooks including methodology for developing and updating their CPGs. Some of these handbooks are very influential and often used in smaller organizations [6, 14]. Even though the methodology developed greatly over the last years, the quality of CPGs is lagging behind [1, 15, 16]. A lack of compliance with state of the art methodology for developing CPGs has been found, and hence the methodological quality of CPGs remained very similar over the last two decades [17, 18]. Little is known about the guidance for updating CPGs included in these handbooks [19, 20]. Therefore, we systematically reviewed CPGs methodological handbooks to identify and describe the methodological guidance about updating.
Methods
Search strategy
We conducted a systematic search in September 2013 in MEDLINE (via PubMed, from 1966 onwards), using a combination of free text terms (Clinical Practice Guidelines, Clinical Guidelines, Guidelines, Methodolog*, Handbook*). The search strategy is available as supplementary data (Additional file 1). In addition, we searched: the database of the Guidelines International Network (http://www.g-i-n.net); the US National Guidelines Clearinghouse database (http://www.guidelines.gov); and the website of institutions that reported to use a methodological handbook in a previous international survey conducted by our group [12]. If necessary, we contacted organizations to obtain the handbooks.
Eligibility criteria
We included methodological handbooks that provide guidance on the updating process of CPGs. Handbooks that exclusively report methodologies for developing de novo guidelines were excluded. We included handbooks regardless of their language or publication status. When necessary, the handbook was translated.
Study selection
Two authors (RV, AJS) independently selected potential handbooks by reviewing titles and abstracts, and finally full text for a more detailed evaluation. Disagreements were initially resolved by consensus, and if necessary, with the help of a third author (PA-C).
Data extraction
Based on our previous experiences concerning updating, including an international survey [12] a systematic review [8] and additional relevant literature [5, 6, 9–11, 14] we developed, reviewed, and piloted iteratively a case report form (CRF). After consensus, the following items are included in the CRF: characteristics of the handbook and institution, group responsible for updating CPGs, strategy for identifying new evidence, methodology for assessing the need for an update, methods for the literature search, evidence selection, evidence assessment, evidence synthesis, external review, and for the edition and dissemination of the updated CPG. The CRF can be made available upon request.
Two authors (RV, AJS) extracted independently the data of the handbooks accepted for inclusion. Disagreements were initially resolved by consensus, and if necessary, with the help of a third author (PA-C). While extracting the data, we considered a strategy to be specific if the handbook included a detailed methodology, enabling the reader to conduct the suggested strategy. We considered a non-specific strategy if not enough methodological guidance is provided to facilitate an adequate approach.
Data analysis
We used descriptive statistics to analyze the extracted data. We calculated absolute frequencies and proportions for all items. In addition, we conducted a narrative synthesis. Data analysis was performed using SPSS statistical software, version 18.0 (SPSS INC., Chicago, IL, USA). By consensus of two authors (RV, AJS), we collected relevant quotations within the themes included in the handbooks and provide these in the free text area.
Results
Handbooks selection
We screened the titles and abstracts of 1,992 references (Figure 1). We selected 94 articles for full-text review. Thirty-eight articles were excluded because they were not methodological handbooks. Additionally, ten handbooks were excluded because they exclusively focused on developing de novo CPGs. We could not locate eight articles and one article was a summary of an included handbook. Two handbooks were excluded because a more recent version was included. Additional file 2 provides an overview of the excluded documents. Finally, we included thirty-five handbooks (Additional file 3) [5, 6, 14, 21–52].
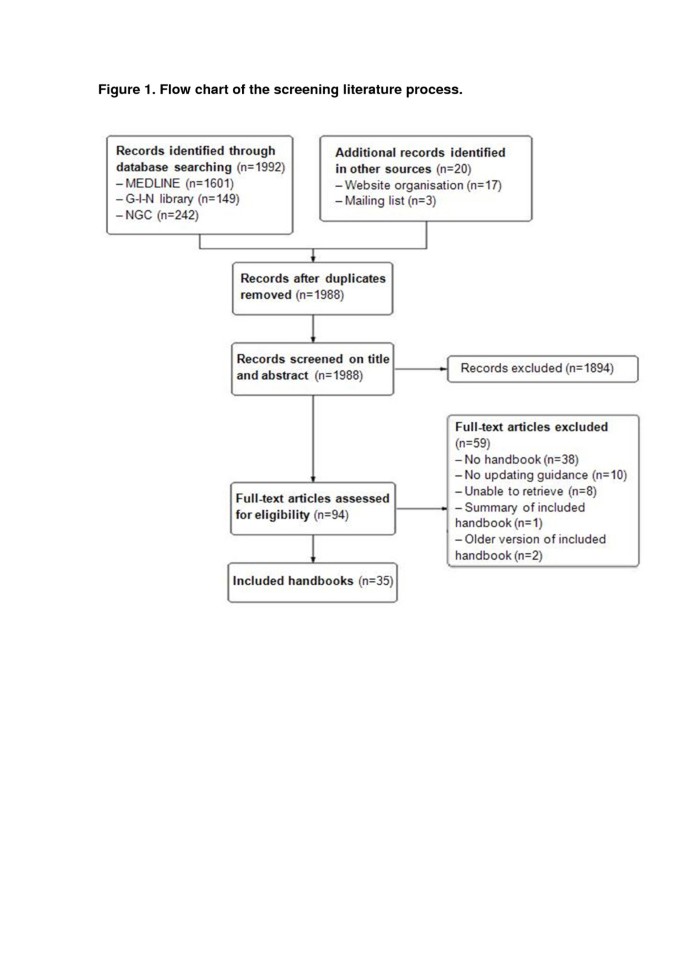
Flow chart of the screening literature process.
Full size image
Handbooks characteristics
In total, 48.6% of the included handbooks are developed by institutions based in Europe [5, 6, 14, 21–34] mostly being public institutions (57.1%) (Table 1) [5, 6, 14, 22–26, 28, 31, 35–43]. One handbook (2.9%) addresses specifically the methodology of updating CPGs [5]; the others (97.1%) focus mainly on developing de novo CPGs, and include variable degrees of information about updating [6, 14, 21–52]. Fourteen handbooks (40.0%) are published between 2005 and 2010 [5, 21, 23, 26, 30, 32, 34, 39],[40, 43, 44, 46, 48, 50].
Characteristics of institutions and handbooks
Full size table
Updating group
The persons responsible for updating the CPG are specified in twelve handbooks (34.3%). Seven handbooks (20.0%) state that the updating group should have a similar structure to the group that contributed to developing the CPG [6, 14, 23, 30, 37, 44, 45]. Four handbooks (11.4%) state that the group, responsible for updating the CPG, should be tailored to the new scope of the guideline [5, 38, 39, 41].
Time between updates
Twenty-five (71.4%) of the included handbooks recommend a time frame between publishing a CPG and commencing an updating process (Table 2), with two to three years being the most frequently recommended (40.0%) [5, 6, 14, 22, 27, 28, 30–32, 37],[39, 41, 45, 46]. Furthermore, three handbooks (8.6%) suggest a time frame of less than one year [33, 34, 44], and eight handbooks (22.9%) include a four to five year time frame [24, 36, 38, 42, 43, 47–49].
Guidance reported in the included handbooks
Full size table
Identification of new relevant evidence
Eleven handbooks (31.4%) provide guidance on how to identify new relevant evidence. Of these eleven handbooks, six (17.1%) suggest using opinions or experiences from experts, users, or members of the original development group for identifying new relevant evidence [5, 14, 23, 37, 43, 46]. Five handbooks (14.3%) provide guidance on conducting limited searches to identify new relevant evidence [5, 37–39, 47]. Furthermore, two handbooks (5.7%) propose the editorial board to have periodic meetings to discuss topics with experts [32, 33]. One handbook (2.9%) suggests collecting alerts to identify newly published articles [5]. Externally reviewing the CPG by experts, who were not involved in developing the CPGs, is recommended by one handbook (2.9%) [47]. Two other handbooks (5.7%) provide a ‘non-specific strategy’ and only emphasize the importance of identifying new relevant evidence (Table 2) [23, 28]. Figure 2 shows examples of relevant passages included in the handbooks.
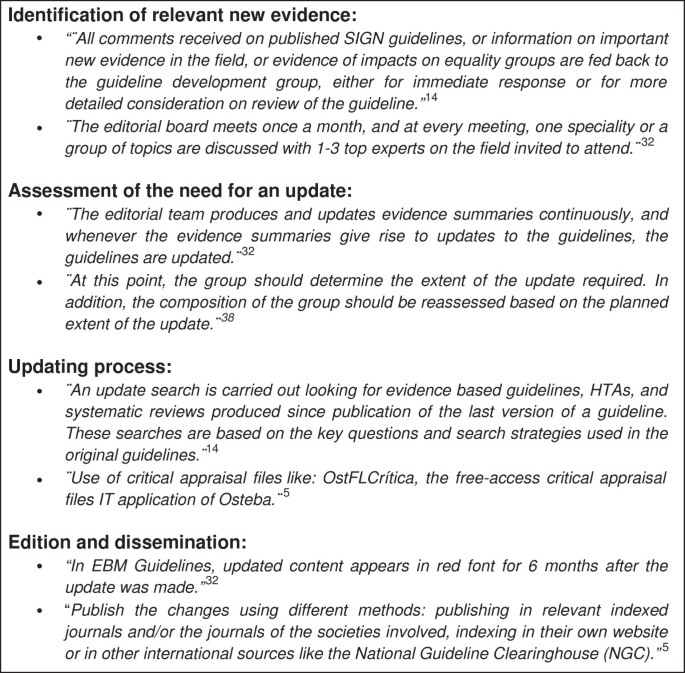
Box of relevant comments.
Full size image
Assessment of the need for an update
The methodology of assessing the need for an update is described in eight handbooks (22.8%). Six of them (17.1%) give guidance on how to assess the importance and relevance of the new evidence, the disagreement between the new evidence and current recommendations, and whether the new knowledge is not yet included [5, 6, 23, 38, 43, 49]. Two handbooks (5.7%) recommend expert judgment to assess the need for an update [38, 40]. Producing and regularly updating evidence summaries and assessing the need for an update with these summaries are described in one handbook (2.9%) (Figure 2) [32].
Updating recommendations
Eight handbooks (22.9%) provide guidance on what type of update is required in specific situations, by making a distinction between partial or full updates (Table 2) [5, 6, 14, 33, 37, 38, 43, 44].
Guidance for conducting a literature search strategy is included in seventeen handbooks (48.6%). Eight of them (22.8%) include guidance to adjust the original search strategy [5, 6, 14, 24, 26, 27, 37, 43]. Four handbooks (11.4%) provide guidance on what kind of evidence to search for, including evidence based guidelines, health technology assessments, systematic reviews, and randomized controlled trials [14, 27, 38, 41]. Two handbooks (5.7%) recommend to include a medical librarian or research officer in the team to conduct the literature searches [41, 48]. Using multiple databases, e.g., MEDLINE and Cochrane Library, in the search strategy is recommended by two handbooks (5.7%) [41, 43]. Furthermore, six handbooks (17.1%) suggest using the original strategy used for the development of the original guideline (Table 2, Figure 2) [23, 28, 34, 40, 44, 50].
Eleven handbooks (31.4%) provide guidance for selecting adequate evidence in the updating process. Three handbooks (8.6%) provide specific guidance on how to discard irrelevant information [5, 14, 44]. Eight handbooks (22.9%) refer the reader to the development process for guidance on evidence selection [6, 27, 28, 34, 37, 38, 48, 50].
Guidance for evidence assessment is provided in thirteen handbooks (37.1%). The assessment of the available evidence on the consistency, directness, validity or reliability is described in four handbooks (11.4%) [14, 37, 43, 48]. Using critical appraisal frameworks, like OstFLCritica, is recommended in one handbook (2.9%) (Figure 2) [5]. Eight handbooks (22.9%) recommend the same original development strategy [6, 23, 27, 28, 34, 38, 44, 50].
Similarly, guidance for the evidence synthesis is described in eight handbooks (22.9%). Three handbooks (8.6%) recommend producing evidence tables including the characteristics of included studies, quality of randomized trials, results for continuous outcomes, and results for dichotomous outcomes [14, 43, 48]. Moreover, five handbooks (14.3%) direct the reader to the section with guidance for evidence synthesis used for developing de novo CPGs [5, 6, 34, 44, 50].
Guidance for an external review of the updated CPG is described in thirteen handbooks (37.1%). Five handbooks (14.3%) describe the process of external reviewing the updated CPG by multiple external reviewers [37, 43, 45, 47, 48]. Furthermore, two handbooks (5.7%) provides ‘non-specific guidance’ for conducting an external review of the updated CPG [28, 38]. Six handbooks (17.1%) refer to the guidance described in the section of developing de novo CPGs [5, 6, 27, 34, 44, 50].
Edition and dissemination
Two handbooks (5.7%) suggest to post a notification on the website of the institution whenever the need for an update is confirmed [28, 29]. Five handbooks (14.3%) include a specific strategy for indicating the changes made in the update (Table 2, Figure 2). These handbooks recommended actions to identify the main changes in the update without any difficulty, including a table of updated evidence, summary reports, or highlight the updated parts in the text with a red font [5, 32, 33, 37, 47].
Three handbooks (8.6%) provide guidance on how to publish and disseminate the updated CPG. All three of them include methods to disseminate the updated CPG as widely as possible by publishing in relevant indexed journals [5], disseminate within the patient organization of the specific disease [48], or working together with public and private partners to reach specific groups and individuals [43].
Discussion
We systematically reviewed 35 methodological handbooks that provide some type of guidance on the updating process of CPGs. Our results show that overall the updating guidance is poorly described. Crucial elements in identifying new evidence, the assessment for the need for an update and the updating strategy itself, are generally lacking or include solely a reference to the development process. Our findings resonate with previous findings that suggest that there is a need for rigorous international guidance for updating CPGs [8, 14].
Figure 3 summarizes an updating process framework for CPGs based on a previous systematic review from our group and the results of the present study [8]. The process of updating a CPG starts with assembling a group responsible for updating the CPG. However, we found that the majority of the institutions (65.7%) do not include any information about this first step. There is no clear consensus on who should participate in an updating process and, consequently different organizations use different strategies, depending on the characteristics of the organization and type of update. An updating working group, should consist of individuals with a background in methodology and experts in the field of interest, just as the original guideline group [5]. New developments in the clinical area, such as new technologies, might require including additional members with different expertise.
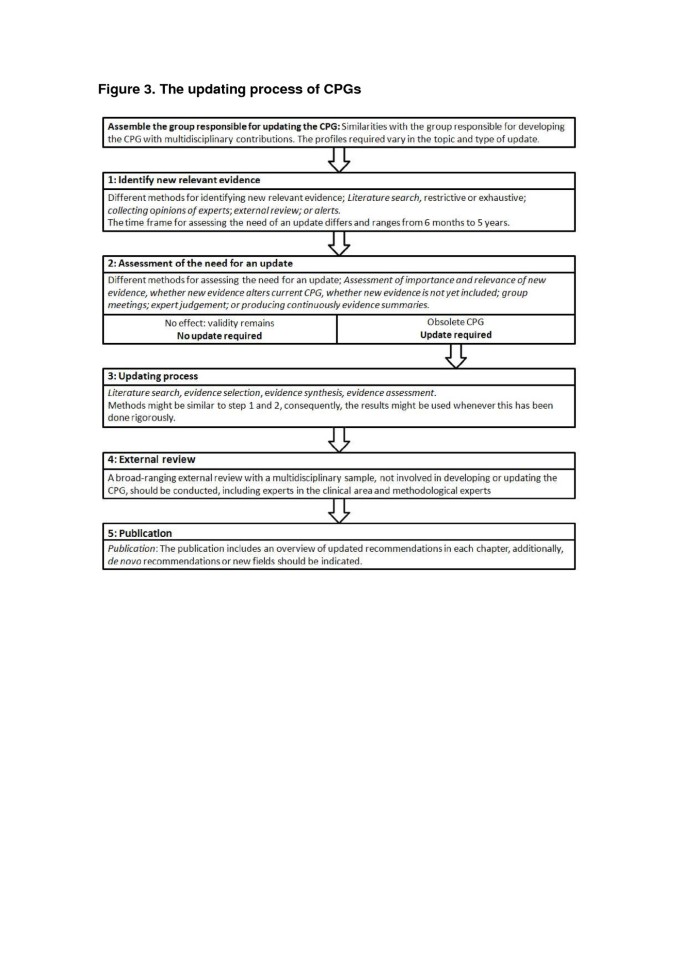
The updating process of CPGs.
Full size image
The actual updating process starts with identifying new relevant evidence. Currently, the period between the last publication of the CPG and starting the updating process (time frame) is frequently determined at the time of publication. The majority of the handbooks (62.9%) include a fixed time frame from two to five years, consistent with the results of previous research by Shekelle et al. [13]. This study including a sample of 17 guidelines, estimated that approximately one-half of the CPGs will be outdated after 5.8 years (95% CI: 5.0 – 6.6), and 10% are obsolete after 3.6 years (95% CI: 2.6 – 4.6) [13]. However, these average estimates can be misleading as CPG deteriorating speed is highly topic-specific, with some fields with rapid developments requiring more frequent surveillance for new evidence than others. Suboptimal time frames are likely to result in guidelines becoming obsolete or inefficient use of resources.
After identifying new relevant evidence, an assessment of the effect of this new evidence should be conducted, determining the need for an update [5, 9–11]. We believe that this process is best conceptualized as a two-stage process because these are two independent stages with identifying possible new relevant evidence as first step, and, subsequently, deciding whether the identified evidence this evidence alters the validity of the current recommendations as second step. However, at the moment, formal explicit procedures for assessing the need for an update are not available, with most of the included handbooks (77.1%) not providing explicit methods for assessing the need for an update.
When the need for an update is confirmed, the new evidence has to be incorporated in the current recommendations. However, less than one-half of the included handbooks state specific methods for this process. Previous studies suggest a model of assessing the need for an update using expert opinion, focused literature reviews, and consensus meeting [11, 13]. A reference to the development process, often included in the evaluated handbooks, is not enough because the aim of any update should be to incorporate new evidence in the context of previous recommendations. More specific methods should be included in the handbooks.
A further problem is that several institutions use different terminology and consequently bring further confusion. Some institutions use the term ‘monitoring’ for the identification of new evidence and assessment of the need for an update, often within an abridged time frame [5, 14, 32, 33, 37, 43, 44, 52]. In addition, the term ‘dynamic updating’ and ‘living guideline’ is used indistinctively, suggesting that CPGs are updated promptly and are always up-to-date [14, 40, 46]. Nevertheless, none of these handbooks provide guidance for conducting these processes and there is no consensus on when a guideline starts being dynamic or can be considered as a living guideline (Figure 3). We suggest avoiding these terms because it solely reflects the aspect of time between two versions. In Figure 3, we include a proposal regarding consistent terminology. Further research and consensus is needed in the international community about coherent terminology.
Our study is, as far as we know, the first study to examine the guidance about the updating process provided by CPG methodological handbooks. Our work has several strengths. We conducted a systematic and exhaustive search that included main databases, clearinghouses, and several institutions identified by a previous survey [12]. In addition, we contacted several organizations to retrieve non-published handbooks; therefore we believe that we included most of the existing handbooks. We independently performed eligibility and data extraction with a CRF developed and piloted by a group with extensive experience in the field.
Our study, however, might be subject to some limitations. It is possible that, after our extensive literature search, we did not identify all available handbooks because some are not indexed nor published, and only used for in-house purposes. However, unpublished handbooks are likely to be of lower quality. If this is the case, it would imply that we overestimated the quality of the updating guidance, further strengthening our conclusions. Finally, the reported methods in handbooks might not reflect the actual updating in CPGs. However, we believe that this is unlikely given previous results of our international survey with CPG developers [12].
Conclusion
Our work shows that updating guidance included in CPGs methodological handbooks is overall of poor quality. CPGs developers should provide more explicit and rigorous guidance and standardize the terminology used. This could, consequently, lead to a more optimal updating process of CPGs, and ultimately, to valid trustworthy guidelines.
Authors’ information
RV is a doctoral candidate at the Paediatrics, Obstetrics and Gynaecology and Preventive Medicine Department, Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona, Barcelona, Spain.
Abbreviations
- CPGs:
-
Clinical practice guidelines
- CRF:
-
Case report form.
References
-
IOM (Institute of Medicine): Clinical Practice Guideline We Can Trust. 2011, Washington, DC: The National Academies Press
Google Scholar
-
Grimshaw JM, Thomas RE, MacLennan G, Fraser C, Ramsay CR, Vale L, Whitty P, Eccles MP, Matowe L, Shirran L, Wensing M, Dijkstra R, Donaldson C: Effectiveness and efficiency of guideline dissemination and implementation strategies. Health Technol Assess. 2004, 8 (6): 1-72.
Article
Google Scholar
-
Woolf SH, Grol R, Hutchinson A, Eccles M, Grimshaw J: Clinical guidelines: potential benefits, limitations and harms of clinical guidelines. BMJ. 1999, 318 (7182): 527-530. 10.1136/bmj.318.7182.527.
Article
CAS
PubMed
PubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
-
European Observatory on Health Systems and Policies: Clinical guidelines for chronic conditions in the European Union. 2013, Geneva: World Health Organisation
Google Scholar
-
Working Group on CPG Updates: Updating Clinical Practice Guidelines in the Spanish National Health System: Methodology Handbook. 2009, Madrid: National Plan for the National Health System of the Spanish Ministry for Health and Social Policy; Aragon Health Sciences Institute (I+CS)
Google Scholar
-
National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence: The guidelines manual. London: National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence. 2012
Google Scholar
-
Shekelle P, Woolf S, Grimshaw JM, Schünemann HJ, Eccles MP: Developing clinical practice guidelines: reviewing, reporting, and publishing guidelines; updating guidelines; and the emerging issues of enhancing guideline implementability and accounting for comorbid conditions in guideline development. Implement Sci. 2012, 7: 62-10.1186/1748-5908-7-62.
Article
PubMed
PubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
-
Martínez Garcia L, Arévalo-Rodríguez I, Solà I, Haynes RB, Vandvik PO, Alonso-Coello P, Updating Guidelines Working Group: Strategies for monitoring and updating clinical practice guidelines: a systematic review. Implement Sci. 2012, 7 (1): 109-10.1186/1748-5908-7-109.
Article
PubMed
PubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
-
Shekelle P, Eccles MP, Grimshaw JM, Woolf SH: When should clinical guidelines be updated?. BMJ. 2001, 323 (7305): 155-157. 10.1136/bmj.323.7305.155.
Article
CAS
PubMed
PubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
-
Banzi R, Cinquini M, Liberati A, Moschetti I, Pecoraro V, Tagliabue L, Moja L: Speed of updating online evidence based point of care summaries: prospective cohort analysis. BMJ. 2011, 343: d5856-10.1136/bmj.d5856.
Article
PubMed
PubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
-
Gartlehner G, West SL, Lohr KN, Kahwati L, Johnson JG, Harris RP, Whitener L, Voisin CE, Sutton S: Assessing the need to update prevention guidelines: a comparison of two methods. Int J Qual Health Care. 2004, 16 (5): 399-406. 10.1093/intqhc/mzh081.
Article
PubMedGoogle Scholar
-
Alonso-Coello P, Martínez García L, Carrasco Gimeno JM, Solà I, Qureshi S, Burgers JS, Díaz del Campo P, Estrada MD, Gracia J, Mengual J, Rico Iturrioz R, Rotaeche del Campo R, Salcedo-Fernandez F: The updating of clinical practice guidelines: insights from an international survey. Implement Sci. 2011, 6: 107-10.1186/1748-5908-6-107.
Article
PubMed
PubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
-
Shekelle P, Ortiz E, Rhodes S, Morton SC, Eccles MP, Grimshaw JM, Woolf SH: Validity of the agency for healthcare research and quality clinical practice guidelines: how quickly do guidelines become outdated?. JAMA. 2001, 286 (12): 1461-1467. 10.1001/jama.286.12.1461.
Article
CAS
PubMedGoogle Scholar
-
Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network: SIGN 50: A guideline developer’s handbook. 2011, Edinburgh: Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network
Google Scholar
-
Brouwers M, Kho ME, Browman GP, Burgers JS, Cluzeau F, Feder G, Fervers B, Graham ID, Grimshaw J, Hanna SE, Littlejohns P, Makarski J, Zitzelsberger L, AGREE Next Steps Consortium: AGREE II: advancing guideline development, reporting and evaluation in healthcare. CMAJ. 2010, 182: 839-842. 10.1503/cmaj.090449.
Article
Google Scholar
-
Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Schünemann HJ, Tugwell P, Knottnerus A: GRADE guidelines: a new series of articles in the journal of clinical epidemiology. J Clin Epidemiol. 2011, 64 (4): 380-382. 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2010.09.011.
Article
PubMedGoogle Scholar
-
Kung J, Miller RR, Mackowiak PA: Failure of clinical practice guidelines to meet institute of medicine standards: two more decades of little, if any, progress. Arch Intern Med. 2012, 172 (21): 1628-1633. 10.1001/2013.jamainternmed.56.
Article
PubMedGoogle Scholar
-
Alonso-Coello P, Irfan A, Solà I, Gich I, Delgado-Noguera M, Rigau D, Tort S, Bonfill X, Burgers J, Schunemann H: The quality of clinical practice guidelines over the last two decades: a systematic review of guideline appraisal studies. Qual Saf Health Care. 2010, 19 (6): e58-
PubMed
Google Scholar
-
Turner T, Misso M, Harris C, Green S: Development of evidence-based clinical practice guidelines (CPGs): comparing approaches. Implement Sci. 2008, 3: 45-10.1186/1748-5908-3-45.
Article
PubMed
PubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
-
Ansari S, Rashidian A: Guidelines for guidelines: are they up to the task? A comparative assessment of clinical practice guideline development handbooks. PLoS One. 2012, 7 (11): e49864-10.1371/journal.pone.0049864.
Article
CAS
PubMed
PubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
-
de Santé HA: Élaboration de recommandations de bonne pratique. 2010, Saint-Denis: Haute Autorité de Santé
Google Scholar
-
Centrul Naţional de Studii Medicina Familiei: Metodologie elaborarii ghidului de practica. http://www.ghidurimedicale.ro/index.php?option=com_content%26;task=view%26;id=19%26;Itemid=27. (accessed 1 August 2012)
-
Kwaliteitsinstituut voor de Gezondheidszorg CBO: Evidence-based Richtlijnontwikkeling Handleiding voor werkgroepleden. 2007, Utrecht: Kwaliteitsinstituut voor de Gezondheidszorg
Google Scholar
-
Van Der WP, Mead J: Framework for Clinical Guideline Development in Physiotherapy. 2004, Limassol: European Region of the World Confederation for Physical Therapy
Google Scholar
-
Agència d’Avaluació de Tecnologia i Recerca Mèdiques: Guies de pràctica clínica. http://www.gencat.cat/salut/depsan/units/aatrm/html/ca/dir252/doc7841.html (accessed 3 August 2012)
-
Schubert I, Lelgemann M, Kirchner H, von Ferber C, von Ferber L, Ollenschläger G: Handbuch zur Entwicklung regionaler Leitlinien. 2006, Berlin: Ärztliches Zentrum für Qualität in der Medizin
Google Scholar
-
Arzneimittelkommission der deutschen Ärzteschaft: Leitfaden für die Erstellung von Therapieempfehlungen. 2011, Berlin: Arzneimittelkommission der deutschen Ärzteschaft
Google Scholar
-
Bundesärztekammer: National Disease Management Guidelines. 2002, Berlin: Bundesärztekammer
Google Scholar
-
Dumonceau JM, Hassan C, Riphaus A, Ponchon T: European society of gastrointestinal endoscopy (ESGE) guideline development policy. Endoscopy. 2012, 44 (6): 626-629.
Article
PubMedGoogle Scholar
-
Iorio A, Ageno W, Cosmi B, Imberti D, Lussana F, Siragusa S, Tormene D, Tosetto A, Cattaneo M: Objectives and methodology: guidelines of the Italian society for haemostasis and thrombosis (SISET). Thromb Res. 2009, 124 (5): 1-5. 10.1016/j.thromres.2009.05.014.
Article
Google Scholar
-
Ärztliche Zentralstelle Qualitätssicherung: National Disease Management Guidelines: Method Report. 2002, Köln: Ärztliche Zentralstelle Qualitätssicherung
Google Scholar
-
Kunnamo I: Duodecim Medical Publications Ltd. Preface: What is Evidence-Based Medicine Guidelines. 2008
Google Scholar
-
Society DFM: Submitted NHS Evidence Accreditation Application. 2001, Helsinki: Duodecim Finnish Medical Society
Google Scholar
-
Chevalier P, de Sutter A, Dirven K, Paulus D, Peremans L, van Royen P, van Welde A: Algemeen Stramien voor de Ontwikkeling van Aanbevelingen van Goede Medische Praktijkvoering. 2007, Antwerpen: Domus Medical Flemish College of General Practitioners
Google Scholar
-
World Health Organization: Guidelines for WHO Guidelines. 2003, Geneva: World Health Organization
Google Scholar
-
National Health and Medical Research Council: A guide to the development, implementation and evaluation of clinical practice guidelines. 1998, Canberra: National Health and Medical Research Council
Google Scholar
-
American Society of Clinical Oncology: American Society of Clinical Oncology Guideline Procedures Manual. 2001, Alexandria: American Society of Clinical Oncology
Google Scholar
-
Rosenfeld RM, Shiffman RN, Robertson P: Clinical practice guideline development manual, third edition: a quality-driven approach for translating evidence into action. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2013, 148 (1 Suppl): S1-S55. 10.1177/0194599812467004.
Article
Google Scholar
-
Harris JS, Sinnott PL, Holland JP, Ording J, Turkelson C, Weiss M, Hegmann KT: Methodology to update the practice recommendations in the American college of occupational and environmental medicine’s occupational medicine practice guidelines, Second Edition. J Occup Environ Med. 2008, 50 (3): 282-295. 10.1097/JOM.0b013e3181651613.
Article
PubMedGoogle Scholar
-
Qaseem A, Snow V, Owens DK, Shekelle P: The development of clinical practice guidelines and guidance statements of the American college of physicians: summary of methods. Ann Intern Med. 2010, 153 (3): 194-199. 10.7326/0003-4819-153-3-201008030-00010.
Article
PubMedGoogle Scholar
-
American Urological Association Education and Research: Overview: Standard Operating Procedures. 2011, Linthicum: American Urological Association
Google Scholar
-
Guidelines and Protocols Advisory Committee: GPAC Handbook. 2011, Victoria: Guidelines and Protocols Advisory Committee
Google Scholar
-
U.S. Preventive Services Task Force: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force Procedure Manual. 2008, Rockville: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality
Google Scholar
-
American College of Cardiology Foundation and American Heart Association: Methodology Manual and Policies From the ACCF/AHA Task Force on Practice Guidelines. 2010, Washington DC: American College of Cardiology Foundation
Google Scholar
-
Joanna Briggs Institute Synthesis Science Unit: Best Practice Information Sheet (BPIS) Procedures. Adelaide: Joanna Briggs Institute
-
Canadian Medical Association: Handbook on Clinical Practice Guidelines. 2007, Ottawa: Canadian Medical Association
Google Scholar
-
Therapeutic Guidelines Limited: How Therapeutic Guidelines are produced. http://www.tg.org.au/?sectionid=81 (accessed 3 August 2012)
-
Caring for Australasians with Renal Impairment: A Guide for Writers. 2009, Concord: Caring for Australasians with Renal Impairment
Google Scholar
-
New Zealand Guidelines Group: Handbook for the Preparation of Explicit Evidence-base Clinical Practice Guidelines. 2001, Wellington: New Zealand Guidelines Group
Google Scholar
-
Gupta S, Bhattacharyya OK, Brouwers MC, Estey EA, Harrison MB, Hernandez P, Palda VA, Boulet LP: Canadian thoracic society: presenting a new process for clinical practice guideline production. Can Respir J. 2009, 16 (6): 62-68.
Article
Google Scholar
-
American College of Chest Physicians: Methodology. http://www.chestnet.org/Guidelines-and-Resources/Guidelines-and-Consensus-Statements/Methodology (accessed 3 August 2012)
-
Murad MH, Montori VM, Sidawy AN, Ascher E, Meissner MH, Chaikof EL, Gloviczki P: Guideline methodology of the society for vascular surgery including the experience with the GRADE framework. J Vasc Surg. 2011, 53 (5): 1375-1380. 10.1016/j.jvs.2011.01.036.
Article
PubMedGoogle Scholar
Download references
Funding
Pablo Alonso-Coello is funded by a Miguel Servet research contract from the Instituto de Salud Carlos III (CP09/00137). Andrea Juliana Sanabria and Laura Martínez García are funded by a Río Hortega research contract from the Instituto de Salud Carlos III (CM12/00168 and CM11/00035 respectively).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
-
Iberoamerican Cochrane Centre, Institute of Biomedical Research (IIB Sant Pau), C/ Sant Antoni Maria Claret 167, Barcelona, 08025, Spain
Robin WM Vernooij, Andrea Juliana Sanabria, Ivan Solà, Pablo Alonso-Coello & Laura Martínez García
-
Department of Health Sciences, Faculty of Earth and Life Sciences, VU University, Amsterdam, The Netherlands
Robin WM Vernooij
Authors
- Robin WM Vernooij
You can also search for this author in
PubMed Google Scholar - Andrea Juliana Sanabria
You can also search for this author in
PubMed Google Scholar - Ivan Solà
You can also search for this author in
PubMed Google Scholar - Pablo Alonso-Coello
You can also search for this author in
PubMed Google Scholar - Laura Martínez García
You can also search for this author in
PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to
Pablo Alonso-Coello.
Additional information
Competing interests
PA-C is an author of one of the included handbooks. For this reason, other authors completed data extraction for this handbook.
Authors’ contribution
Conceiving the review: PA-C, LM. Design of the study: PA-C, LM, RV, AJS. Undertaking searches: IS, RV. Screening and extracting data: RV, AJS. Writing the review: RV, AJS, PA-C. Comment and editing of review drafts: all authors. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Electronic supplementary material
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Rights and permissions
Open Access
This article is published under license to BioMed Central Ltd. This is an Open Access article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0
), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Reprints and Permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vernooij, R.W., Sanabria, A.J., Solà, I. et al. Guidance for updating clinical practice guidelines: a systematic review of methodological handbooks.
Implementation Sci 9, 3 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1186/1748-5908-9-3
Download citation
-
Received: 12 June 2013
-
Accepted: 19 December 2013
-
Published: 02 January 2014
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1748-5908-9-3
Keywords
- Clinical practice guidelines
- Evidence-based medicine
- Handbooks
- Methodology
- Systematic review
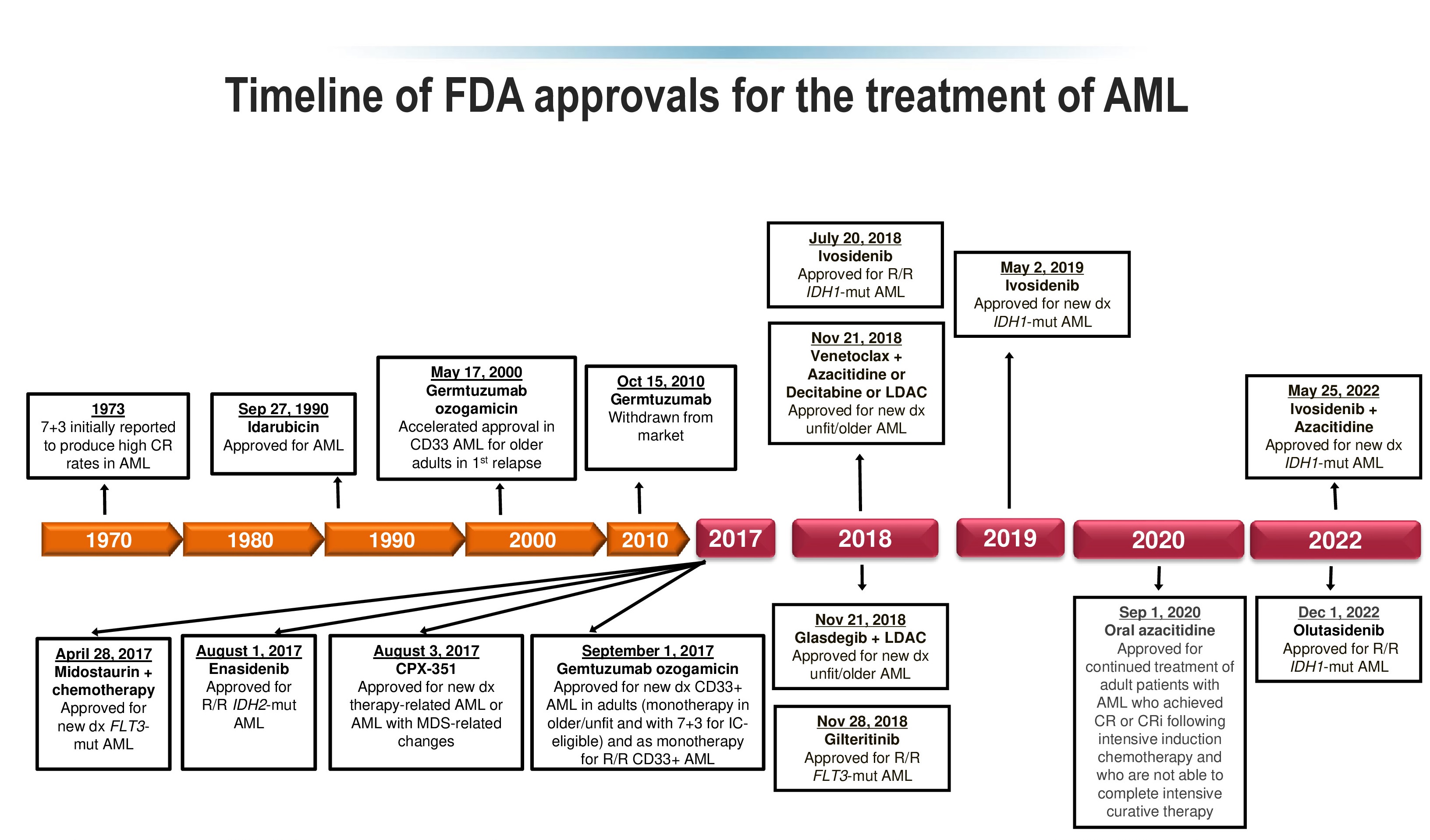
Недавно, European LeukemiaNet обновила клиническое руководство по острому миелоидному лейкозу, а также недавно были обновлены документы ВОЗ и ICC по миелоидной неоплазии. Вместе, эти документы обновляют классификацию, стратификацию риска, прогнозирование, рекомендации по мониторингу, и оценку ответа у пациентов с острым миелоидным лейкозом. Всё большее понимание генетических драйверов острого миелоидного лейкоза и всё большее понимание биологии острого миелоидного лейкоза привели к разработке новых видов терапии и более сложных клинических руководств по лечению.
В данной статье обсуждается подход к острому миелоидному лейкозу в ежедневной клинической практике с учётом этих недавних обновлений в контексте новых видов лечения и открытий.
Подробнее смотрите в прикрепленном файле
Автор обзоров мировой медицинской периодики на портале MedElement — врач общей практики, хирург Талант Иманалиевич Кадыров.
Закончил Киргизский Государственный медицинский институт (красный диплом), в совершенстве владеет английским языком. Имеет опыт работы хирургом в Чуйской областной больнице; в настоящий момент ведет частную практику.
Регулярное повышение квалификации: курсы Advanced Cardiac Life Support, International Trauma Life Support, Family Practice Review and Update Course (Англия, США, Канада).
Посмотреть другие обзоры
Уважаемые коллеги!
Общероссийская общественная организация «Российское общество специалистов по опухолям головы и шеи» сообщает о пересмотре следующих клинических рекомендаций:
1. «Злокачественные новообразования губы» (взрослые; С00).
2. «Злокачественные новообразования полости рта» (взрослые; C02.0, C02.1, C02.2, C02.3, C02.8, C02.9, С03, С04, C05.0, С06).
3. «Рак гортани» (взрослые; С32).
4. «Рак гортаноглотки» (взрослые; С12/C13).
5. «Рак носоглотки» (взрослые; С11).
6. «Рак ротоглотки» (взрослые; С01, С02.4, C05.1, С05.2, C09, C10).
7. «Рак полости носа и придаточных пазух» (взрослые; С30, C31).
8. «Злокачественные опухоли слюнных желез» (взрослые; С07, С08).
9. «Дифференцированный рак щитовидной железы» (взрослые; С73)
10. «Медуллярный рак щитовидной железы» (взрослые, дети; С73)
Приглашаем профессиональное сообщество, а также образовательные и научные организации с 05.07.2022 по 05.08.2022 принять участие в общественном обсуждении проектов пересмотренных клинических рекомендаций.
Ваши предложения, комментарии и замечания присылайте на адрес электронной почты: hnonco@yvalymov.ru
Клинические рекомендации. Злокачественные новообразования губы.
Клинические рекомендации. Медуллярный рак щитовидной железы.
Клинические рекомендации. Злокачественные новообразования полости рта.
Клинические рекомендации. Рак гортани.
Клинические рекомендации. Рак гортаноглотки.
Клинические рекомендации. Рак носоглотки.
Клинические рекомендации. Рак полости носа.
Клинические рекомендации. Рак ротоглотки.
Клинические рекомендации. Рак слюнных желез.
Клинические рекомендации. Дифференцированный рак щитовидной железы.
Обновленное клиническое руководство по ведению детей с экссудативным средним отитом
Это обновление совместного клинического руководства, которое было разработано Американской академией отоларингологии, хирургии головы и шеи (AAO-HNS), Американской академией педиатрии (ААР) и Американской академией семейных врачей (AAFP) и впервые опубликовано в 2004 году.
Документ содержит научно обоснованные рекомендации по ведению пациентов с экссудативным средним отитом. При обновлении были учтены новые данные 4 клинических руководств, 20 систематических обзоров и 49 рандомизированных контролируемых исследований по сравнению с предыдущей версией консенсуса.
Введение
Экссудативным средним отитом (ЭСО) называют наличие жидкости в среднем ухе (рис. 1) без признаков или симптомов острой ушной инфекции. К наиболее распространенным синонимам ЭСО относятся негнойный, секреторный, серозный средний отит.
Данное состояние является достаточно распространенным, что позволяет называть его «профессиональным» заболеванием детей раннего возраста. В среднем примерно 90% детей хотя бы однократно переносят ЭСО. В возрасте 5-6 лет, то есть в начальной школе, жидкость в одном или обоих ушах выявляют у 1 из 8 детей.
Ежегодно в США диагностируется около 2,2 млн случаев ЭСО, лечение которых обходится в 4 млн долларов. Вероятно, косвенные расходы гораздо выше, поскольку ЭСО часто остается незамеченным, но приводит к нарушениям слуха у детей и проблемам с успеваемостью в школе.
ЭСО может возникать вследствие инфекции верхних дыхательных путей, спонтанно из-за дисфункции евстахиевой трубы или как результат воспаления, сохраняющегося после острого среднего отита (ОСО). У детей евстахиева труба короче, более подвижна и расположена более горизонтально, что делает ее менее эффективной для вентиляции и защиты среднего уха, чем у взрослого человека (рис. 2).
В противоположность ЭСО, ОСО является инфекционным заболеванием и характеризуется быстрым появлением признаков и симптомов воспаления в среднем ухе, часто сопровождается ушной болью и выпячиванием барабанной перепонки (рис. 3).
Большинство эпизодов ЭСО разрешаются спонтанно в течение 3 мес, но примерно у 30-40% детей возникают повторные эпизоды, причем от 5-10% из них длятся ≥1 года.
Жидкость в полости среднего уха приводит к снижению подвижности барабанной перепонки и мешает звукопроводимости. Поэтому ЭСО может ассоциироваться со снижением слуха, плохой успеваемостью в школе, поведенческими расстройствами, снижением качества жизни.
Научно обоснованные рекомендации этого руководства отображают как качество доказательной базы, так и предполагаемый баланс между пользой и вредом в случае следования этим положениям. Их классификация представлена в таблице 1.
Ключевые положения
ПОЛОЖЕНИЕ 1а. ПНЕВМАТИЧЕСКАЯ ОТОСКОПИЯ. Для установления диагноза ЭСО у ребенка врач должен документировать наличие экссудата в барабанной полости с помощью пневматической отоскопии (табл. 2). Сильная рекомендация.
ПОЛОЖЕНИЕ 1б. ПНЕВМАТИЧЕСКАЯ ОТОСКОПИЯ. Врач должен провести пневматическую отоскопию (табл. 2) для исключения или подтверждения ЭСО у ребенка с оталгией и/или снижением слуха. Сильная рекомендация.
ПОЛОЖЕНИЕ 2. ТИМПАНОМЕТРИЯ. Проведение тимпанометрии (рис. 4, 5) показано у детей с подозрением на ЭСО, когда пневматическая отоскопия дала неопределенные результаты. Сильная рекомендация.
ПОЛОЖЕНИЕ 3. НЕВЫПОЛНЕННЫЙ АУДИОЛОГИЧЕСКИЙ СКРИНИНГ НОВОРОЖДЕННЫХ. Необходимо информировать родителей детей с ЭСО, которые не прошли аудиологический скрининг в период новорожденности, о важности последующего наблюдения, чтобы убедиться в том, что слух после разрешения ЭСО восстановился и для исключения нейросенсорной тугоухости; консультирование следует документировать в медицинской карте. Рекомендация.
ПОЛОЖЕНИЕ 4а. ВЫЯВЛЕНИЕ ДЕТЕЙ ГРУППЫ РИСКА. Следует определить, входит ли ребенок с ЭСО в группу повышенного риска развития проблем с речью или успеваемостью из-за физических, когнитивных, поведенческих и других факторов. Рекомендация.
ПОЛОЖЕНИЕ 4б. ОБСЛЕДОВАНИЕ ДЕТЕЙ ГРУППЫ РИСКА. Детей из группы риска необходимо обследовать на наличие ЭСО сразу после диагностики состояний, связанных с риском, а затем повторно в возрасте 12-18 мес, если в группу риска они были включены в более младшем возрасте. Рекомендация.
ПОЛОЖЕНИЕ 5. СКРИНИНГ ЗДОРОВЫХ ДЕТЕЙ. Рутинный скрининг на ЭСО детей, которые не находятся в группе риска и не имеют указывающих на ЭСО симптомов (снижение слуха, нарушение равновесия, плохая успеваемость в школе, поведенческие расстройства или дискомфорт в ухе), не целесообразен. Рекомендация против.
ПОЛОЖЕНИЕ 6. ОБУЧЕНИЕ ПАЦИЕНТОВ. Следует информировать семьи детей с ЭСО о природе и течении заболевания, необходимости дальнейшего наблюдения и возможных осложнениях. Рекомендация.
ПОЛОЖЕНИЕ 7. ВЫЖИДАТЕЛЬНАЯ ТАКТИКА. Детям с ЭСО, которые не находятся в группе риска, показано динамическое наблюдение в течение 3 мес с момента начала заболевания или постановки диагноза, если время начала заболевания неизвестно. Сильная рекомендация.
ПОЛОЖЕНИЕ 8а. КОРТИКОСТЕРОИДЫ. Не рекомендуется применять интраназальные или системные кортикостероиды для лечения ЭСО. Сильная рекомендация против.
ПОЛОЖЕНИЕ 8б. АНТИБИОТИКИ. Не рекомендуется применять системные антибиотики для лечения ЭСО. Сильная рекомендация против.
ПОЛОЖЕНИЕ 8б. АНТИГИСТАМИННЫЕ СРЕДСТВА И ДЕКОНГЕСТАНТЫ. Не рекомендуется применять антигистаминные средства и/или деконгестанты для лечения ЭСО. Сильная рекомендация против.
ПОЛОЖЕНИЕ 9. АУДИОМЕТРИЯ. Следует проводить соответствующее возрасту аудиометрическое исследование, если ЭСО длится ≥3 мес или при любой продолжительности ЭСО у детей из группы риска. Рекомендация.
ПОЛОЖЕНИЕ 10. РЕЧЬ. Необходимо информировать семьи с детьми с билатеральным ЭСО и документированным снижением слуха о потенциальном воздействии патологии на развитие речи. Рекомендация.
ПОЛОЖЕНИЕ 11. НАБЛЮДЕНИЕ ЗА ДЕТЬМИ С ХРОНИЧЕСКИМ ЭСО. Детей с хроническим ЭСО следует осматривать каждые 3-6 мес до разрешения заболевания, выявления значительного снижения слуха или подозрения на структурные аномалии барабанной перепонки или среднего уха. Рекомендация.
ПОЛОЖЕНИЕ 12а. ХИРУРГИЧЕСКОЕ ЛЕЧЕНИЕ ДЕТЕЙ <4 ЛЕТ (табл. 3). При показаниях для хирургического лечения ЭСО у детей <4 лет следует рекомендовать тимпаностомию. Аденоидэктомия не показана при отсутствии четких показаний для ее проведения помимо ЭСО (например, назальная обструкция, хронический аденоидит). Рекомендация.
ПОЛОЖЕНИЕ 12б. ХИРУРГИЧЕСКОЕ ЛЕЧЕНИЕ ДЕТЕЙ ≥4 ЛЕТ (табл. 3). При показаниях для хирургического лечения детей ≥4 лет следует рекомендовать тимпаностомию, аденоидэктомию или обе операции. Рекомендация.
ПОЛОЖЕНИЕ 13. ОЦЕНКА ИСХОДОВ. При ведении ребенка с ЭСО врачу следует фиксировать в истории болезни разрешение ЭСО, улучшение слуха или повышение качества жизни. Рекомендация.
Ключевые положения руководства и их связь между собой представлены в виде алгоритма на рисунке 6.
- Номер:
- Тематичний номер «Педіатрія» №1 (36), березень 2016 р.
СТАТТІ ЗА ТЕМОЮ Педіатрія
22.04.2023
Педіатрія
Вроджена гіперплазія кори наднирникових залоз у дітей
Термін «вроджена гіперплазія наднирникових залоз» (ВГНЗ) – це група аутосомно-рецесивних захворювань, що включає дефіцит ферментів, які беруть участь у синтезі кортизолу, альдостерону чи обох гормонів. У деяких випадках ці прояви відображаються при збільшенні попередників адренокортикальних гормонів. Фенотип залежить від ступеня або типу генної делеції чи мутації та є результатом дефіциту ферменту, що бере участь у стероїдогенезі (табл. 1) [3, 5]. …
22.04.2023
Педіатрія
Пульсоксиметричний скринінг критичних вроджених вад серця у новонароджених
Організація надання медичної допомоги новонародженим дітям передбачає заходи, спрямовані на покращення результатів виходжування новонароджених шляхом оптимізації діагностики та забезпечення раннього виявлення критичних вроджених вад серця (КВВС). Ці стандарти медичної допомоги є сучасними рекомендаціями щодо скринінгу КВВС у новонароджених дітей….
Порядок обновления клинических рекомендаций.
Механизм обновления клинических рекомендаций предусматривает их систематическую актуализацию — не реже чем один раз в три года, а также при появлении новых данных с позиции доказательной медицины по вопросам диагностики, лечения, профилактики и реабилитации конкретных заболеваний, наличии обоснованных дополнений/замечаний к ранее утвержденным КР, но не чаще 1 раза в 6 месяцев.
Приложение А3
СПРАВОЧНЫЕ МАТЕРИАЛЫ,
ВКЛЮЧАЯ СООТВЕТСТВИЕ ПОКАЗАНИЙ К ПРИМЕНЕНИЮ
И ПРОТИВОПОКАЗАНИЙ, СПОСОБОВ ПРИМЕНЕНИЯ И ДОЗ ЛЕКАРСТВЕННЫХ
ПРЕПАРАТОВ, ИНСТРУКЦИИ ПО ПРИМЕНЕНИЮ
ЛЕКАРСТВЕННОГО ПРЕПАРАТА
Данные клинические рекомендации разработаны с учетом следующих нормативно-правовых документов:
1) Приказ Министерства здравоохранения Российской Федерации от 20.10.2020 N 1130н «Об утверждении Порядка оказания медицинской помощи по профилю «акушерство и гинекология» (Зарегистрирован 12.11.2020 N 60869);
2) Национальное руководство гинекология. под руководством Савельевой Г.М., Сухих Г.Т., Серова В.Н., Радзинского В.Е., Манухина И.Б. 2017.
3) Краснопольский В.И., Буянова С.Н., Щукина Н.А. Гнойная гинекология. Руководство. Москва. Медпресс. 2001. С. 288.
4) Программа СКАТ (Стратегия Контроля Антимикробной Терапии) при оказании стационарной медицинской помощи: Российские клинические рекомендации/Под ред. С.В. Яковлева, Н.И. Брико, С.В. Сидоренко, Д.Н. Проценко. — М.: Издательство «Перо», 2018. — 156 с.
5) Клиническая хирургия: национальное руководство: в 3 т./под ред. В.С. Савельева, А.И. Кириенко. — М.: ГЭОТАР-Медиа, 2010.
6) Woodward C., Fisher M.A. Drug treatment of common STDs: Part II. Vaginal infections, pelvic inflammatory disease and genital warts. Am Fam Physician. 1999 Oct 15; 60(6): 1716-22. PMID: 10537386
Рекомендуемые схемы антибактериальной терапии при ВЗОМТ [2, 46 — 48]
Скачать документ целиком в формате PDF